Using the Java EE Service Engine to Create a Composite Application
This tutorial is designed to showcase the Java EE Service Engine's functionality. This example is designed to show how the Java EE Service Engine implements a Web Service from a WSDL file accessing it through the HTTP Binding Component.
We will create a Composite Application so that Java EE SE will be used in the service and we will then run a test case to test our service. This tutorial also uses the features of the HTTP Binding Component.
What You Need to Know
These topics provide information you need to know before you start the tutorial:
What You Need to Do
This tutorial includes instructions on how to perform these tasks:
Tutorial Requirements
Before you proceed, make sure you review the requirements in this section.
Prerequisites
This tutorial assumes that you have some basic programming experience with the Java language and platform, and knowledge of the NetBeans IDE.
System Requirements
This tutorial assumes that your system meets the requirements specified in the System Requirements topic of the NetBeans IDE 6.1 Release Notes. NetBeans IDE runs on operating systems that support the Java VM (Virtual Machine).
Tutorial Scenario
The following sample illustrates how Java EE Service Engine implements a Web Service from WSDL.
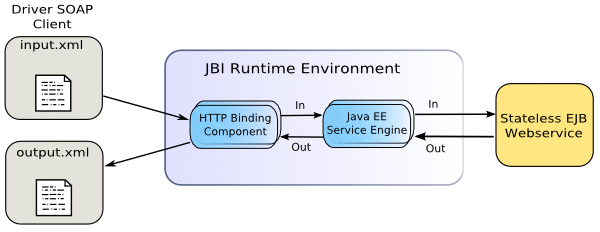
Configuring the Tutorial Environment
Before you deploy your composite application, the application server and the appropriate JBI components must be configured correctly and must be running.
The following software is required for this tutorial:
-
GlassFish ESB (Installation Instructions) includes the following:
-
GlassFish V2 Update Release 2 (UR2)
-
NetBeans IDE 6.1
-
Open ESB core components
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) service engines
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) binding components
-
Java Business Integration (JBI) component tooling
-
Note –
Glassfish ESB installer installs all the components including NetBeans IDE. To download only the NetBeans IDE, see NetBeans IDE Download.
Note –
You must have the JDK (Java Development Kit) software installed and JAVA_HOME set as an environment variable, prior to installing the GlassFish ESB or the installation will halt midway. See Installing the JDK Software and Setting JAVA_HOME for details.
Starting the GlassFish Software
The Java EE Service Engine starts together with GlassFish. Before deploying and performing test runs of a Composite Application project in the NetBeans IDE, make sure that the GlassFish Application Server is started.
 To Check the Status of the GlassFish V2 Application
Server in the NetBeans IDE
To Check the Status of the GlassFish V2 Application
Server in the NetBeans IDE
-
If the Services window is not visible, on the NetBeans IDE menubar choose Window -> Services.
-
In the Services window, expand the Servers node.
The Servers node should contain a GlassFish V2 subnode. If the GlassFish V2 node is not visible, see To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server with the NetBeans IDE.
If a green arrow icon appears on the GlassFish V2 node, the server is running. If no green arrow icon appears, see To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server in the NetBeans IDE.
 To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server
with the NetBeans IDE
To Register the GlassFish V2 Application Server
with the NetBeans IDE
-
If the Services window is not visible, on the NetBeans IDE menubar choose Window -> Services.
-
In the Services window, right-click the Servers node and choose Add Server from the pop-up menu.
The Add Server Instance dialog box opens.
-
In the Choose Server page of the dialog box, select GlassFish V2 from the Server drop-down list.
-
If you want to change the server name that the IDE uses to identify the server, type it in the Name field.
-
Click Next .
The Platform Location Folder page opens.
-
In the Platform Location field, click Browse and select the installation location of the application server.
-
Select the Register Local Default Domain option and click Next.
-
Type the user name and password for the domain's administrator.
If you accepted the default values during the installation, the user name is admin and the password is adminadmin.
-
Click Finish.
 To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server
in the NetBeans IDE
To Start the GlassFish V2 Application Server
in the NetBeans IDE
-
On the NetBeans IDE page, in the Services window, right-click the GlassFish V2 node and choose Start.
-
Wait until the following message appears in the Output window:
"Application server startup complete."
When the server is running, the IDE displays a green arrow icon on the GlassFish V2 node.
The Java EE Service Engineis represented as sun-javaee-engine in the Services window of the IDE, under the GlassFish V2->JBI->Service Engines nodes.
Enabling the JBI Framework
In some cases, you might have to enable the JBI framework to deploy a Java EE Service Engine component. The following command enables the JBI framework:
asadmin enable --user adminuser JBIFramework
Creating an EJB Module Project
In this section you will create a new EJB module project called Hello. You will also create a WSDL document, a web service and then clean and build the EJB module project.
 To Create the EJB Module Project
To Create the EJB Module Project
-
From the NetBeans IDE's main menu, choose File -> New Project.
The New Project wizard opens.
-
In the Categories list, select the Enterprise node and in the Projects list select EJB Module.
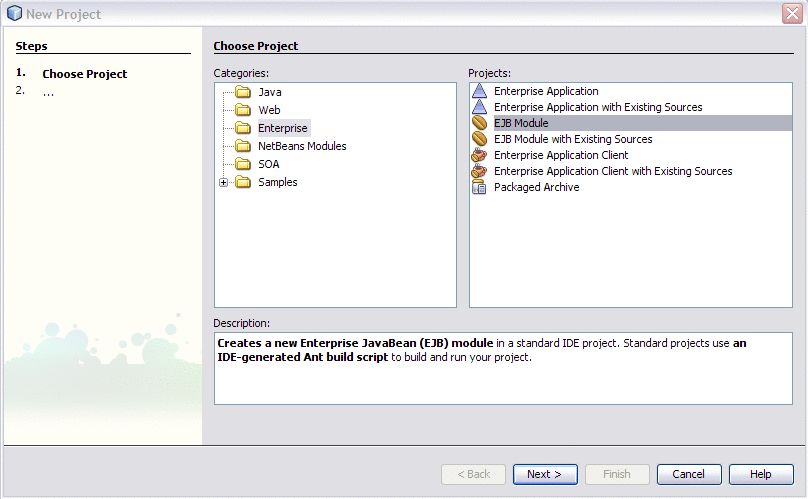
-
Click Next.
-
In the Project Name field, type Hello.
You may choose to change the Project Location or use the default location.
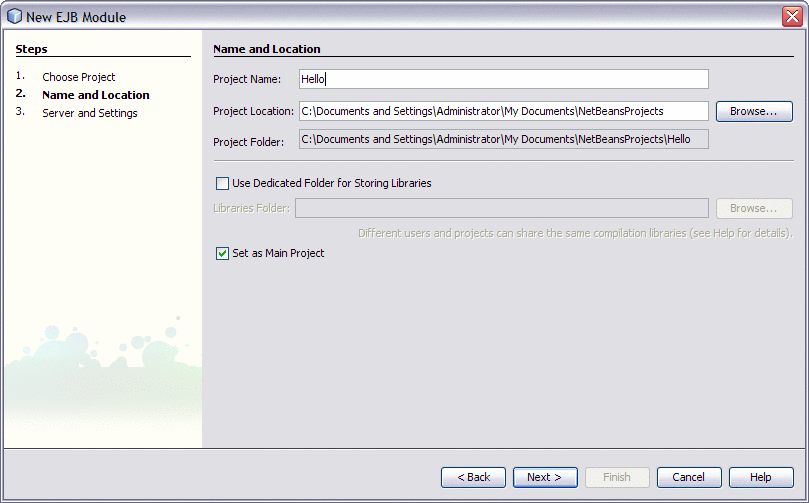
-
Click Next.
-
In the Server field select your server and in Java EE Version field select the appropriate version.
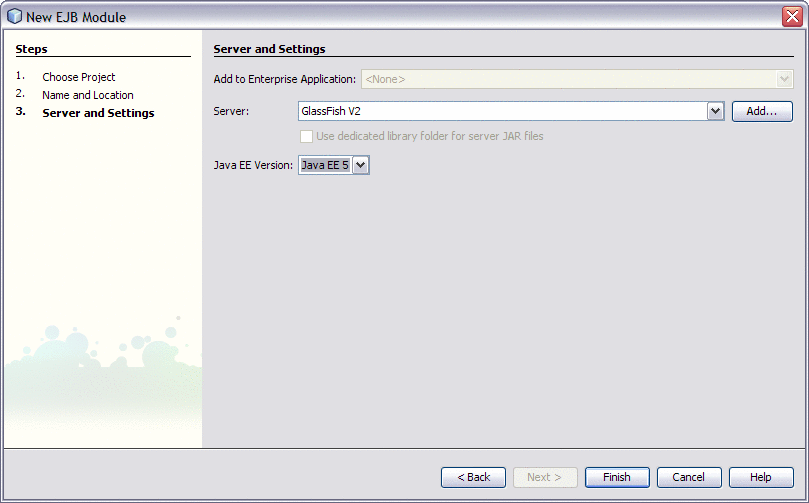
-
Click Finish.
The Projects window now contains a node for a EJB Module project called Hello.
 To Create a WSDL Document
To Create a WSDL Document
-
In the Projects window of the IDE, right-click the Hello node and choose New -> WSDL Document.
-
In the File Name field type HelloWSDL.
-
In the WSDL Type, select the Concrete WSDL Document option.
-
In the Binding field, select SOAP and in the Type field, select RPC Literal.
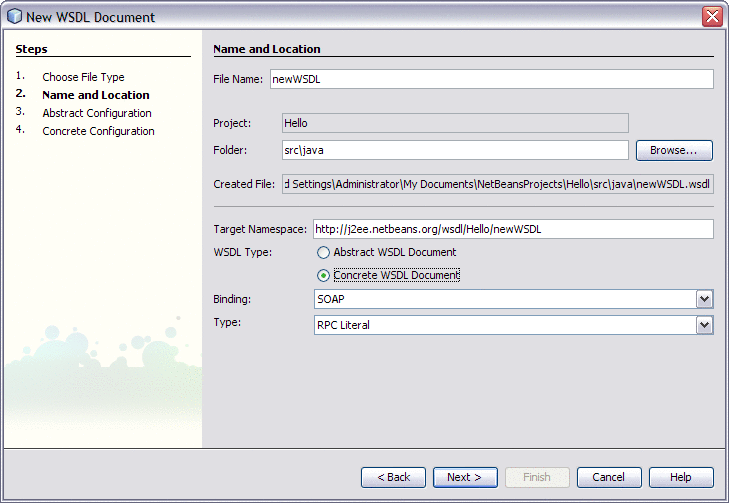
-
Click Next.
-
On the Abstract Configuration page, in Input, under the Message Part Name double-click Part1 and change the value to in and press Return.
-
Doing the same way in Output, change Part2 to out under Message Part Name and press Return.
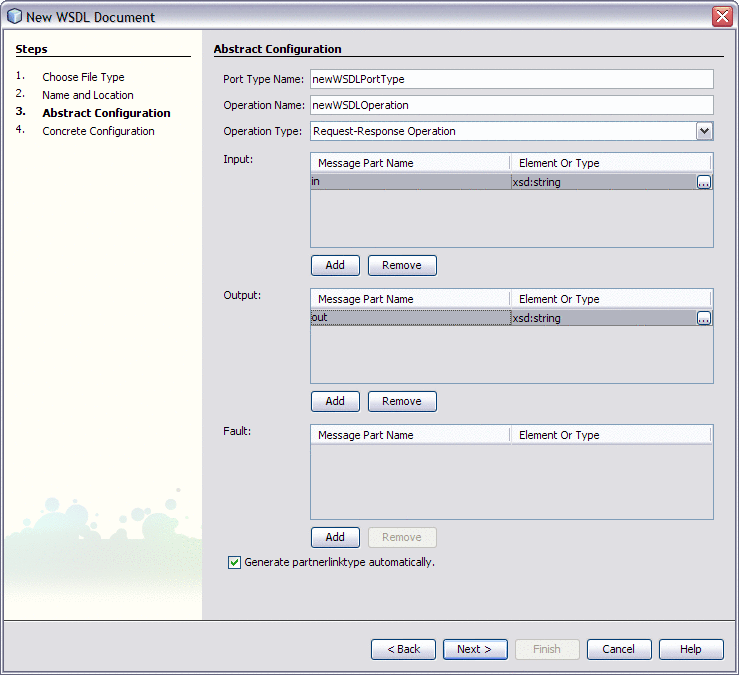
-
Click Next.
-
Choose the defaults and click Finish on the Concrete Configuration page.
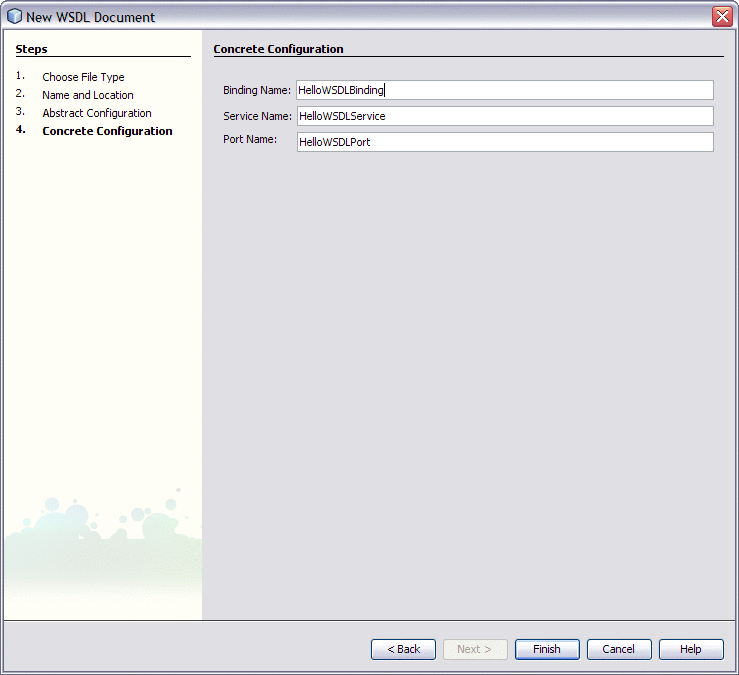
 To Create a Web Service from WSDL
To Create a Web Service from WSDL
-
In the Projects window of the IDE, right-click the Hello node and choose New -> Other.
-
In the Categories list select Web Services and in File Types select Web Service from WSDL.
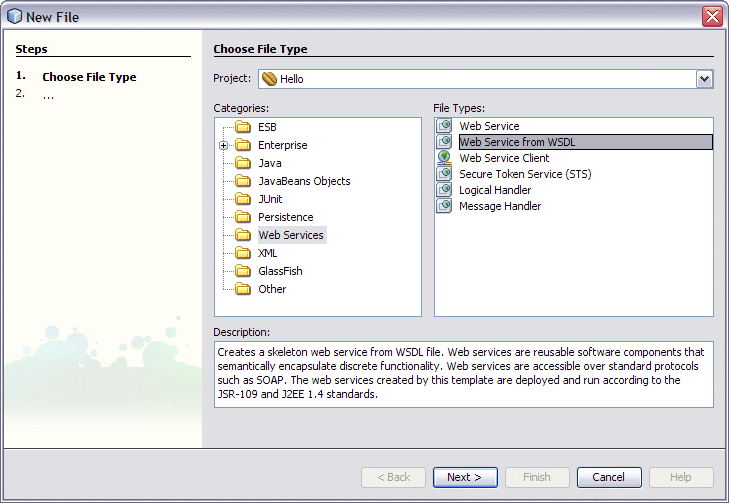
-
Click Next.
-
Type the Web Service Name as HelloWebWSDL and the Package name as Hello1.
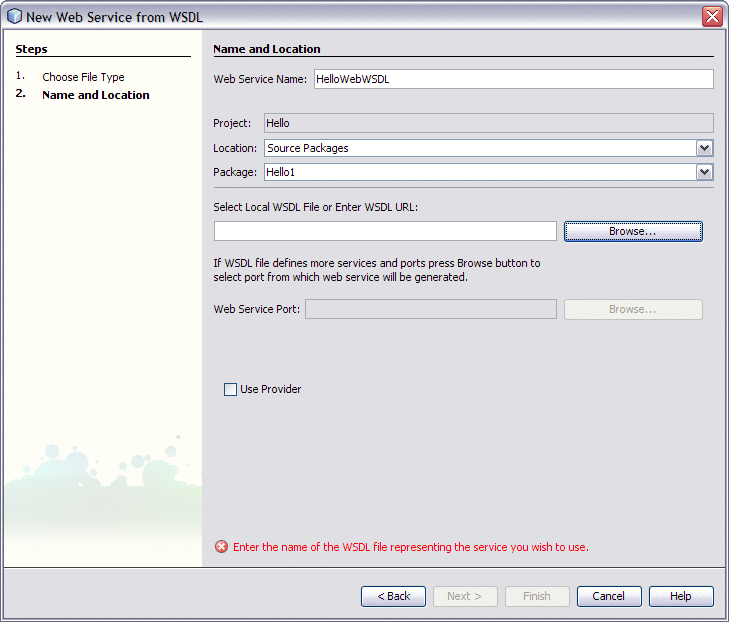
-
Click the Browse button to select local WSDL file or the WSDL URL and then click Open.
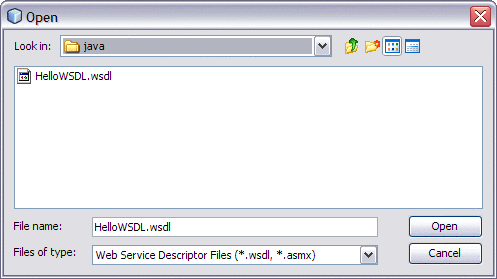
Note –This WSDL File or the WSDL URL is located in the NetBeans Projects folder. For example: C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\My Documents\NetBeansProjects\Hello\src\java This path is valid if you have used the default project location while creating the EJB module project.
-
Click Finish.
-
Click the Source button and add the following line to the public class.
return "Java EE Service Engine" + in;
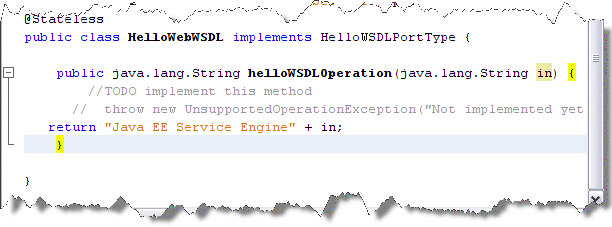
-
From the NetBeans IDE toolbar click Save All button.
 To Clean and Build the EJB Module Project
To Clean and Build the EJB Module Project
-
In the Projects window right-click the Hello node and choose Clean and Build.
When the build is complete the Output window reports BUILD SUCCESSFUL.
If the Output window is not visible, choose Window -> Output -> Output.
Creating a Composite Application Project
A EJB Module project is not directly deployable. You must first add a EJB Module project, as a JBI module, to a Composite Application project. You can then deploy the Composite Application project. Deploying the project makes the service assembly available to the application server and enables its service units to run.
 To Create a Composite Application Project
To Create a Composite Application Project
-
From the NetBeans IDE's main menu, choose File -> New Project.
The New Project wizard opens.
-
In the Categories list, select the SOA node and in the Projects list select Composite Application .
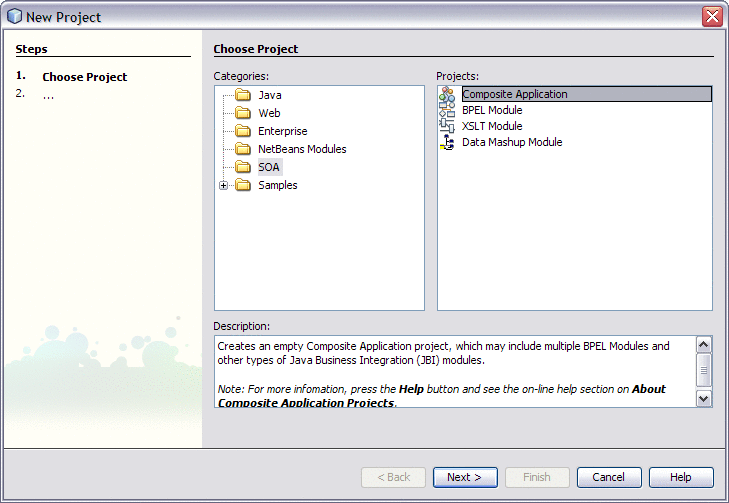
-
Click Next.
-
In the Name and Location page, change the project name to HelloCompositeApp, and specify the location of project files or just use the default location.
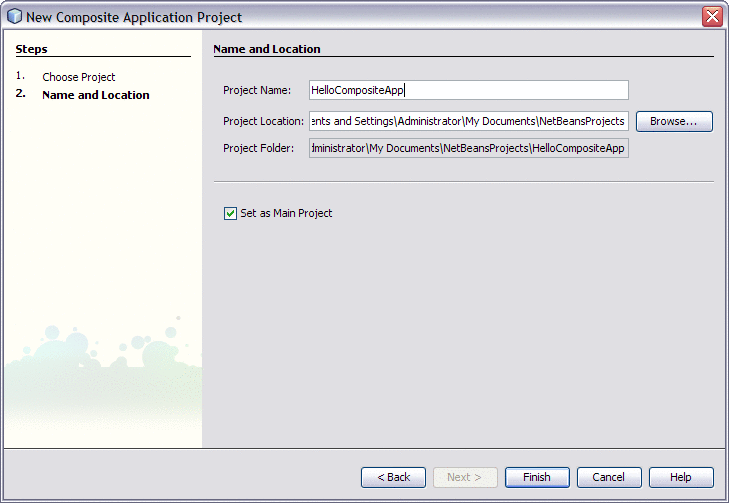
-
Leave the Set as Main Project option selected and click Finish.
-
To add the EJB Module as a JBI module to the Composite Application project, right-click HelloCompositeApp and choose Add JBI Module.
The Select Project dialog box opens.
-
Select the Hello project you created earlier and select dist/Hello.jar under Project JAR Files and click Add Project JAR Files button.
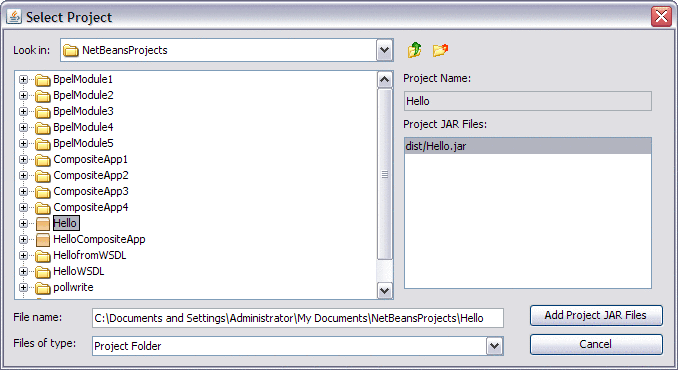
The Select Project dialog box closes and the Hello.jar file is added to the JBI Modules node of the HelloCompositeApp Composite Application in the Projects window.
Building and Deploying the Composite Application Project
Deploying the project makes the service assembly available to the application server, which allows its service units to run. Before you deploy the EJB Module project, you must add the JBI module to the deployment project.
 To Build and Deploy the Composite Application
To Build and Deploy the Composite Application
-
Right-click the HelloCompositeApp node, and choose Build from the pop-up menu.
When the build is complete the Output window reports BUILD SUCCESSFUL.
-
Right-click the HelloCompositeApp node, and choose Deploy.
Deployment is successful when you see the BUILD SUCCESSFUL message in the build.xml (run) tab of the Output window.
-
Open the Services window of the IDE and expand Servers -> GlassFish V2 -> JBI -> Service Assemblies to see your new deployed Service Assembly.
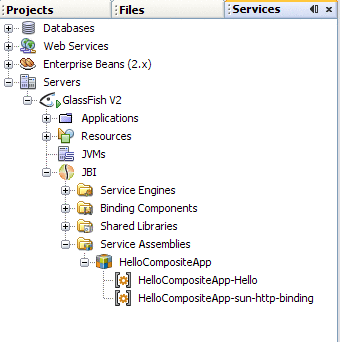
If you do not see the deployed project, right-click the Service Assemblies node and choose Refresh.
Testing the Composite Application
You can enhance the Composite Application project by adding test cases, binding to the operation, supplying input, and then using the Tester. You have to first add a test case and then run the test case.
 To Add a Test Case
To Add a Test Case
-
In the Projects window of the IDE, expand the HelloCompositeApp project node, right-click the Test node, and choose New Test Case from the pop-up menu.
The New Test Case wizard opens.
-
Accept the default test case name, TestCase1, and click Next.
-
From the Select the WSDL Document page, expand the Hello - Hello, src , java nodes, and select HelloWSDL.wsdl.
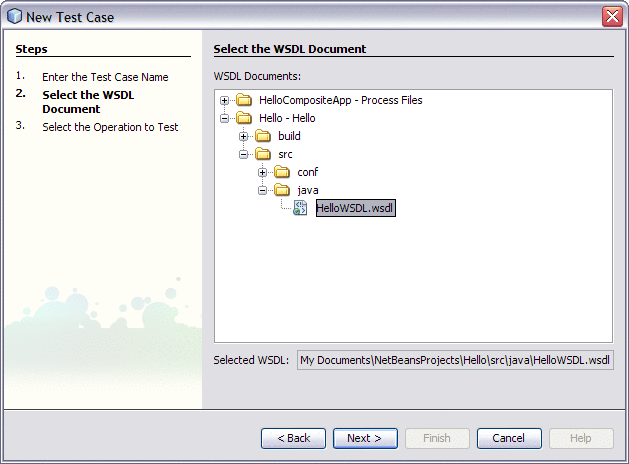
-
Click Next.
-
From the Select the Operation to Test page, select HelloWSDLOperation and click Finish.
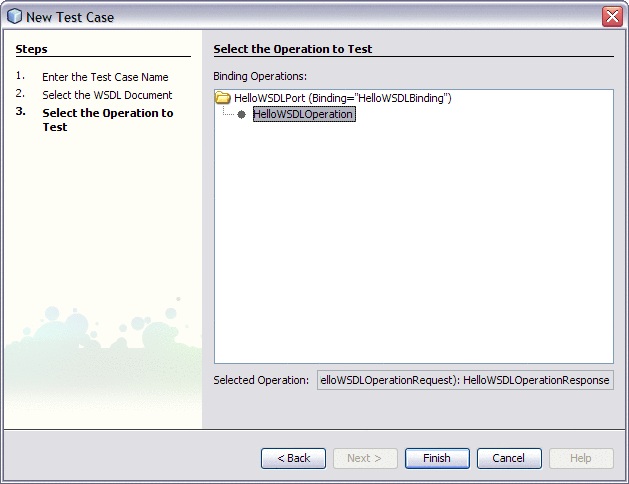
A new TestCase1 node is added under the project's Test node in the Projects window, containing two subnodes, Input and Output.
The Source Editor appears containing the Input file, Input.xml
Note –If the Source Editor does not contain a tab for Input.xml, double-click the Input node in the Projects window to open the file.
-
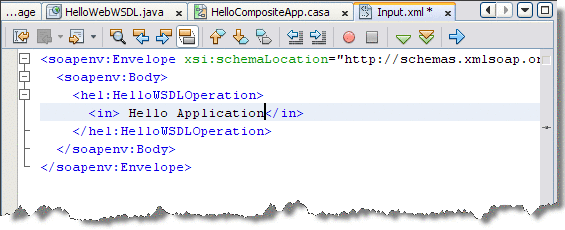
From the Input.xml tab of the Source Editor, locate the line:
<in>?string?</ in>
-
Replace the string ?string? with Hello Application, so that it appears as:
<in> Hello Application</ in>
-
From the NetBeans IDE toolbar, click the Save All button.
 To Run the Test Case
To Run the Test Case
-
In the Projects window, expand the HelloCompositeApp -> Test -> TestCase1 nodes, right-click TestCase1 for the specific test case, and then choose Run.
In the Output window the first run correctly reports that it failed. This happens because the output produced does not match the (empty) Output.xml file, and the file's null content is replaced with the output of the first run.
-
When the Overwrite Empty Output dialog box appears, click Yes to accept new output.
To compare the output with newly generated output, we have to right-click the generated Output file in the projects window and choose Use Recent Result as Output option. From the next run onwards the system compares the generated output with the output.xml file and provides the result.
-
Run the test again.
The test case is compared to the current output file and succeeds.
-
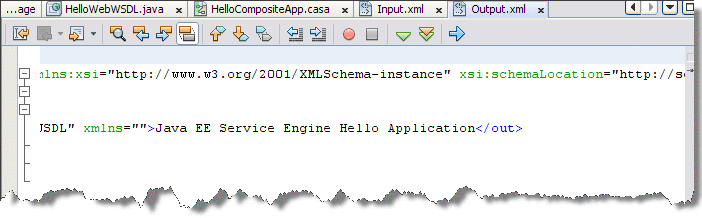
To check the output, double-click the Output node under TestCase1.
In the Output.xml tab, according to this tutorial example, the result should have a string as shown in the figure below.
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned how the Java EE Service Engine implements a Web Service derived from WSDL, and you created and tested a composite application.
This tutorial demonstrates how to:
-
Create a EJB Module project
-
Create a WSDL document and a Web Service from WSDL
-
Build and deploy a Composite Application project to GlassFish
-
Create and run test cases
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
