Key Concepts
Figure 1–1 illustrates the key concepts of the Java DMK and shows how the components relate to each other.
In this example, the MBeans for two resources are registered with the agent's MBean server. An agent service such as monitoring is registered as another MBean. The agent contains a connector server for one of the following protocols: RMI, HTTP, or HTTPS. It also contains a protocol adaptor, either for SNMP or HTML. An agent can have any number of communicator components, one for each of the protocols and one for each of the ports through which it communicates.
Figure 1–1 Key Concepts of the Java DMK
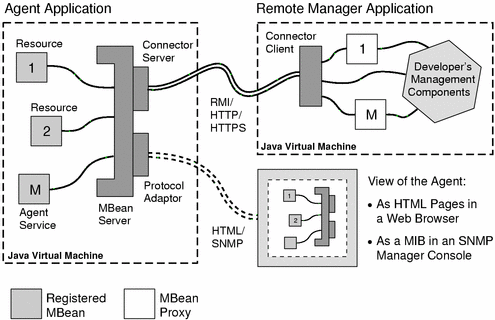
The remote manager is a Java application running on a distant host. It contains the connector client for the chosen protocol and proxy MBeans representing the two resources. When the connector client establishes the connection with the agent's connector server, the other components of the application can issue management requests to the agent. For example, it can call the proxy objects to invoke an operation on the first resource and configure the monitoring service to poll the second resource.
With the HTML adaptor, you can view the agent through a web browser, which provides a simple user interface. Each MBean is represented as a separate HTML page, from which you can interact with text fields to set attributes and click buttons to invoke operations. There is also an administration page for creating or removing MBeans from the MBean server.
Each of these concepts is further defined in Chapter 2, Architectural Components.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
