The prjBatch_Streaming Sample Project
This topic describes how the components of the prjBatch_Streaming sample Project are created. To create the Project manually, do the following:
 To Create a Project
To Create a Project
The first step is to create a new Project in the NetBeans IDE
.
-
Start the NetBeans IDE
-
Click the New Project icon, or select File⇒New Projectto initiate the New Project wizard.
-
In Step 1 of the Wizard, select CAPS⇒ESB from the Categories column and CAPS Repository-Based Project from the Projects column, and click Next.
-
In Step 2 of the Wizard, specify your Project Name (for this Project , use prjBatch_Streaming), and click Finish.
Creating a Java Collaboration Definition
In this task, you create a Java Collaboration using the Collaboration Definition Wizard (Java). Once a Collaboration Definition has been created, the Business Rules of the Collaboration are written using the Collaboration Editor.
 To Create the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration
To Create the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration
-
From the Project Explorer, right-click the prjBatch_Streaming Project and select New⇒Collaboration Definition (Java) from the context menu.
The Collaboration Definition Wizard (Java) appears.
-
Enter a Collaboration Definition name (for this Project, use jcdBatch_Streaming) and click Next.
-
For Step 2 of the Wizard, from the Web Services Interfaces selection window, double-click CAPS Components Library⇒Adapters⇒BatchAdapter⇒BatchInbound⇒receive.
The File Name field now displays receive.
-
Click Next.
-
For Step 3 of the Wizard, from the Select OTDs selection window, double-click CAPS Components Library⇒Adapters⇒BatchAdapter, and select the following three OTDs:
-
BatchFTP
-
BatchLocalFile
-
BatchRecord
-
-
From the Select OTDs selection window, double-click CAPS Components Library⇒Adapters⇒File, and select the FileClient OTD.
The Selected OTDs field now displays the four OTDs.
-
Click Finish.
The Java Collaboration Editor opens to the new Collaboration in the right pane of the NetBeans IDE.
Using the Java Collaboration Editor
The prjBatch_Streaming Project uses the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration created in the Creating a Java Collaboration Definition. To complete the Collaboration, use the Collaboration Editor to create the Business Rules.
 To Create the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration Business Rules
To Create the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration Business Rules
-
From the Project Explorer tree, double-click jcdBatch_Streaming.
The Java Collaboration Editor opens to the jcdBatch_Streaming Collaboration.
-
To create comments for the Business Rules, from the Business Rules toolbar, click the comment icon.
The Enter a Comment dialog box appears.
-
Enter the comment and click OK.
The comment is placed on the Business Rules tree under the last selected item. Click the comment to drag it up or down the Business Rules tree to a new location.
-
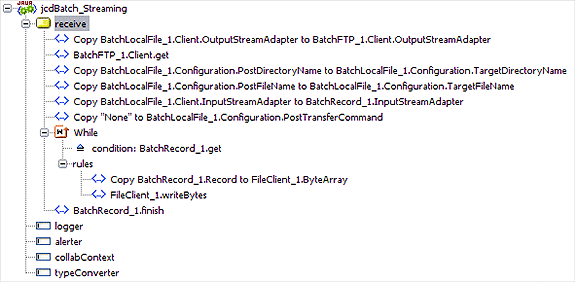
Create the CopyBatchLocalFile_1.Client.OutputStreamAdapter to BatchFTP_1.Client.OutputStreamAdapter rule:
The CopyBatchLocalFile_1.Client.OutputStreamAdapter to BatchFTP_1.Client.OutputStreamAdapter rule configures the BatchFTP and BatchLocalFile stream adapters so that the BatchFTP Adapter does a stream get, and the BatchLocalFile Adapter receives the stream.
-
Click rule on the Business Rules toolbar to add a new rule.
-
Map OutputStreamAdapter under BatchLocalFile_1 ⇒ Client in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, under to OutputStreamAdapter under BatchFTP_1 ⇒ Client in the right pane of the Business Rules Designer. To do this, Click on OutputStreamAdapter under BatchLocalFile_1 ⇒ Client in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, and drag your cursor to OutputStreamAdapter under BatchFTP_1 ⇒ Client in the right pane of the Business Rules Designer. A link now connects the two nodes.
-
-
Create the BatchFTP_1.Client.get rule:
The BatchFTP_1.Client.get rule gets the file.
-
Click rule on the Business Rules toolbar to add a new rule.
-
Under BatchFTP_1 in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, right-click Client, and click Select method to call from the context menu.
The method selection window appears.
-
Select get() from the method selection window.
The get method box appears in the Business Rules Designer canvas.
-
-
Create the Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostDirectoryName to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.TargetDirectoryName rule:
The Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostDirectoryName to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.TargetDirectoryName rule dynamically configures the name of the target directory to the post directory name.
-
Create the Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostFileName to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.TargetFileName rule:
The Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostFileName to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.TargetFileName rule dynamically configures the name of the target file to the post file name.
-
Create the Copy "None" to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostTransferCommand rule:
The Copy "None" to BatchLocalFile_1.Configuration.PostTransferCommand rule dynamically configures the post transfer command to None so that no post transfer will take place.
-
From the Business Rules Designer’s String menu, select Literal String.
The String literal box appears.
-
Double-click the value field of the String literal box and enter None as the value.
-
Map the None output node of the String literal box to PostTransferCommand under BatchLocalFile_1⇒Configuration in the right pane of the Business Rules Designer
-
-
Create the Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Client.InputStreamAdapter to BatchRecord_1.InputStreamAdapter rule:
The Copy BatchLocalFile_1.Client.InputStreamAdapter to BatchRecord_1.InputStreamAdapter rule configures the BatchLocalFile and BatchRecord stream adapters so that the BatchLocalFile Adapter does a stream get, and the BatchRecord Adapter receives the stream.
-
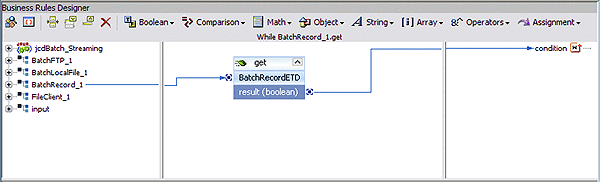
Create the While statement:
The While statement’s rules get the record, publish it to the outbound File Adapter, and the File Adapter writes the file to a local directory.
-
Click While on the Business Rules toolbar to add a new while statement in the Business Rules pane.
-
From the Business Rules tree, expand the While statement and select the condition.
-
From the Business Rules Designer, right-click BatchRecord_1 in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, and click Select method to call from the context menu.
The method selection window appears.
-
Select get() from the method selection window.
The get method box appears in the Business Rules Designer canvas.
-
Map the output node of the get method box to result (boolean) condition in the right pane of the Business Rules Designer.
-
-
Create the Copy BatchRecord_1.Record to FileClient_1.ByteArray rule under the while statement:
-
To create the FileClient_1.write rule under the while statement do the following:
-
Click rule on the Business Rules toolbar to add a new rule under the While statement.
-
Right-click FileClient_1 in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, and click Select method to callfrom the context menu.
The method selection window appears.
-
Select write() from the method selection window.
The write method box appears in the Business Rules Designer canvas.
-
-
Create the BatchRecord_1.finish rule:
-
Select the while statement on the Business Rules tree and click rule on the Business Rules toolbar.
A new rule is added to the Business Rules tree.
-
Right-click BatchRecord_1 in the left pane of the Business Rules Designer, and click Select method to call from the context menu.
The method selection window appears.
-
Select finish() from the method selection window.
The finish method box appears.
-
-
From the editor’s toolbar, click Validate to check the Collaboration for errors.
-
Save the Project.
 To Create a Connectivity Map
To Create a Connectivity Map
The Connectivity Map provides a canvas for configuring a Project’s components.
-
In Enterprise Explorer’s Project Explorer, right-click the new Project (prjBatch_Streaming) and select New ⇒ Connectivity Map from the context menu.
The new Connectivity Map appears and a node for the new Connectivity Map is added under the Project on the Project Explorer tree labeled CMAP1.
-
Rename the Connectivity Map to cmBatch_Streaming.
 To Generate the Connectivity Map
To Generate the Connectivity Map
Once your Java Collaboration Definition is completed you can use it to generate your Connectivity Map. Generating the Connectivity Map will automatically populate the canvas with the correct components and bind the components according to the information provided by the Java Collaboration Definition.
-
Drag and drop the jcdBatch_Streaming Java Collaboration Definition from the Project window to the Connectivity Map canvas.
The cmBatch_Streaming_jcdBatch_Streaming1 service is added to the canvas.
-
Click the Connectivity Map Generator icon. The Connectivity Map Generator dialog box appears listing the necessary components and bindings to generate the Connectivity Map. Click OK.
The External applications are added to the Connectivity Map and the Bindings are created. The red squares in the bindings represent the Batch Adapters. The red color indicates that the adapter properties have not been configured.
-
Save your current work.
 To Create an Environment
To Create an Environment
Environments include the External Systems, Logical Hosts, Sun Java System Application Servers and Message Servers used by a Project and contain the configuration information for these components.
-
From the NetBeans IDE, click the Services tab.
-
Right-click the Repository and select New Environment.
-
Rename the new Environment envBatch_Streaming.
-
Right-click the envBatch_Streaming Environment and select New⇒BatchInbound External System.
-
Name this External System esBatchInbound.
The esBatchInbound window is added to the Environment Editor.
-
Right-click envBatch_Streaming and select New⇒BatchFTP External System.
-
Name this External System esBatchFTP.
-
Right-click envBatch_Streaming and select New⇒BatchLocalFile External System.
-
Name the External System esBatchLocalFile.
-
Right-click envBatch_Streaming and select New⇒BatchRecord External System.
-
Name the External System esBatchRecord.
-
Right-click envBatch_Streaming and select New⇒File External System.
-
Name this External System esFile.
-
Right-click envBatch_Streaming and select New Logical Host.
The LogicalHost1 box is added to the Environment and LogicalHost1 is added to the Environment Editor tree.
-
From the Services tree, right-click LogicalHost1 and select New Sun Java System Application Server.
A new Sun Java System Application Server is added to the Services tree under LogicalHost1.
-
Save the Project.
Configuring the Adapter Properties
The prjBatch_Streaming Project uses five Adapters, each represented in the Connectivity Map as a node between an External Application and a Service.
 To Configure the BatchInbound Adapter Properties
To Configure the BatchInbound Adapter Properties
-
From the Connectivity Map, double-click the BatchInbound Adapter.
The Adapter Properties Editor appears.
-
Modify the properties for your system, including the settings for the BatchInbound Adapter in the following table, and click OK.
BatchInbound Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
Settings - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Directory Name
Your input directory
File Name
BatchInbound.txt
Note –The BatchInbound Adapter Environment properties can keep the default settings for this sample.
Configuring the BatchFTP Adapter Properties
 To Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
To Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
-
From the Connectivity Map, double-click the BatchFTP Adapter.
The Adapter Properties Editor appears.
-
Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Connectivity Map properties for your system, including the settings in the following table, and click OK.
BatchFTP Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
Target Location - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Target Directory Name
The directory (absolute path) from which files are retrieved
Target File Name
BatchFTPIn.txt
 To Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Properties
To Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Properties
-
From the Services tree, right-click the BatchFTP External System (esBatchFTP in this sample), and select Properties.
The Properties Editor opens to the BatchFTP Adapter Environment properties.
-
Modify the BatchFTP Adapter Environment properties for your system, including the settings in the following table, and click OK.
BatchFTP Adapter Environment Properties
FTP - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings.
Host Name
localhost
Server Port
Port number to use to connect to the FTP server
User Name
User ID used to log into the system
Password
Password required to log into the system
 To Configure the BatchLocalFile Adapter Properties
To Configure the BatchLocalFile Adapter Properties
The BatchLocalFile Adapter’s specific properties are set from the Connectivity Map. Environment properties can use the default settings.
-
Double-click the BatchLocalFile Adapter.
The Adapter Properties Editor appears.
-
Modify the properties for your system, including the settings in the following table, and click OK.
BatchLocalFile Adapter Properties
Post Transfer - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Post Directory Name
X:/Batch51/ready
Post File Name
BatchLocalFileReady.txt
Target Location - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Target File Name
The name of the file to be sent.
Target Directory Name
The directory on the system where files are sent.
 To Configure the BatchRecord Adapter Properties
To Configure the BatchRecord Adapter Properties
The BatchRecord Adapter’s specific properties are set from the Connectivity Map. Environment properties can use the default settings.
-
From the Connectivity Map, double-click the BatchRecord Adapter.
The Properties Sheet opens to the Adapter Connectivity Map properties.
-
Modify the configuration for your system, including the settings in the following table.
BatchRecord Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
General Settings - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Parse or Create Mode
Parse
Record - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Delimiter on Last Record
Yes
Record Delimiter
\n
Record Type
Delimited
Configuring the File Adapter Properties
 To Modify the outbound File Adapter Connectivity Map properties
To Modify the outbound File Adapter Connectivity Map properties
-
From the Connectivity Map, double-click the outbound File1 Adapter.
The Properties Editor opens to the outbound File Adapter properties.
-
Modify the configuration for your system, including the settings in the following table.
Outbound File Adapter Connectivity Map Properties
Parameter Settings - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings
Output File Name
FileOutput%d.txt
 To Modify the File Adapter Environment properties
To Modify the File Adapter Environment properties
-
From the Services tree, right-click the esFile External System, and select Properties.
The Properties Editor opens to the File Adapter Environment properties.
-
Modify the File Adapter Environment properties for your system, including the settings in the following table, and click OK.
File Adapter Environment Properties
Parameter Settings - Set as directed, otherwise use the default settings.
Directory
The directory on the system where files are sent.
 To Create the Deployment Profile
To Create the Deployment Profile
A Deployment Profile is used to assign Collaborations and message destinations to the Sun Java System Application Server and message server. Deployment Profiles are created using the Deployment Editor.
-
From the Enterprise Explorer’s Project Explorer, right-click the Project (prjBatch_Inbound_FTPIn_LocalFileOut) and select New ⇒ Deployment Profile.
-
Enter a name for the Deployment Profile (for this Project, use dpBatch_Inbound_FTPIn_LocalFileOut).
Make sure that the selected Environment is envBatch_Inbound_FTPIn_LocalFileOut.
-
Click OK.
-
The Project’s components are automatically mapped to their respective system windows.
Note –If any of your Project components did not successfully map to an external system, open each of your Adapter’s configuration properties (Connectivity Map and Environment) and click OK to close and save the current configuration, then click Automap again.
-
Save the Project.
Creating and Starting the Domain
A domain is an instance of a Logical Host. After the domain is created, the Project is built and then deployed.
 To Create and Start the Domain
To Create and Start the Domain
-
Navigate to your JavaCAPS6\logicalhost directory, where JavaCAPS6 is the location of your Java CAPS installation.
-
Double-click the domainmgr.bat file.
The Domain Manager appears.
-
Do one of the following:
-
If you have already created a domain, select your domain in the Domain Manager and click Start an Existing Domain.
-
If there are no existing domains, click Yes.
The Create Domain dialog box appears.
-
Make any necessary changes to the Create Domain dialog box and click Create.
-
Select the domain and click the Start an Existing Domain button.
The new domain is added to the Domain Manager.
-
-
Once your domain is started, a green check mark indicates that the domain is running.
-
Building and Deploying the Project
The Build process compiles and validates the Project’s Java files and creates the Project EAR file.
 To Build the Project
To Build the Project
-
From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Build icon.
If there are any validation errors, a Validation Errors pane will appear at the bottom of the Deployment Editor and displays information regarding the errors.
-
Make any necessary corrections and click Build again.
 To Deploy the Project
To Deploy the Project
-
From the Deployment Editor toolbar, click the Deploy icon.
The Deploy prompt appears.
-
Click Yes.
A message appears when the project is successfully deployed.
 To Run the Sample
To Run the Sample
To run your deployed sample Project do the following
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
