Putting Role Types to Work
The following discussion describes how to use role types effectively. For role type descriptions, see the previous section.
Managing Roles Created In Versions Prior to Version 8.0
Organizations that upgraded from an earlier version of Identity Manager to version 8.0 will automatically have their legacy roles converted to IT Roles. These IT Roles will remain directly assigned to users. Legacy roles will not be assigned a role owner as part of the upgrade process. A role owner can be assigned later, however. (For information on role owners, see Designating Role Owners and Role Approvers.)
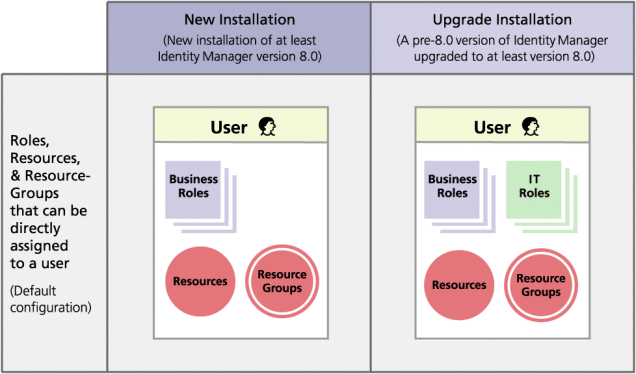
By default, organizations that upgrade to version 8.0 can directly assign both IT Roles and Business Roles to users (see Figure 5–2).
Organizations with legacy roles should consider creating new roles based on the guidelines outlined in the next section.
Using Role Types to Design Flexible Roles
IT Roles, Applications, and Assets are the role designer’s building blocks. These three role types are used in combination to build up user entitlements (or, access rights). IT Roles, Applications, and Assets are then assigned to Business Roles.
Designing Business Roles
In Identity Manager, a user can be assigned one or more roles, or no role. With the introduction of role types in Identity Manager 8.0, it is recommended that you only directly assign Business Roles to users. In fact, by default, you cannot directly assign any of the other role types to users unless your organization had a pre-8.0 version of Identity Manager installed and upgraded to at least version 8.0. This default restriction can be changed by modifying the role configuration object (Configuring Role Types).
To reduce complexity, Business Roles cannot be nested. In other words, one Business Role cannot contain another Business Role. In addition, Business Roles cannot directly contain resources and resource groups. Instead, resources and resource groups should be assigned to either an IT Role or an Application, which can then be assigned to one or more Business Roles.
Designing IT Roles
IT Roles can contain Applications, and Assets, as well as other IT Roles. IT Roles can also contain resources and resource groups.
IT Roles are intended to be created and managed either by your organization’s IT staff, or by the resource owners who understand the entitlements that are required to enable specific privileges within the resource.
Designing Applications and Assets
Applications and Assets are role types that are intended to represent commonly used business terms to describe things that end-users need in order to do their jobs. For example, an Application role could be named “Customer Support Tools” or “Intranet HR-Tool Admin.“
-
Applications cannot contain roles, but they can contain resources and resource groups. Applications can also define specific entitlements that restrict access to only specific applications on contained resources.
-
Assets are (typically) non-connected or non-digital resources, such as mobile phones and portable computers, that require manual provisioning. Consequently, assets cannot contain roles, resources, or resource groups.
Applications and Assets are intended to be assigned to Business Roles and IT Roles.
Note –
Role administrators should be assigned one or more of the following capabilities:
-
Asset Administrator
-
Application Administrator
-
Business Role Administrator
-
IT Role Administrator
See Assigning Capabilities to Users for more information.
Role Types in Summary
The following figure shows which role-types, resources, and resource-groups can be assigned to each of the four role-types. The figure also shows that role-type exclusions can be assigned to all four role-types. (For a description of Role exclusions, see To Assign Resources and Resource Groups.)
Figure 5–1 The Business Role, IT Role, Application, and Asset Role-Types
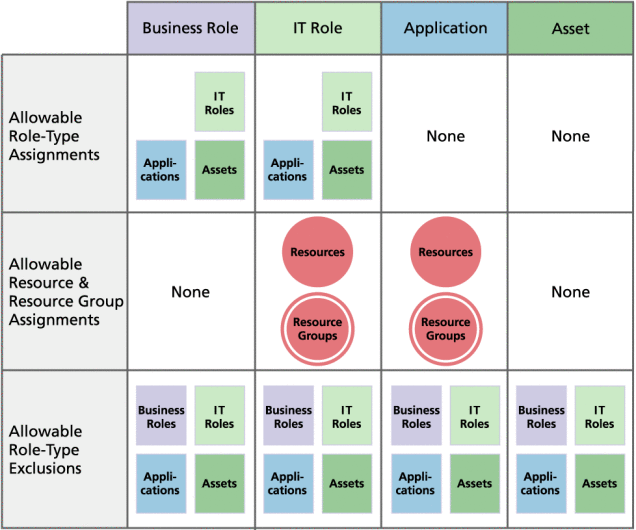
Optional, conditional, and required contained-roles (What are Roles?) provide added flexibility. Flexible role definitions can reduce the total number of roles your organization needs to manage.
Figure 5–2 shows that Business Roles and IT Roles are directly assignable to users if a pre-8.0 version of Identity Manager is upgraded to at least version 8.0. On upgrade, legacy roles are converted to IT Roles, and, to ensure backwards compatibility, IT Roles are directly assigned to users. If Identity Manager was not upgraded from a pre-8.0 version, then only Business Roles are directly assignable to users.
Figure 5–2 Roles and resources that can be directly assigned to users.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
