Configuring Identity Manager Policies
Read this section for information about configuring user policies.
This section contains the following topics:
What are Policies?
Identity Manager policies set limitations for Identity Manager users by establishing constraints for Identity Manager accountID, login, and password characteristics.
Note –
Identity Manager also provides Audit policies that are specifically designed to audit user compliance. Audit policies are discussed in Chapter 13, Identity Auditing: Basic Concepts
Policies are categorized as the following types:
-
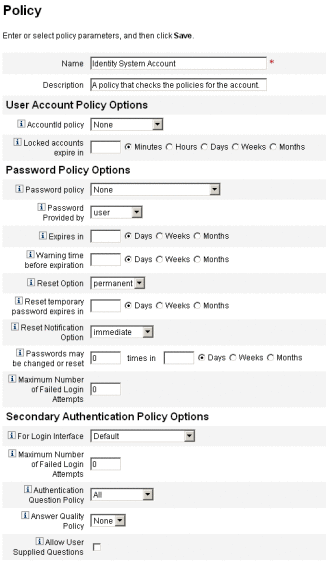
Identity System Account policies. Establish user, password, and authentication policy options and constraints. You assign Identity System Account policies to organizations from the Create and Edit Organization pages or to users from the Create and Edit User pages.
You can set or select the following options:
-
User Account Policy Options. Specify how Identity Manager treats user accounts if a user fails to correctly answer authentication questions.
-
Password Policy Options. Set password expiration, warning time before expiration, and reset options.
-
Secondary Authentication Policy Options. Determine how authentication questions are presented to the user, whether the user can provide his own authentication questions, enforce authentication at login, and establish the bank of questions that can be presented to a user.
-
-
Service Provider System Account policies. Use this policy type in a service provider implementation to establish user, password, and authentication policy options and constraints for service provider users. You assign the policies to organizations from the Create and Edit Organization pages or to users from the Create and Edit Service Provider User pages.
-
String Quality Policies. Includes policy types such as password, accountID, and authentication. Use to set length rules, character type rules, allowed words, and attribute values. This policy type is tied to each Identity Manager resource and is set on each resource page. The following figure provides an example.
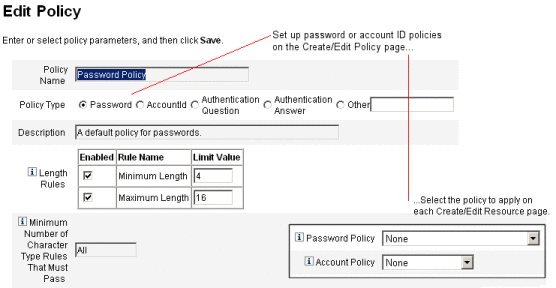
You can set the following options and rules for passwords and accountIDs:
-
Length rules. Determine minimum and maximum length.
-
Character type rules. Set minimum and maximum allowable values for alphabetic, numeric, uppercase, lowercase, repetitive, and sequential characters.
-
Password re-use limits. Specify the number of passwords preceding the current password that cannot be reused. When a user attempts to change his password, the new password will be compared to the password history to ensure this is a unique password. For security reasons, a digital signature of the previous passwords is saved; new passwords are compared to this.
-
Prohibited words and attribute values. Specify words and attributes that cannot be used as part of an ID or password.
-
 To Open the Policies Page
To Open the Policies Page
You create and edit Identity Manager user policies from the Policies page. To open this page, follow these steps:
-
Log in to the Administrator interface.
-
Click the Security tab, then click the Policies subtab.
The Policies page opens as shown in the following figure.
Must Not Contain Attributes in Policies
You can change the allowed set of “must not contain” attributes in the UserUIConfig configuration object.
Attributes are listed in UserUIConfig as follows:
-
<PolicyPasswordAttributeNames> attribute. Policy type Password
-
<PolicyAccountAttributeNames> attribute. Policy type AccountId
-
<PolicyOtherAttributeNames> attribute. Policy type Other
What is a Dictionary Policy?
A dictionary policy enables Identity Manager to check passwords against a word database to ensure that they are protected from a simple dictionary attack. By using this policy with other policy settings to enforce the length and makeup of passwords, Identity Manager makes it difficult to use a dictionary to guess passwords that are generated or changed in the system.
The dictionary policy extends the password exclusion list that you can set up with the policy. (This list is implemented by the Must Not Contain Words option on the Administrator Interface password Edit Policy page.)
 To Configure a Dictionary Policy
To Configure a Dictionary Policy
To set up a dictionary policy, you must:
-
Configure dictionary server support
-
Load the dictionary
-
Open the Policies page as described in To Open the Policies Page.
-
Click Configure Dictionary to display the Dictionary Configuration page.
-
Select and enter database information.
Database information includes:
-
Database Type. Select the database type (Oracle, DB2, SQLServer, or MySQL) that you will use to store the dictionary.
-
Host. Enter the name of the host where the database is running.
-
User. Enter the user name to use when connecting to the database.
-
Password. Enter the password to use when connecting to the database.
-
Port. Enter the port on which the database is listening.
-
Connection URL. Enter the URL to use when connecting. These template variables are available:
-
%h - host
-
%p - port
-
%d - database name
Driver Class. Enter the JDBC driver class to use while interacting with the database.
-
-
Database Name. Enter the name of the database where the dictionary will be loaded.
-
Dictionary Filename. Enter the name of the file to use when loading the dictionary.
-
-
Click Test to test the database connection.
-
If the connection test is successful, click Load Words to load the dictionary. The load task may take a few minutes to complete.
-
Click Test to ensure that the dictionary was loaded correctly.
 To Implement a Dictionary Policy
To Implement a Dictionary Policy
Use the following steps to implement a dictionary policy:
-
Open the Policies page as described in To Open the Policies Page.
-
Click the Password Policy link to edit the password policy.
-
On the Edit Policy page, select the Check passwords against dictionary words option.
-
Click Save to save your changes.
Once implemented, all changed and generated passwords will be checked against the dictionary.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
