GSS-API Status Codes
Major status codes are encoded in the OM_uint32 as shown in Figure B–1.
Figure B–1 Major-Status Encoding
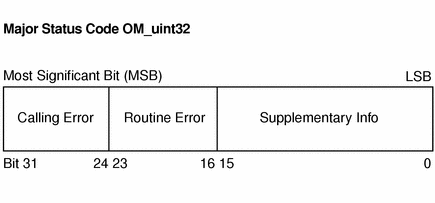
If a GSS-API routine returns a GSS status code whose upper 16 bits contain a non-zero value, the call has failed. If the calling error field is non-zero, the invoking application's call of the routine was erroneous. Calling errors are listed in Table B–2. If the routine error field is non-zero, the routine failed because of a routine-specific error, as listed below in Table B–3. Whether or not the upper 16 bits indicate a failure or a success, the routine might indicate additional information by setting bits in the supplementary information field of the status code. The meaning of individual bits is listed in Table B–4.
GSS-API Major Status Code Values
The following tables lists calling errors returned by the GSS-API; that is, errors that are specific to a particular language-binding (C, in this case).
Table B–2 Calling Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_READ |
1 |
A required input parameter could not be read |
|
GSS_S_CALL_INACCESSIBLE_WRITE |
2 |
A required output parameter could not be written |
|
GSS_S_CALL_BAD_STRUCTURE |
3 |
A parameter was malformed |
The following table lists the routine errors (that is, generic errors returned by GSS-API functions).
Table B–3 Routine Errors|
Error |
Value in Field |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_BAD_MECH |
1 |
An unsupported mechanism was requested |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAME |
2 |
An invalid name was supplied |
|
GSS_S_BAD_NAMETYPE |
3 |
A supplied name was of an unsupported type |
|
GSS_S_BAD_BINDINGS |
4 |
Incorrect channel bindings were supplied |
|
GSS_S_BAD_STATUS |
5 |
An invalid status code was supplied |
|
GSS_S_BAD_MIC, GSS_S_BAD_SIG |
6 |
A token had an invalid MIC |
|
GSS_S_NO_CRED |
7 |
No credentials were supplied, or the credentials were unavailable or inaccessible |
|
GSS_S_NO_CONTEXT |
8 |
No context has been established |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_TOKEN |
9 |
A token was invalid |
|
GSS_S_DEFECTIVE_CREDENTIAL |
10 |
A credential was invalid |
|
GSS_S_CREDENTIALS_EXPIRED |
11 |
The referenced credentials have expired |
|
GSS_S_CONTEXT_EXPIRED |
12 |
The context has expired |
|
GSS_S_FAILURE |
13 |
Miscellaneous failure (see text) |
|
GSS_S_BAD_QOP |
14 |
The quality-of-protection requested could not be provided |
|
GSS_S_UNAUTHORIZED |
15 |
The operation is forbidden by local security policy |
|
GSS_S_UNAVAILABLE |
16 |
The operation or option is unavailable |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_ELEMENT |
17 |
The requested credential element already exists |
|
GSS_S_NAME_NOT_MN |
18 |
The provided name was not a Mechanism Name (MN) |
The routine documentation also uses the name GSS_S_COMPLETE, which is a zero value, to indicate an absence of any API errors or supplementary information bits.
The following table lists the supplementary information values returned by GSS-API functions.
Table B–4 Supplementary Information Codes|
Code |
Bit Number |
Meaning |
|---|---|---|
|
GSS_S_CONTINUE_NEEDED |
0 (LSB) |
Returned only by gss_init_sec_context() or gss_accept_sec_context(). The routine must be called again to complete its function |
|
GSS_S_DUPLICATE_TOKEN |
1 |
The token was a duplicate of an earlier token |
|
GSS_S_OLD_TOKEN |
2 |
The token's validity period has expired |
|
GSS_S_UNSEQ_TOKEN |
3 |
A later token has already been processed |
|
GSS_S_GAP_TOKEN |
4 |
An expected per-message token was not received |
The GSS major status code GSS_S_FAILURE is used to indicate that the underlying mechanism detected an error for which no specific GSS–API status code is defined. The mechanism-specific status code (minor-status code) will provide more details about the error.
For more on status codes, see Status Codes.
Displaying Status Codes
The function gss_display_status() translates GSS-API status codes into text format, allowing them to be displayed to a user or put in a text log. Because gss_display_status() only displays one status code at a time, and some functions can return multiple status conditions, it should be invoked as part of a loop. As long as gss_display_status() indicates a non-zero status code (in Example B–1, the value returned in the message_context parameter), another status code is available for the function to fetch.
Example B–1 Displaying Status Codes with gss_display_status()
OM_uint32 message_context;
OM_uint32 status_code;
OM_uint32 maj_status;
OM_uint32 min_status;
gss_buffer_desc status_string;
...
message_context = 0;
do {
maj_status = gss_display_status(
&min_status,
status_code,
GSS_C_GSS_CODE,
GSS_C_NO_OID,
&message_context,
&status_string);
fprintf(stderr, "%.*s\n", \
(int)status_string.length, \
(char *)status_string.value);
gss_release_buffer(&min_status, &status_string,);
} while (message_context != 0);
Status Code Macros
The macros GSS_CALLING_ERROR(), GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() and GSS_SUPPLEMENTARY_INFO() are provided, each of which takes a GSS status code and removes all but the relevant field. For example, the value obtained by applying GSS_ROUTINE_ERROR() to a status code removes the calling errors and supplementary information fields, leaving only the routine errors field. The values delivered by these macros can be directly compared with a GSS_S_xxx symbol of the appropriate type. The macro GSS_ERROR() is also provided, which when applied to a GSS–API status code returns a non-zero value if the status code indicated a calling or routine error, and a zero value otherwise. All macros defined by the GSS-API evaluate their argument(s) exactly once.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
