File and Folder Ownership and Security
The traditional UNIX file and folder protection scheme provides read, write, and execute permissions for three user types: owner, group, and other. These are called basic permissions.
Access Control Lists (ACLs) provide greater control over file and folder permissions than do basic permissions. ACLs enable you to define file or folder permissions for the owner, owner's group, others, and specific users and groups, and default permissions for each of these categories.
Basic Permissions
The permissions on a file or folder specify how it can be accessed. These permissions apply to the basic user types as well as to the ACL default types described in "Setting Default Permissions Through an Access Control List".
-
Read Permission - Allows access to retrieve, copy, or view the contents of the object.
-
Write Permission - For a file, allows access to change the contents of the file. For a folder, allows access to create or delete objects from the folder.
-
Execute Permission - For a file, allows access to run the file (for executable files, scripts, and actions). For a folder, allows access to search and list the folder's contents.
If you do not have permission to write inside a folder, the folder will look like this:
If you do not have read or execute permission for a folder, the folder will look like this:
Basic User Types
For a file or folder, the three basic types of users are:
-
Owner - The user who owns the file or folder. Only a system administrator (root user) can change the owner of a file or folder.
-
Group - Users who have been grouped together by the system administrator. For example, the members of a department might belong to the same group. This group is the owning group and usually includes the file or folder's owner.
-
Other - All other users on the system besides the owner and owning group.
Examples
To make a folder private:
-
Change the folder's properties, giving yourself (the owner) read, write, and execute permission, but giving no permissions for group and other. This means that only you and the root user can view the contents of the folder.
To make an object that you've created available for everyone to use but protect it so it isn't inadvertently overwritten:
-
Change the file's properties, giving read and execute permission to owner, group, and other. Don't give anyone write permission.
To View a File or Folder's Permissions
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose permissions you want to view.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu, or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
-
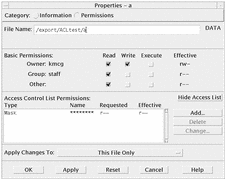
Examine the file or folder's Basic Permissions in the Effective column ("r" stands for Read permission, "w" stands for Write permission, and "x" stands for Execute permission).
-
Owner - The permissions granted to the file or folder's owner
-
Group - The permissions granted to the file or folder's group
-
Other - The permissions granted to everyone besides the owner and group
Note -The Read, Write, and Execute columns in the dialog box represent requested permissions, and may be different than the permissions that are actually in effect (which are shown in the Effective column). The requested permissions may not be in effect because of the mask (see "Permissions Mask").
If you want to look at the permissions for another file or folder, select the object and choose Properties from the Selected menu. If you display the Properties dialog box by typing sdtfprop& on the command line, you can click Browse in the dialog box and select the file or folder name to view properties.
-
To Modify Basic Permissions
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose permissions you want to modify.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
Click the check boxes to set the Owner, Group, and Other permissions.
The mask restricts the Group permissions, but does not affect Owner or Other permissions. The actual read, write, and execute permissions that Owner, Group, and Other receive appear in the Effective column.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the changes.
For files, the options are This File Only (default), All Files in Parent Folder, and All Files in Parent Folder and its Subfolders. For folders, the options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK on the Permissions dialog box to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the Permissions dialog box.
If you want to modify the permissions for another file or folder, select the object and choose Properties from the Selected menu. If you display the Properties dialog box by typing sdtfprop& on the command line, you can click Browse in the dialog box and select the file or folder name to modify properties.
See "Permissions Mask" for a discussion of the mask.
To Change File or Folder Ownership
Note -
If you do not have permission to change the properties, some of the controls in the Permissions dialog box are unavailable.
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose ownership you want to modify.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
To change the owner, type the new owner name into the Owner text field. To change the owning group, type the new group name into the Group text field.
You can specify a different owning group only if you are also a member of another group, even if you are not the file or folder owner.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the Permissions dialog box.
To Browse and Edit Properties of Multiple Files and Folders
-
Open the Properties dialog box by typing sdtfprop& at the command line.
You can edit the File Name text field and click Browse to open the File Selection dialog box only if you open the Properties dialog box from the command line.
-
Click Browse or type the name of a file or folder in the File Name field.
-
Browse or edit the file or folder properties.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings and continue the browsing and editing process.
Access Control Lists
ACLs enable you to define file or folder permissions for the owner, owner's group, others, and specific users and groups, and default permissions for each of these categories. You can set up only one ACL per file or folder. An ACL consists of ACL entries. Each entry has a user type associated with it, much as basic permissions have Owner, Group, or Other associated with them.
If you want to grant file or folder access to a particular user or group, use the User or Group type ACL entry, respectively. You must specify the name of the user or group when you create the ACL entry. For example, you can use an ACL to grant a friend read permission on your resume, while protecting it from being read by the rest of the world (besides yourself).
To create, modify, or view ACLs on a file or folder, it must reside on a server or system running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible versions, and you must be running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible versions. Such files and folders are called ACL-enabled. To set, modify, and view basic permissions and ACLs using the Properties Graphical User Interface (GUI), you must be running CDE 1.1 or later.
You must be the owner of the file or folder to create or modify basic permissions or ACLs for that file or folder. If you are not the owner, all fields in the Properties dialog box are displayed as read-only.
Note -
ACL terminology in this section refers to terminology used in the Properties GUI. Command-line terminology may be slightly different.
To View an Access Control List
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose Access Control List (ACL) you want to view.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Properties dialog box appears.
If the file or folder has an ACL, it appears in the scrolling list labeled Access Control List Permissions. If the file or folder has no ACL, the scrolling list is hidden.
The Requested column shows the permissions that the owner requests for each ACL entry. These permissions are restricted by the mask, and the actual ACL entry permissions appear in the Effective column. See "Permissions Mask" for a discussion of the mask.
Note -To create, modify, or view ACLs on a file or folder, it must reside on a server or system running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible systems, and you must be running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible systems.
To Add an Access Control List Entry
Note -
Adding the first Access Control List entry creates the Access Control List.
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose ACL you want to modify.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
Click Show Access Control List if the ACL portion of the Permissions dialog box is not visible.
-
Click the Add button.
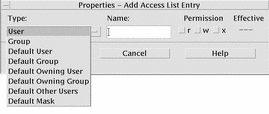
The Add Access List Entry dialog box appears.
-
Select an option from the Type option button.
-
Enter the name associated with the chosen Type, if it has one in the Name field.
-
Click the Permission check boxes to reflect the values you want for the new ACL entry.
The status line at the bottom of the dialog box informs you if the permissions you request are restricted by the mask.
-
Click Add in the Add Access List Entry dialog box.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the change.
For files, the options are This File Only (default), All Files in Parent Folder, and All Files in Parent Folder and its Subfolders. For folders, the options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
To Change an Access Control List Entry
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder for which you want to change an ACL entry.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
Select the entry in the Access Control List Permissions scrolling list that you want to change.
-
Click Change.
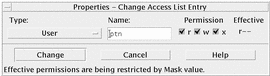
The Change Access List Entry dialog box appears.
-
Click the Permission check boxes to reflect the values you want for the ACL entry.
The status line at the bottom of the dialog box informs you if the permissions you request are restricted by the mask.
-
Click the Change button in the Change Access List Entry dialog box.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the change.
For files, the options are This File Only (default), All Files in Parent Folder, and All Files in Parent Folder and its Subfolders. For folders, the options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
To Delete an Access Control List Entry
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder for which you want to delete an ACL entry.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
Select the entry in the Access Control List Permissions scrolling list that you want to delete.
-
Click the Delete button.
A dialog box appears asking you to confirm this deletion. If you delete any of the four required ACL default entries, all ACL default entries will be deleted. See "Setting Default Permissions Through an Access Control List" for a description of required and optional default ACL entries.
Note -Removing all entries (except Mask) removes the entire Access Control List.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the change.
For files, the options are This File Only (default), All Files in Parent Folder, and All Files in Parent Folder and its Subfolders. For folders, the options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
Setting Default Permissions Through an Access Control List
When you create a file or folder within a folder, it inherits the basic permissions set by the system administrator. (To determine the current defaults, create a new file or folder and then choose Properties from the Selected menu to view the permissions.)
You can use an Access Control List to set default basic permissions yourself for any file or folder that is created within a folder. The ACL for that folder must contain entries for all four of the following required Default entry types: Default Owning User, Default Owning Group, Default Other, and Default Mask. An ACL can contain only one entry of each required type.
The file or folder inherits the values for Owner, Group, and Other from the person who creates it and inherits the basic permissions from the required ACL Default entry types on the containing folder. ACL entries of these types do not have names associated with them.
You can also set optional Default entry types--Default User and Default Group-- for any file or folder that is created within a folder. You can create as many Default User or Default Group ACL entries as you want. You must specify the name of the user or group when you create the ACL entry.
Any ACL in which you want to put a Default User or Default Group entry must also contain one of each required entry type.
Example
Suppose that the values for Owner and Group for a user named Carla are otto and otto_staff, respectively. The value for Other (call it otto_other) is everyone at Carla's company except for Carla and the members of otto_staff. Carla creates these required Default ACLs on her folder named Project1:
-
Default Owning User with permissions rwx (read, write, execute)
-
Default Owning Group with permissions rx (read, execute)
-
Default Other with permissions no-read, no-write, no-execute
-
Default Mask with permissions rw (read, write)
Any file or folder subsequently placed in the Project1 folder inherits these basic permissions from Project1:
-
The file or folder Owner value is otto and otto has read, write, and execute permission on that file or folder
-
The file or folder Group value is otto_staff and otto_staff has read and execute permission on that file or folder
-
The file or folder Other value is otto_other and otto_other has no-read, no-write, and no-execute permission on that file or folder
Also, the file or folder has a Mask entry in the Access Control List Permissions scrolling list with the value rw (read, write).
If Carla also adds an optional ACL of type Default User (Default Group) for the Project1 folder, then any file or folder subsequently placed in Project1 will inherit an ACL of type User (Group).
To Set Required Default Entry Types
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the folder for which you want to set the required ACL Default entry types.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
-
Click the Show Access Control List button if the folder has no ACL defined.
If the folder has an ACL defined, it will be visible when you open the Permissions dialog box.
-
Click Add and select an ACL entry of type Default Owning User, Default Owning Group, Default Other, or Default Mask.
A message appears reminding you that the other required ACL Default entries will also be added.
-
Click the Permission check boxes to set the permissions for the Default entry.
-
Click Add in the Add Access List Entry dialog box.
The other three required ACL Default entries are automatically created for you, with permissions set to no-read, no-write, no-execute.
-
(Optional) Change the permissions for the required ACL Default entries that were automatically created in Step 6 above.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the changes.
The options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
To Delete Required ACL Default Entry Types
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the folder for which you want to delete an ACL Default entry.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
-
Select required ACL Default entry and click Delete.
A message appears to remind you that once you delete one of the required default ACL entries, the other three are automatically deleted for you.
-
Click Delete in the confirmation dialog box.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the change.
The options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
To Set Optional ACL Default Entry Types
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the folder for which you want to set an optional ACL Default entry type.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
-
Click the Show Access Control List button if the folder has no ACL defined.
If the folder has an ACL defined, it will be visible when you open the Permissions dialog box.
-
Click Add and select an ACL entry of type Default User or Default Owning Group.
If the ACL does not contain the required default entries, they will also be created, with permissions set to no-read, no-write, no-execute.
-
Click the Permission check boxes to set the permissions for the Default entry.
-
Click Add in the Add Access List Entry dialog box.
-
Continue to add as many ACL entries of type Default User or Default Owning Group as you want.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the changes.
The options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
Permissions Mask
ACL-enabled files and folders have a mask defined whose default permissions are the group permissions for the file or folder. The mask is the maximum allowable permissions granted to any user on all ACL entries and for Group basic permissions. It does not restrict Owner or Other basic permissions. For example, if a file's mask is read-only, then you cannot create an ACL with write or execute permission for a user without changing the mask value.
Use the mask as a quick way to limit permissions for users and groups.
To Modify the Mask
-
In File Manager, select the icon of the file or folder whose mask you want to modify.
-
Choose Properties from the File Manager Selected menu or from the icon's pop-up menu (displayed by pressing Shift+F10 or mouse button 3).
The Permissions dialog box appears.
-
Click the Show Access Control List button if the folder has no ACL defined.
If the folder has an ACL defined, it will be visible when you open the Permissions dialog box.
-
Select the Mask entry in the Access Control List Permissions scrolling list.
The current mask permissions appear in the Effective column.
-
Click the Change button.
-
Click the Permission check boxes to reflect the values you want for the mask.
-
Click the Change button in the Change Access List Entry dialog box.
-
Use the Apply Changes To option button to choose the scope of the permissions changes.
For files, the options are This File Only (default), All Files in Parent Folder, and All Files in Parent Folder and its Subfolders. For folders, the options are This folder only (default) and This folder and its Subfolders.
-
Click OK to apply the current settings and dismiss the dialog box. Click Apply to apply the settings without dismissing the dialog box.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
