Memory Module (DIMM) Reference
|
When replacing or upgrading a DIMM on the Sun Netra X6270 M2 server module, see the following sections:
D.1 Memory Module Installation Considerations
The Sun Netra X6270 M2 server module supports a variety of DIMM configurations that can include single-rank (SR) DIMMs, dual-rank (DR) DIMMs, or quad-rank (QR) DIMMs. When replacing or adding memory modules to the Sun Netra X6270 M2 server module, you should consider the following:
- Physical layout of the DIMMs and CPUs
For details, see DIMM and CPU Physical Layout.
For details, see DIMM Population Rules.
- DIMM classification labels
For details, see DIMM Rank Classification Labels.
- Error correction and parity
For details, see Error Correction and Parity
D.1.1 DIMM and CPU Physical Layout
The physical layout of the DIMMs and CPUs on a Sun Netra X6270 M2 server module is shown in FIGURE D-1.
FIGURE D-1 CPU and DIMM Physical Layout
Figure Legend CPU and DIMM Physical Layout
|
CPU 0 location
|
|
|
CPU 1 location
|
|
|
Channel locations for CPU 0
Three channels per CPU with each channel containing three color-coded DIMM slots (black, white, and blue).
|

|
|
Channel locations for CPU 1
Three channels per CPU with each channel containing three color-coded DIMM slots (blue, white and black).
|

|
|
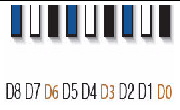
DIMM slot numbering per CPU; with D8 as the slot furthest away from processor.
|
P0:

P1:
|
D.1.2 DIMM Population Rules
The DIMM population rules for Oracle’s Sun Netra X6270 M2 server module are as follows:
1. Do not populate any DIMM socket next to an empty CPU socket. Each processor contains a separate memory controller.
2. Each CPU can support a maximum of:
- Nine dual-rank (DR) or single-rank (SR) DIMMs; or
- Six quad-rank (QR) DIMMs with two per memory channel; or
- Three QR DIMMs with one per channel and three DR or SR DIMMs.
3. Populate DIMMs by location according to the following rules:
- Populate the DIMM slots for each memory channel that are the farthest from the CPU first.
For example, populate D8/D5/D2 first; then D7/D4/D1 second; and finally, D6/D3/D0. See FIGURE D-1.
- Populate QR DIMMs first, followed by SR or DR DIMMs.
- Populate QR DIMMs in blue sockets (D8/D5/D2) first then white sockets (D7/D4/D1). See FIGURE D-1.
Note that QR DIMMs are supported only in white sockets if adjacent blue socket contains a QR DIMM.
4. For maximum performance, apply the following rules:
- The best performance is ensured by preserving symmetry. For example, adding three of same kind of DIMMs, one per memory channel, and ensuring that both CPUs have the same size of DIMMs populated in the same manner.
- In certain configurations, DIMMs will run slower than their individual maximum speed. See TABLE D-1 for further details.
TABLE D-1 Memory Considerations and Limitations
|
1
|
DIMMs are available in two speeds: 1066 MHz and 1333 MHz.
|
|
2
|
DIMM speed rules are as follows:
3x DIMM per channel = 800 MHz
2x DIMM per channel = 1333 MHz (for single-rank and dual-rank DIMMs)
or = 800 MHz (for quad-rank DIMMs)
1x DIMM per channel = 1333 MHz (if using 1333 MHz DIMMs1)
1x DIMM per channel = 1066 MHz (if using 1066 MHz DIMMs)
|
|
3
|
The system operates all memory only as fast as the slowest DIMM configuration.
|
|
|
D.1.3 DIMM Rank Classification Labels
DIMMs come in a variety of ranks: single, dual, or quad. Each DIMM is shipped with a label identifying its rank classification. TABLE D-2 identifies the corresponding rank classification label shipped with each DIMM.
TABLE D-2 DIMM Classification Labels
|
Rank Classification
|
Label
|
|
Quad-rank DIMM
|
4Rx4
|
|
Dual-rank DIMM
|
2Rx4
|
|
Single-rank DIMM
|
1Rx4
|
D.1.4 Error Correction and Parity
The server’s processor provides parity protection on its internal cache memories and error-correcting code (ECC) protection of the data. The system can detect and log the following types of errors:
- Correctable and uncorrectable memory ECC errors
- Uncorrectable CPU internal errors
Advanced ECC corrects up to 4 bits in error on nibble boundaries, as long as they are all in the same DRAM. If a DRAM fails, the DIMM continues to function.
Refer to the Oracle Integrated Lights Out Manager (ILOM) 3.0 Documentation Collection for information on how to access the error log.
| Sun Netra X6270 M2 Server Module Service Manual
|
821-0939-10
|
    |
Copyright © 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
