Multipoint Configurations Supported by PPP
Two types of multipoint links you can configure with PPP are:
-
Dial-in server with multipoint connections to remote machines, as shown in Figure 21-4
-
Logical, or virtual, network consisting of three or more nomadic computers, as shown in Figure 21-5
The following sections summarize these configurations; Chapter 22, Planning for PPP explains how to set up the configuration.
Multipoint Dial-in Servers
Figure 21-3 shows three geographically isolated computers communicating through a point-to-point link to an endpoint machine on a network. However, the network endpoint machine can communicate with the nomadic computers through a multipoint link, thus making it a multipoint dial-in server. (You can also set up a dial-in server with dynamic point-to-point connections, as explained in "Dial-in Server With Dynamic Point-to-Point Links".)
The dial-in server can communicate with all the machines on the other end of its multipoint PPP link. Though the machines in Figure 21-4 can directly communicate with the multipoint dial-in server, they cannot communicate directly with each other. They must pass information to each other through the dial-in server.
Virtual Networks
You can use PPP to set up a virtual network wherein the modems, PPP software, and telephone wires become the "virtual" network media. In a physical network, such as Ethernet or Token Ring, computers are directly cabled to the network media. In a virtual network, no true network media exist.
Machines become peer hosts on the virtual network when you configure each with a multipoint communications link. Then each host can dial out through its modem over phone lines to reach another endpoint machine. Each computer also functions as a dial-in machine, permitting its peer hosts on the virtual network to dial in to it.
The following figure depicts a virtual network consisting of nomadic computers connected to each other through modems and telephone lines.
Figure 21-5 Virtual Network of Nomadic Computers
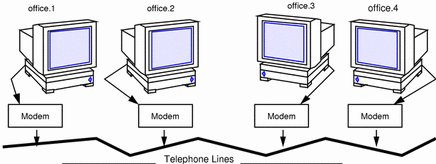
Each machine exists in a different office, perhaps in a different town from other members of the virtual network. However, each machine can establish communications with its peer hosts over its multipoint communications links.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
