Chapter 7 Preparing to Install Solaris Software Over the Network
The typical way to install the Solaris software on a system is to use a system's CD-ROM drive. However, if you have systems on a network, you can also install Solaris software on systems over the network instead of using the systems' CD-ROM drives.
Network installations enable you to install the Solaris software from a system that has access to a Solaris CD image, called an install server, to other systems on the network. An install server can either have the Solaris CD image in its CD-ROM drive, or you can copy the Solaris CD to the install server's hard disk. Network installations that use a Solaris CD image copied on an install server's hard disk are usually faster than installations from a CD-ROM drive.
Note -
The name of this product is Solaris 7 but code and path or package path names may use Solaris 2.7 or SunOS 5.7. Always follow the code or path as it is written.
Task Map: Preparing to Install Solaris Software Over the Network
Table 7-1 Task Map: Preparing to Install Solaris Over the Network|
Task |
Description |
For Instructions, Go To |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Create an Install Server |
|
You can create an install server by copying the Solaris CD to the server's hard disk (setup_install_server command) or by mounting the Solaris CD from its CD-ROM drive. |
| "How to Create an Install Server" |
|
|
|
Create Boot Servers |
If you want to install systems over the network that are not on the same subnet as the install server, you must create a boot server on the subnet to boot the systems. Use the setup_install_server -b command to create a boot server. | "How to Create a Boot Server on a Subnet " | |||||
|
Set Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network |
Using Solstice Host Manager Host Manager provides an easy-to-use, graphical user interface that enables you to add network installation information about a system to the name service, so the system can be installed over the network. You should use this tool if you want to use the NIS or NIS+ name service to store the network installation information. | "How to Set Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network With Host Manager" | |||||
|
Using the add_install_client Command The add_install_client command provides a command-line way to add network installation information about a system to an install or boot server's /etc files, so the system can install over the network. | "How to Set Up Systems to be Installed Over the Network With add_install_client" | ||||||
Servers Required for Network Installation
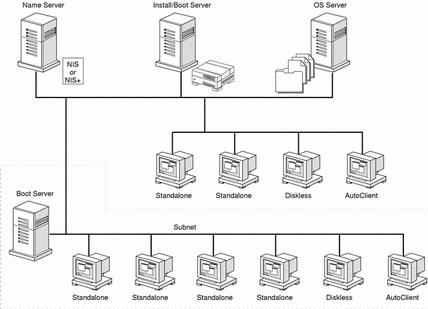
As shown in Figure 7-1, systems that install Solaris software over the network require:
-
Install server - A networked system that provides a Solaris CD image for systems on the network to install from. You can create an install server by copying the Solaris CD to the server's hard disk or by mounting the Solaris CD from its CD-ROM drive.
By copying Solaris CDs, you enable a single install server to provide Solaris CD images for multiple releases, including Solaris CD images for different platforms. For example, a SPARC install server could provide the Solaris 2.6 and Solaris 7 CD images for SPARC systems, and the same SPARC install server could also provide the Solaris 7 CD image for x86 systems.
-
Name server - A system that manages a distributed network database (such as NIS or NIS+) containing information about users and other systems on the network.
Note -The install server and name server may be the same or separate systems.
-
Boot server - A system used to boot the system to be installed over the network. A boot server and install server are typically the same system. However, if the system to be installed is on a different subnet than the install server, a boot server is required on that subnet.
A single boot server can provide Solaris boot software for multiple releases, including the Solaris boot software for different platforms. For example, a SPARC boot server could provide the Solaris 2.6 and Solaris 7 boot software for SPARC systems, and the same SPARC boot server could also provide the Solaris 7 boot software for x86 systems.
-
OS server - A system that provides Solaris operating environment software including services and/or file systems.
Figure 7-1 Network Installation Servers
Network Installation Commands
Table 7-2 lists the commands that you need to use for setting up network installations.
Table 7-2 Network Installation Commands
Creating an Install Server and Boot Servers
You must create an install server, and possibly a boot server, to install the Solaris software on a system over the network. This section describes how to:
-
Create an install server by copying the Solaris CD to the server's hard disk or by mounting the Solaris CD from its CD-ROM drive.
Note -If you intend to do frequent installations over the network, you should copy the Solaris CD to an install server's hard disk. Network installations from an install server's hard disk are faster than from its CD-ROM drive, and using the hard disk also frees the CD-ROM drive for other uses.
Note -You cannot use a SunOS 4.1.x system as an install server for Solaris-based systems.
-
Create separate boot servers (required only if systems are not on the same subnet as the install server) for each subnet. Instead of creating separate boot servers, you can create an install server for each subnet; however, this requires more disk space or CD-ROM resources.
How to Create an Install Server
-
On the system that is going to be the install server, log in and become root.
This system must have a CD-ROM drive and be part of the site's network and name service. The system must also be in the NIS or NIS+ name service. (If your site doesn't use the NIS or NIS+ name service, you must distribute information about this system by following your site's policies.)
Note -This procedure assumes that the system is running Volume Management. For detailed information about managing CDs without Volume Management, see the System Administration Guide, Volume I.
-
Insert the Solaris CD into the CD-ROM drive.
This is the Solaris CD that you want to provide to the systems over the network.
-
Mount the Solaris CD (if needed).
Volume management automatically mounts the Solaris CD on /cdrom/cdrom0/s0 or /cdrom/cdrom0/s2.
-
Determine your next step based on whether or not you want to copy the Solaris CD to the install server's hard disk.
If You ...
Then ...
Want to copy the Solaris CD
Go to Step 5.
Do not want to copy the Solaris CD
Go to Step 7.
-
Change directory to the Tools directory on the mounted Solaris CD.
# cd Solaris_2.7/Tools
-
Copy the Solaris CD to the install server's hard disk by using the setup_install_server command.
# ./setup_install_server install_dir_path
install_dir_path
Specifies the directory where the Solaris CD will be copied. The directory must be empty.
Note -The setup_install_server command indicates if you do not have enough disk space for the Solaris CD. Use the df -kl command to determine available disk space.
Note -After copying the Solaris CD, you can use the patchadd -C command to patch the files located on the mini root (i.e. Solaris_2.7/Tools/Boot)on the net install image created by setup_install_server. This enables Solaris installation commands and other mini root commands to be patched.
-
Determine your next step based on whether or not the install server is on the same subnet as the system to be installed.
If Install Server Is ...
Then ...
On same subnet as the system to be installed
You don't need to create a boot server. Go to "Setting Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network".
Follow the steps in "How to Create a Boot Server on a Subnet ". You must complete this procedure when the install server is not on the same subnet as the system to be installed.
Example-Creating an Install Server
The following example creates an install server by copying the Solaris CD to the install server's /export/install directory.
# cd /cdrom/cdrom0/s0/Solaris_2.7/Tools # ./setup_install_server /export/install |
Where to Go Next
The install server is now created. If the install server is not on the same subnet as the system to be installed, go to "How to Create a Boot Server on a Subnet ". To set up systems to be installed from the install server, go to "Setting Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network".
How to Create a Boot Server on a Subnet
You can install Solaris software over the network from any install server on the network. However, a system that needs to use an install server on another subnet requires a separate boot server on its own subnet. A boot server contains enough of the boot software to boot systems over the network, and then the install server takes over to install the Solaris software.
-
On the system that will be the boot server for the subnet, log in and become root.
This system must have a local CD-ROM drive or have access to a remote Solaris CD image. The system must also be in the NIS or NIS+ name service. (If your site doesn't use the NIS or NIS+ name service, you must distribute information about this system by following your site's policies.)
Note -This procedure assumes that the system is running Volume Management. For detailed information about managing CDs without Volume Management, see the System Administration Guide, Volume I.
-
Determine your next step based on where you want to access the Solaris CD image from.
You must use the Solaris CD image of the same release and platform type that is being used to install the systems.
-
Change directory to the Tools directory on the Solaris CD image.
# cd Solaris_2.7/Tools
-
Copy the boot software to the boot server by using the setup_install_server command.
# ./setup_install_server -b boot_dir_path
Specifies that the system will be set up as a boot server.
boot_dir_path
Specifies the directory where the boot software will be copied. The directory must be empty.
Note -The setup_install_server command indicates if you do not have enough disk space to copy the platform dependent information. Use the df -kl command to determine available disk space.
Example-Creating a Boot Server on a Subnet
The following example creates a boot server on a subnet by copying the boot software from the Solaris CD image to /export/install/boot on the system's local disk.
# cd /cdrom/cdrom0/s0/Solaris_2.7/Tools # ./setup_install_server -b /export/install/boot |
Where to Go Next
The boot server is now set up to boot supported systems on a subnet. To continue, go to "Setting Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network".
Setting Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network
After you've created an install server and possibly a boot server, you are ready to install the Solaris software on other systems over the network. However, to be installed over the network, a system needs to know where to:
-
Install from (install server)
-
Boot from (install server or boot server)
-
Find its profile during a custom JumpStart installation (JumpStart directory on the profile server)
Because a system looks for this information in the name service (bootparams database in the /etc files, NIS, or NIS+) when it installs over the network, you must add this information into the name service for every system that is going to be installed over the network. You can do this by using Solstice Host Manager or the add_install_client command.
Note -
If you use the /etc files to store network installation information, the information must reside on the install server or the boot server (if a boot server is required).
How to Set Up Systems to Be Installed Over the Network With Host Manager
You should use Host Manager if you want:
-
A centralized way to set up systems to be installed over the network
-
An easy-to-use graphical user interface
-
To use the NIS or NIS+ name service to store network installation information
Note -
If you want to preconfigure system configuration information by using a remote sysidcfg file, you must use the add_install_client command to set up systems to be installed over the network.
This procedure assumes that you have already installed Host Manager at your site and have the required permissions to use it. For detailed information about setting up Host Manager, refer to the Host Manager documentation.
-
Log in to a system that has access to Host Manager.
-
Start the Solstice AdminSuite with the following command.
$ /usr/bin/solstice &
-
After the Solstice AdminSuite main window appears, click on the Host Manager icon.
-
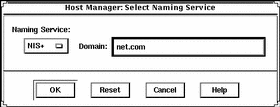
On the Host Manager: Select Naming Service screen, select a naming service and click on the OK button. See the sample Naming Service screen below.
If the Name Service Is ...
Then Select ...
NIS+
NIS+. Host Manager will update the NIS+ tables.
NIS
NIS. Host Manager will update the NIS maps.
None
None. Host Manager will store the information you provide in the /etc files on the appropriate systems. This will provide enough information for systems to boot and to install Solaris software over the network.
-
On the Host Manager main window, choose Add... from the Edit menu.
-
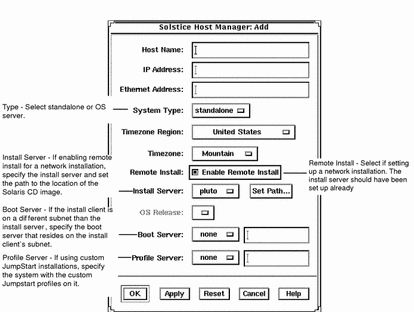
On the Host Manager: Add screen, complete all fields and click on the OK or Apply button.
-
On the Host Manager main window, choose Save Changes from the File menu.
Where to Go Next
The system is now ready to be installed over the network. To install the system, see Chapter 3, Performing a Custom JumpStart Installation.
How to Set Up Systems to be Installed Over the Network With add_install_client
If Host Manager is not available, you can use the add_install_client command to set up systems to be installed over the network. The add_install_client updates only the /etc files.
-
Become root on the install server (or the boot server if a system requires one).
-
Make sure the following information about the system to be installed has been added to the name service (/etc files, NIS, or NIS+).
-
Host name
-
IP address
-
Ethernet address
-
-
Change directory to the Tools directory on the install server's Solaris CD image or the boot server's boot directory.
# cd Solaris_2.7/Tools
-
Set up a system to be installed over the network with the add_install_client command.
# ./add_install_client [-c server:jumpstart_dir_path] [-s install_server:install_path] [-p server:path] host_name platform_group
Specifies a JumpStart directory for custom JumpStart installations. This option and its arguments are required only for custom JumpStart installations.
server is the host name of the server on which the JumpStart directory is located. jumpstart_dir_path is the absolute path to the JumpStart directory.
-s install_server:install_dir_path
Specifies the install server. This option is required only when you are using add_install_client on a boot server.
install_server is the host name of the install server. install_dir_path is the absolute path to the Solaris CD image.
-p server:path
Specifies the sysidcfg file for preconfiguring system information. server is either a valid host name or IP address for the server that contains the file. path is the absolute path to the sysidcfg file.
Is the host name of the system to be installed over the network. (This is not the host name of the install server). The host must be in the name service for this command to work.
Is the platform group of the system to be installed. (For a detailed list of platform groups, see Appendix C, Platform Names and Groups.)
SPARC: Example: Adding Systems to Be Installed Over the Network With add_install_client
The following example adds a system named basil, which is a SPARCstation 10, to be installed over the network. The system requires a boot server, so the command is run on the boot server; the -s option is used to specify the install server named install_server1, which contains a Solaris CD image in /export/install.
# cd /export/boot/Solaris_2.7/Tools # ./add_install_client -s install_server1:/export/install basil sun4m |
Where to Go Next
The system is now ready to be installed over the network. To install the system, see Chapter 3, Performing a Custom JumpStart Installation.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
