| Netra™ High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services NMA Programming Guide |
| C H A P T E R 1 |
This chapter describes how to access the Node Management Agent (NMA) and introduces the master node view and the floating external address.
The NMA is a management agent that conforms to the Java Management Extensions (JMX) v1.1 Maintenance Release. The NMA is based on the Java Dynamic Management Kit (DMK) 5.0 APIs.
The NMA monitors the performance and the status of the following Netra HA Suite software components:
The NMA exposes this information through a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) management information base (MIB) and a JMX-compliant interface. The JMX specification defines a three-level management architecture:
The instrumentation level makes resources manageable as Java objects called MBeans.
The distributed services level allow remote access and security.
By programmatically accessing these MBeans, management applications can be used to help perform tuning operations, diagnostic operations, and troubleshooting.
The NMA also provides a method for provoking a master node switchover, and emits notifications which can be used to keep up to date with the current state of certain aspects of the cluster.
The Java DMK implements the JMX specification. The NMA requires the Java DMK runtime libraries. You can use the Java DMK to develop a remote Java manager to access the NMA. Alternately, access the NMA MIB by using an off-the-shelf or custom SNMP manager, or any JMX-compliant Java manager.
An external manager can communicate with the NMA using any of the following protocols:
Note - The floating external address cannot be used when you are using the SNMP protocol. See Floating External Address for more information on the floating external address. |
Use SNMPv3 to take advantage of the enhanced security mechanism introduced in SNMPv3. Note that not all protocol interfaces are enabled by default. See the nma.properties4 man page for information on how to enable, disable, and configure protocol interfaces.
HTML can be used to view the NMAs in a running cluster through an HTML browser. By default port 8082 exports this view. To interact with the NMA on a node, access the URL of the form http://nodeIPAddress:portNumber
See HTML Protocol Adaptor in the Java Dynamic Management Kit 5.0 Tutorial for more information.
Note that if you provoke a switchover using the HTML Protocol Adaptor connected to the floating external address, the connection to the NMA might be broken prematurely and the information transfer will not finish. If this happens, stop the transfer and reload the page to get the correct node information.
FIGURE 1-1 represents the communication paths between an external manager and the cluster:
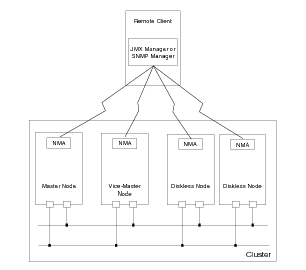
The NMA running on the master node makes information from the NMAs running on all nodes visible in the NMA running on the master node through a cascading connection. The MBeans listed in MBean Instances on the Master Node are available on the master node only.
FIGURE 1-2 shows how information is cascaded from all NMAs to the NMA on the master node.
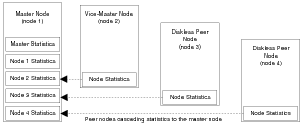
Note - The master view is only available to a Java manager that communicates using the HTTP protocol. |
All of the agents must use the same port number for the service used to implement cascading. If this is not the case, the master agent will start the cascading service but will not enable the cascading connections to NMA.
Cascading is controlled by the following properties, which are defined in the nma.properties file:
| com.sun.nhas.ma.cascading.enabled | Set to true to enable cascading. |
| com.sun.nhas.ma.cascading.retries.max | The maximum number of times that the master node tries to create a cascading connection to an NMA on another node. |
| com.sun.nhas.ma.cascading.retries.delay | The time in milliseconds between each attempt to establish a cascading connection. |
| com.sun.nhas.ma.cascading.comm.protocol | The protocol can be http or rmi. |
| com.sun.nhas.ma.cascading.socket.timeout.wait | The timeout in milliseconds for a cascading connection to terminate cleanly in the case of a communication fault. After this time has elapsed, the cascading connection attempt will be forcibly aborted and then restarted. |
| com.sun.nhas.ma.eam.polling | The time interval between checks of the floating addresses and IP Network Multipathing (IPMP) groups. If NMA notices a difference between the floating addresses and IPMP groups, NMA will send an SMTP trap to inform you of the difference. If the property is not present in this file, which is the default, the value is 113000 milliseconds. |
One instance of each of the following MBeans is instantiated on the master node of the cluster.
RnfsMasterStatisticsMBean on a configuration using StorEdge™ Network Data Replicator (SNDR)
SDMasterStatisticsMBean on a configuration using shared disks
An RnfsReplicatedSliceMBean is instantiated on the master node and on the vice-master node for each Reliable NFS partition.
One instance of each of the following MBeans is instantiated on each peer node of the cluster:
Multiple instances of the following MBeans might be instantiated:
| CgtpReliableLinkStatisticsMBean | One instance for each reliable link |
| PmdNameTagStatisticsMBean | One instance for each group of processes monitored by the Daemon Monitor |
An external Java manager can use the floating external address (for example, 10.250.10.1) to communicate with the master node. After failover and switchover, the floating address is reassigned to the new master node. The external Java manager must then connect to the new master node, but can connect to the same IP address as before. SNMP cannot use the floating external address to communicate with the master node.
Copyright © 2008, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.