HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 3
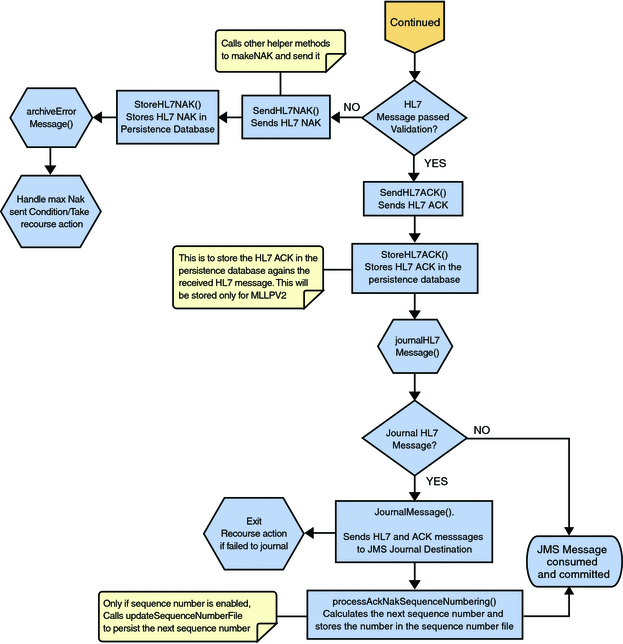
If no exception occurs, validateHL7Message() is called, which validates the message to determine whether to ACK or NAK the message. Other helper methods are also called to validate the HL7 message.
If the HL7 message does not pass validation, the Collaboration calls makeNak() and sendHL7Nak() to create and send the NAK to the external. The HL7 message, with the NAK, is archived to the Error Queue. If the number of consecutive NAKs sent surpasses the maximum number of retries, the associated recourse action is taken.
If the HL7 message passes validation, the Collaboration calls makeAck() and sendHL7Ack() to create and send the ACK to the external.
The HL7 ACK/NAK are stored in the persistent database. This ACK/NAK is stored against the Inbound HL7 message received.
After the ACK is sent, the HL7 message and the ACK are journaled to the JMS Queue Journal destination. If the message fails to journal the associated recourse action is taken.
If Sequence Numbering is enabled, the processAckNakSequenceNumbering method calculates the next sequence number and stores the number in the sequence number file by calling the updateSequenceNumberFile method to persist the next sequence number.
Figure 1–34 HL7 V2 Standard Inbound Message Mode Data Flow over MLLPV2 — Part 3
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
