Modifying DHCP Service Options
You can change values for some additional features of the DHCP service, some of which were not offered during the initial configuration with DHCP Manager. If you configured your server with dhcpconfig, you may have been prompted to select values for most of these options. You can use the Modify Service Options dialog box in DHCP Manager or specify options on the in.dhcpd command to change service options.
The following task map shows the tasks related to service options and the procedures to use:
Table 11-1 Modify DHCP Service Options Task Map|
Tasks... |
Description |
For Instructions, Go To... |
|---|---|---|
|
Change logging options |
Enable or disable verbose logging, enable or disable logging of DHCP transactions, and select a syslog facility to use for logging DHCP transactions. |
"How to Generate Verbose DHCP Log Messages (DHCP Manager)" "How to Generate Verbose DHCP Log Messages (Command Line)" "How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging (DHCP Manager)" "How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging for Current Session (Command Line)" "How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File"
|
|
Enable or disable duplicate IP address detection |
Enable or disable the DHCP server's checking that an IP address is not already in use before offering it to a client. |
"How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (DHCP Manager)" "How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (Command Line)" |
|
Change options for DHCP server's reading of configuration information |
Enable or disable automatic reading of dhcptab at specified intervals, or change the interval between reads |
"How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (DHCP Manager)" "How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (Command Line)" |
|
Change the number of relay agent hops |
Increase or decrease the number of networks a request can travel through before being dropped by the DHCP daemon. |
"How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (DHCP Manager)" "How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (Command Line)" |
|
Change the length of time an IP address offer is cached |
Increase or decrease the number seconds that the DHCP service will reserve an offered IP address before offering to a new client |
"How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (DHCP Manager)" "How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (Command Line)" |
The following figure shows DHCP Manager's Modify Services dialog box.
Figure 11-3 Modify Service Options Dialog Box
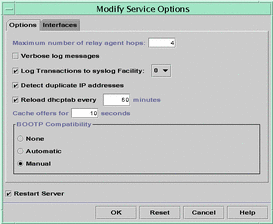
Changing DHCP Logging Options
The DHCP service can log DHCP service messages and DHCP transactions to syslog. See the syslogd(1M) and syslog.conf(4) manual pages for more information about syslog.
DHCP service messages logged to syslog include:
-
Error messages, which notify the administrator of conditions that prevent the DHCP service from fulfilling a request by a client or by the administrator.
-
Warnings and notices, which notify the administrator of conditions that are abnormal, but do not prevent the DHCP service from fulfilling a request.
You can increase information reporting by using the verbose option for the DHCP daemon. Verbose message output can be useful in troubleshooting DHCP problems. See "How to Generate Verbose DHCP Log Messages (DHCP Manager)".
Another useful troubleshooting technique is transaction logging. Transactions provide information about every interchange between a DHCP server or BOOTP relay and clients. DHCP server transactions include:
-
ASSIGN -- IP address assignment
-
EXTEND -- Lease extension
-
RELEASE -- IP address release
-
DECLINE -- Client declining address assignment
-
INFORM -- Client requesting network configuration parameters but not an IP address
-
NAK -- Server does not acknowledge a client's request to use a previously used IP address
-
ICMP_ECHO -- Server detects potential IP address for offering is already in use by another host.
BOOTP relay transactions include:
-
RELAY-CLNT -- Message being relayed from the DHCP client to a DHCP server
-
RELAY-SRVR -- Message being relayed from the DHCP server to the DHCP client
Transaction logging is disabled by default. When enabled, transaction logging uses the local0 syslog facility by default. DHCP transaction messages are generated with a syslog severity level of notice, so by default transactions are logged to the file where other notices are logged. However, because they use a local facility, the transaction messages can be logged separately from other notices if you edit the syslog.conf file to specify a separate log file.
You can disable or enable transaction logging, and specify a different syslog facility, from 0 through 7, as explained in "How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging (DHCP Manager)". If you edit the server system's syslog.conf file, you can also instruct syslogd to store the DHCP transaction messages in a separate file, as explained in "How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File".
How to Generate Verbose DHCP Log Messages (DHCP Manager)
-
Choose Modify from the Services menu.
-
Select Verbose Log Messages.
-
Select Restart Server if it is not already selected.
-
Click OK.
Verbose mode can reduce daemon efficiency because of the time taken to display messages.
How to Generate Verbose DHCP Log Messages (Command Line)
-
Become superuser on the DHCP server system.
-
Type the following commands to stop the DHCP daemon and restart it in verbose mode:
# /etc/init.d/dhcp stop # /usr/lib/inet/in.dhcpd -v options
where options are any other options you normally use to start the daemon.
The daemon runs in verbose mode for this session only.
Verbose mode can reduce daemon efficiency because of the time taken to display messages.
How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging (DHCP Manager)
This procedure enables/disables transaction logging for all subsequent DHCP server sessions.
-
Choose Modify from the Service menu.
-
Select Log Transactions to Syslog Facility.
To disable transaction logging, deselect this option.
-
(Optional) Select a local facility from 0 to 7 to use for logging transactions.
By default, DHCP transactions are logged to the location where system notices are logged, which depends on how syslogd is configured. If you want the DHCP transactions to be logged to a file separate from other system notices, see "How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File".
Message files can quickly become very large when transaction logging is enabled.
-
Select Restart Server if it is not already selected.
-
Click OK.
How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging for Current Session (Command Line)
-
Become superuser on the DHCP server system.
-
Type the following commands:
# /etc/init.d/dhcp stop # /usr/lib/inet/in.dhcpd -l syslog-local-facility
where syslog-local-facility is a number from 0 through 7. If you omit this option, 0 is used by default. See "How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging (DHCP Manager)".
Note -To disable transaction logging, omit the -l option when starting in.dhcpd.
By default, DHCP transactions are logged to the location where system notices are logged, which depends on how syslogd is configured. If you want the DHCP transactions to be logged to a file separate from other system notices, see "How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File".
Message files can quickly become very large when transaction logging is enabled.
How to Enable and Disable DHCP Transaction Logging for All Sessions (Command Line)
-
Become superuser on the DHCP server system.
-
Type the following to start dhcpconfig:
# /usr/sbin/dhcpconfig
-
Select Configure DHCP Service.
-
Press Return for the following prompts to accept the default values, which may differ from the values shown here:
Would you like to stop the DHCP service? (recommended) ([Y]/N): ### DHCP Service Configuration ### ### Configure DHCP Database Type and Location ### Enter datastore (files or nisplus) [nisplus]: Enter absolute path to datastore directory [dhcp.test.]: Warning: Setting NIS_GROUP to admin.dhcp.test.
-
Type Y for the following prompts as shown:
### Common daemon option setup ### Would you like to specify nondefault daemon options (Y/[N]):Y Do you want to enable transaction logging? (Y/[N]):Y
-
Type a number from 0 through 7 at the following prompt:
Which syslog local facility [0-7] do you wish to log to? [0]:
By default, DHCP transactions are logged to the location where system notices are logged, which depends on how syslogd is configured. If you want the DHCP transactions to be logged to a file separate from other system notices, see "How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File".
Message files can quickly become very large when transaction logging is enabled.
How to Log DHCP Transactions to a Separate Syslog File
-
Become superuser on the DHCP server system.
-
Edit the /etc/syslog.conf file on the server system and add a line having the following format:
localn.notice path-to-logfile
where n is the syslog facility number you specified for transaction logging, and path-to-logfile is the complete path to the file to use for logging transactions.
For example, you might add the following line:
local0.notice /var/log/dhcpsrvc
See syslog.conf(4) man page for more information about the syslog.conf file.
Customizing DHCP Service Performance Options
You can change options which affect the performance of the DHCP service. These options are described in the following table.
Table 11-2 Options Affecting DHCP Server Performance
The following procedures describe how to change these options.
How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (DHCP Manager)
-
To change the number of BOOTP relay agents a request can pass through, type the number of Maximum Number of Relay Agent Hops.
-
To have the DHCP server verify that an IP address is not in use before offering it to a client, select Detect Duplicate IP Addresses.
-
To have the DHCP server read dhcptab at specified intervals, select Reload dhcptab Every n Minutes, and type the number of minutes for the interval.
-
To change the length of time the server holds an IP address open after making an offer, type the number of seconds in the field Cache Offers for n Seconds.
-
Select Restart Server if it is not already selected.
-
Click OK.
How to Customize DHCP Server Performance Options (Command Line)
Changing options using this procedure affect only the current server session. If the DHCP server system is rebooted, the DHCP server starts using the settings specified during server configuration. If you want to change settings to apply to all future sessions, you must run dhcpconfig and answer the prompts as described in "How to Configure a DHCP Server (dhcpconfig) ".
-
Become superuser on the DHCP server system.
-
Type the following command:
# /etc/init.d/dhcp stop # /usr/lib/inet/in.dhcpd options
where options are any of the following:
- -h relay-hops
-
Specifies the maximum number of relay agent hops that can occur before the daemon drops the DHCP/BOOTP datagram.
- -n
-
Disables automatic duplicate IP address detection. This is not recommended.
- -t dhcptab_rescan_interval
-
Specifies the interval in minutes that the DHCP server should use to schedule the automatic rereading of the dhcptab information.
- -o seconds
-
Specifies the number of seconds the DHCP server should cache the offers it has extended to discovering DHCP clients. The default setting is 10 seconds.
For example, the following command sets the hop count to 2, disables duplicate IP address detection, sets the rescan interval to 30 minutes, and sets the offer time to 20 seconds.
# /usr/lib/inet/in.dhcp -h 2 -n -t 30 -o 20
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
