Session Validation
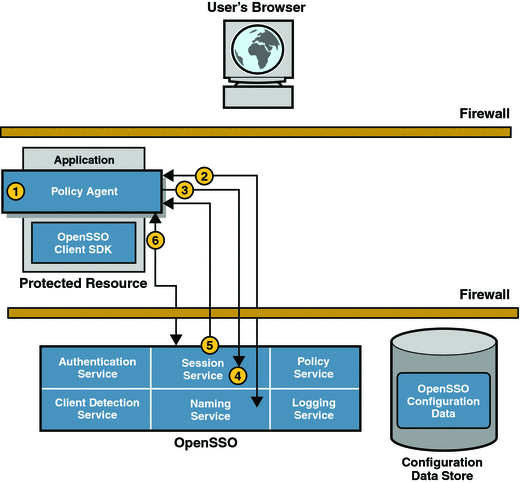
After successful authentication, the user’s browser redirects the initial HTTP request to the server a second time for validation. The request now contains a session token in the same DNS domain as OpenSSO Enterprise. The events in Figure 6–3 illustrate this process.
Figure 6–3 Session Validation
-
The policy agent intercepts the second access request.
-
To determine the validity of the session token, the policy agent contacts the Naming Service to learn where the session token originated.
The Naming Service allows clients to find the URL for internal OpenSSO Enterprise services. When contacted, the Naming Service decrypts the session token and returns the corresponding URL which can be used by other services to obtain information about the user session.
-
The policy agent, using the information provided by the Naming Service, makes a POST request to the Session Service to validate the included session token.
-
The Session Service receives the request and determines whether the session token is valid based on the following criteria:
-
Has the user been authenticated?
-
Does a session data structure associated with the session token exist?
-
-
If all criteria are met, the Session Service responds that the session token is valid.
This assertion is coupled with supporting information about the user session itself.
-
The policy agent creates a Session Listener and registers it with the Session Service, enabling notification to be sent to the policy agent when a change in the session token state or validity occurs.
The next part of the user session is Policy Evaluation and Enforcement.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
