Creating a DB2 Connect OTD
The Database OTD Wizard generates OTDs by connecting to external data sources and creating corresponding Object Type Definitions. The OTD Wizard can create OTDs based on any combination of Tables and Stored Procedures or Prepared SQL Statements. Field nodes are added to the OTD based on the Tables in the external data source. Java method and parameter nodes are added to provide the appropriate JDBC functionality. For more information about the Java methods, refer to your JDBC developer’s reference.
Note –
Database OTDs are not messagable. For more information on messagable OTDs, see the Sun Enterprise Service Bus User’s Guide.
The following steps are required to create a new OTD for the DB2 Connect Adapter.
Select Wizard Type
Select the type of wizard required to build an OTD in the New Object Type Definition Wizard.
 To Select the Oracle Database OTD Wizard
To Select the Oracle Database OTD Wizard
-
On the project tree, right click on the project and select Create an Object Type Definition from the shortcut menu.
-
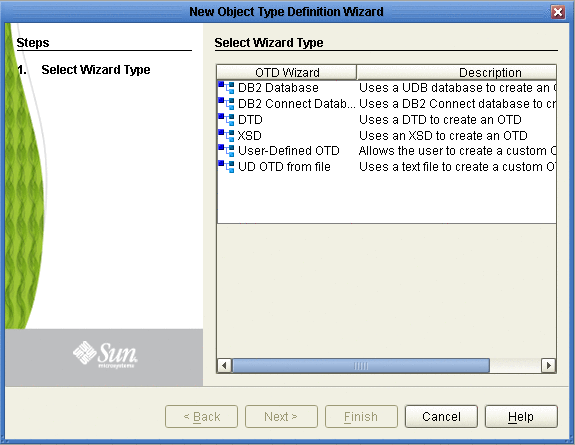
From the OTD Wizard Selection window, select the DB2 Connect Database and click Next (see the following figure).
Figure 1–7 OTD Wizard Selection
Connecting to Database
Enter the DB2 Connect connection information in the Connection Information frame.
 To Connect to a Database
To Connect to a Database
-
Select the Connection type using the drop-down list (see the following figure). The resulting Connection Information fields displayed will depend on your selection (i.e. selecting a Type 2 or Type 4 connector).
-
Specify the applicable connection information (depending on the Connection type) for your database including:
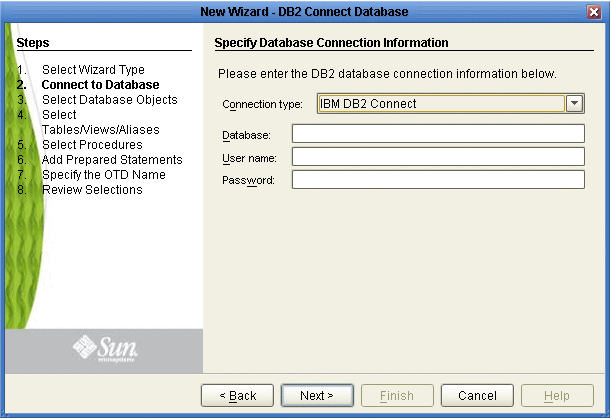
For the Type 2 Connection (shown above):
-
Database - The name of the database instance.
-
User Name - The user name that the Adapter uses to connect to the database.
-
Password - The password used to access the database.
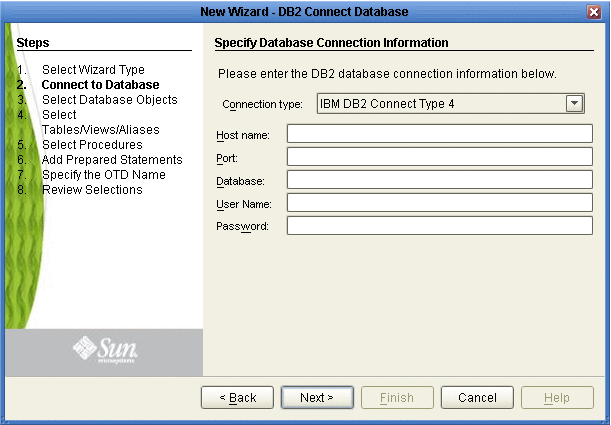
For the Type 4 Connection(shown above):
-
Host Name - The server where DB2 Connect resides.
-
Port - The port number of DB2 Connect.
-
Database - The name of the database instance that the DB2 is running on Windows/Unix. The name of the locator for the DB2 running in z/OS or AS/400.
-
User Name - The user name that the adapter uses to connect to the database.
-
Password - The password used to access the database.
-
-
Click Next. The Select Database Objects window appears.
Selecting Database Objects
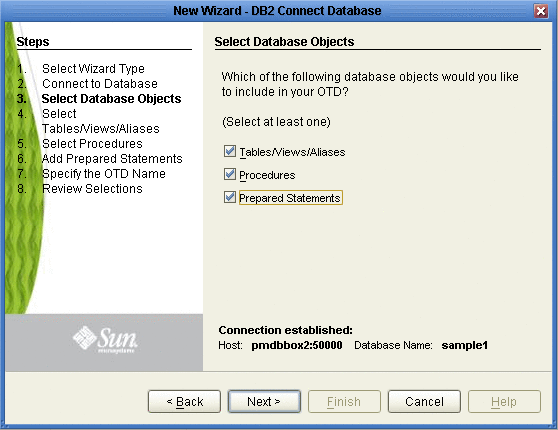
Select the type of DB2 Connect objects you want included in the OTD.
 To Select Database Objects
To Select Database Objects
-
When selecting Database Objects, you can select any combination of Tables, Views, Procedures, or Prepared Statements you would like to include in the .otd file. Click Next to continue. (See the following figure).
Note –Views are read-only and are for informational purposes only.
-
Click Next to continue. The Select Tables/Views/Aliases window appears.
Selecting Table/Views/Aliases
Select the types of tables or views required in the OTD.
 To Select Table/Views/Aliases
To Select Table/Views/Aliases
-
In the Select Tables/Views window, click Add (see the figure below).
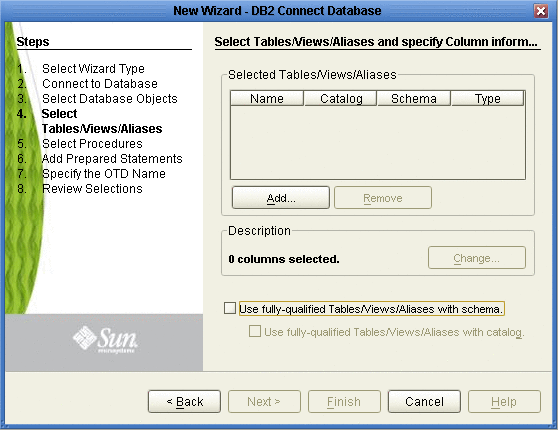
-
In the Add Tables window, select the type of criteria to be used for your search, consisting of table data, view only data, or both. You can include system tables in your search by selecting the checkbox.
-
From the Table/View Name drop down list, select the location of your database table and click Search (see the following figure). You can search for Table/View Names by entering a table name. The use of wildcard characters of ”?’, and ”*’ as part of your Table/View name search allow for greater search capabilities. For example, “AB?CD” or “AB*CD”.
-
Select the table of choice and click OK. The table selected is added to the Selected window (see the following figure).
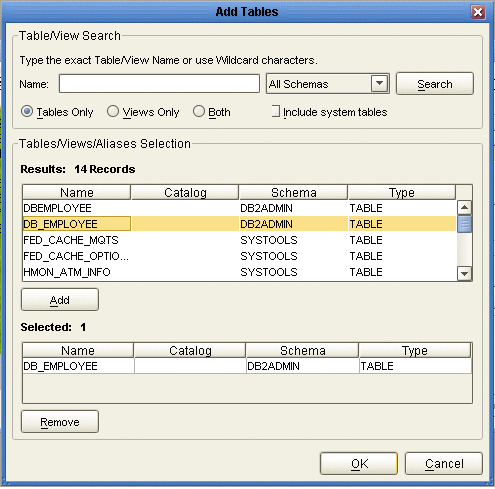
-
On the Selected Tables/Views window, review the table(s) you have selected. To make changes to the selected Table or View, click Change. If you do not wish to make any additional changes, click Next to continue.
-
If you clicked Change on the Selected Tables/Views window, you can select or deselect your table columns on the Table/View Columns window. You can also change the data type for each table by highlighting the data type and selecting a different one from the drop down (see the following figure).
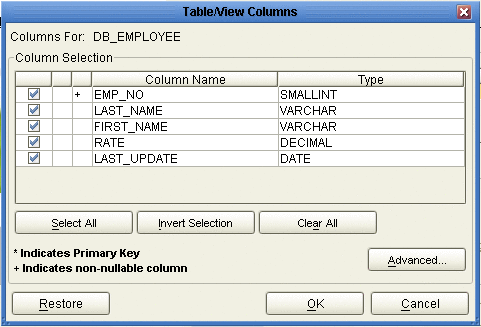
-
Click Advanced to change the data type, precision/length, or scale. In general, do not change the precision/length or the scale. Once you have finished your table choices, click OK (see the following figure).
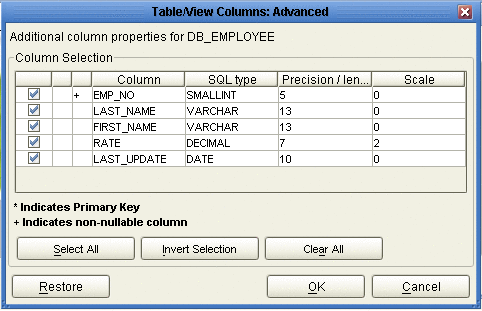
-
When using Prepared Statement packages, select Use fully qualified table/view names in the generated Java code.
Selecting Procedures
Select the procedure required in the OTD.
 To Select Procedures
To Select Procedures
-
On the Select Procedures and specify Resultset and Parameter Information window, click Add.
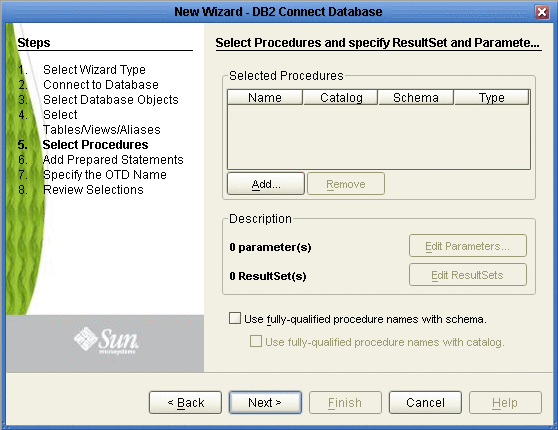
-
On the Select Procedures window, enter the name of a Procedure or select a table from the drop down list. Click Search. Wildcard characters can also be used.
-
In the resulting Procedure Selection list box, select a Procedure. Click OK.
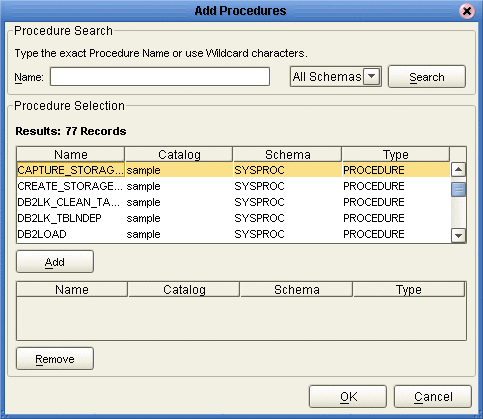
-
On the Select Procedures and specify Resultset and Parameter Information window click Edit Parameters to make any changes to the selected Procedure. (see the following figure).
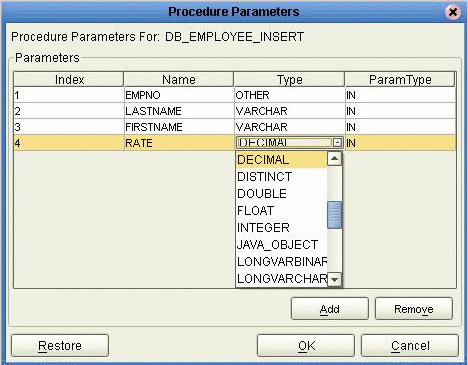
-
To restore the data type, click Restore. When finished, click OK.
-
To select how you would like the OTD to generate the nodes for the Resultset click Edit Resultsets.
-
Click Add to add the type of Resultset node you would like to generate (see the following figure).
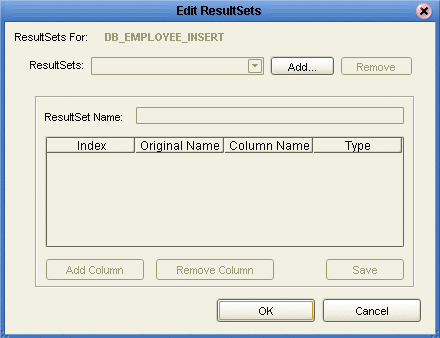
The DBWizard provides three different ways to generate the ResultSet nodes of a Stored Procedure. They are the "By Executing", "Manually", and "With Assistance" modes.
By Executing Mode
“By Executing” mode executes the specified Stored Procedure with default values to generate the ResultSet(s). Depending on the business logic of the Stored Procedure, zero or more ResultSets can be returned from the execution. In the case that there are multiple ResultSets and "By Executing" mode does not return all ResultSets, one should use the other modes to generate the ResultSet nodes.
With Assistance Mode
"With Assistance" mode allows users to specify a query and execute it to generate the ResultSet node. To facilitate this operation, the DBWizard tries to retrieve the content of the specified Stored Procedure and display it. However, content retrieval is not supported by all types of Stored Procedures. We can roughly classify Stored Procedures into two types: SQL and external. SQL Stored Procedures are created using CREATE PROCEDURE SQL statements while external Stored Procedures are created using host languages (e.g. Java). Since external Stored Procedures do not store their execution plans in the database, content retrieval is impossible. When using "Assist" mode, highlight the execute statement up to and including the table name(s) before executing the query.
Manually Mode
"Manually" mode is the most flexible way to generate the result set nodes. It allows users to specify the node name, original column name and data type manually. One drawback of this method is that users need to know the original column names and data types. This is not always possible. For example, the column name of 3*C in this query.
SELECT A, B, 3*C FROM table T
is generated by the database. In this case, "With Assistance" mode is a better choice.
If you modify the ResultSet generated by the “Execute” mode of the Database Wizard you need to make sure the indexes match the Stored Procedure. This assures your ResultSet indexes are preserved.
-
On the Select Procedures and specify Resultset and Parameter Information window click Next to continue.
Adding Prepared Statements
A Prepared Statement OTD represents a SQL statement that has been compiled. Fields in the OTD correspond to the input values that users need to provide. Prepared statements can be used to perform insert, update, delete and query operations. A prepared statement uses a question mark (?) as a place holder for input. For example: insert into EMP_TAB (Age, Name, Dept No) values (?, ?, ?)
 To Add Prepared Statements
To Add Prepared Statements
To execute a prepared statement, set the input parameters and call executeUpdate() and specify the input values if any.
Note –
When using a Prepared Statement, the ”ResultsAvailable()’ method will always return true. Although this method is available, you should not use it with a ”while’ loop. Doing so would result in an infinite loop at runtime and will stop all of the system’s CPU. If it is used, it should only be used with the ”if’ statement.You can process a resultset by looping through the next() method.
-
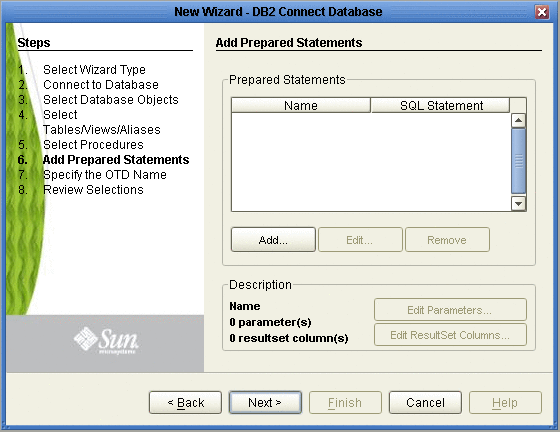
On the Add Prepared Statements window, click Add.
-
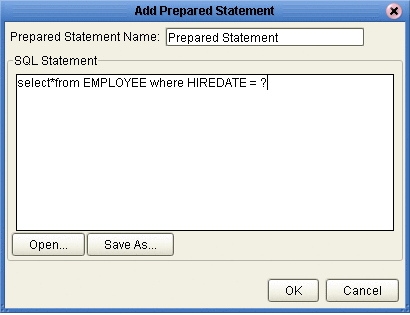
Enter the name of a Prepared Statement or create a SQL statement by clicking in the SQL Statement window. When finished creating the statement, click Save As giving the statement a name. This name will appear as a node in the OTD. Click OK (see the following figure).
-
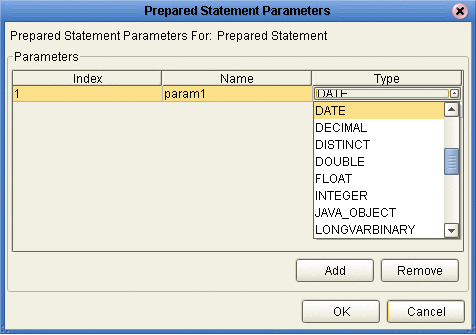
On the Add Prepared Statement window, the name you assigned to the Prepared Statement appears. To edit the parameters, click Edit Parameters. You can change the data type by clicking in the Type field and selecting a different type from the list.
Note –When doing a Prepared Statement with two or more tables, where multiple tables have the same column name, you must put the table name qualifier in the Prepared Statement to build the OTD.
-
Click Add if you want to add additional parameters to the Statement or highlight a row and click Remove to remove it. Click OK. (see the following figure).
-
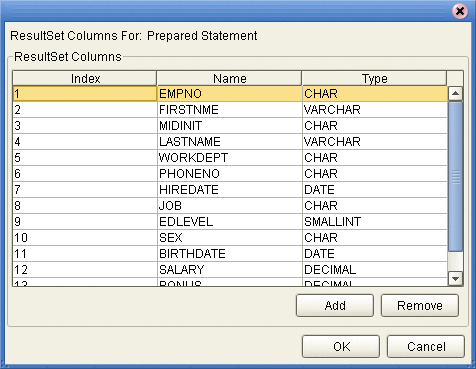
To edit the Resultset Columns, click Edit Resultset Columns. Both the Name and Type are editable but it is recommend you do not change the Name. Doing so will cause a loss of integrity between the Resultset and the Database. Click OK (see the following figure).
Note –The OTD Wizard fails to create OTDs with complex prepared statements that use the same column name in different tables. This problem is resolved by modifying the SQL statement to use column name aliases.
-
On the Add Prepared Statements window, click OK.
Specifying the OTD Name
Specify the name that your OTD will display in the Java CAPS IDE.
 To Specify the OTD Name
To Specify the OTD Name
-
Enter a name for the OTD.
The OTD contains the selected tables and the package name of the generated classes (see the following figure).
-
Click Next to continue. The Review your Selections window appears.
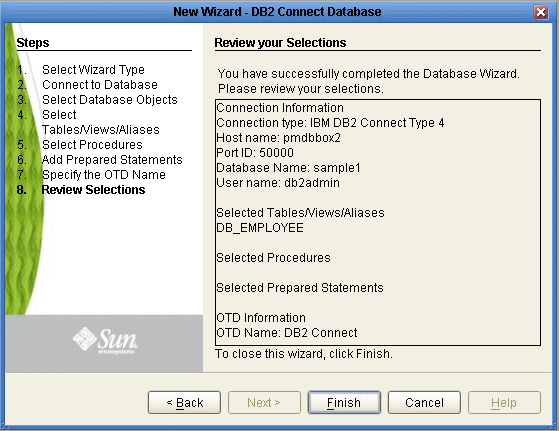
Review Selections
Review the selections made for the new OTD.
 To Review Your OTD Selections
To Review Your OTD Selections
-
View the summary of the OTD. If you find you have made a mistake, click Back and correct the information.
-
If you are satisfied with the OTD information, click Finish to begin generating the OTD (see the following figure).
Figure 1–8 Database Wizard - Summary
The resulting OTD appears on the Java CAPS IDE’s canvas.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
