| Netra™ High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Installation Guide |
| C H A P T E R 1 |
After you have chosen your cluster configuration (including hardware and software) and your installation server (hardware and software), as described in the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Getting Started Guide, install and configure the hardware for both.
Once you have installed and configured the hardware, install
and configure the software on your installation server. Then, connect
the installation server to the cluster through a private or a public
network. After completing these tasks, you are ready to install
the software on the cluster (including the operating system and
the Netra HA Suite software)
using the installation method of your choice.
HA Suite software)
using the installation method of your choice.
For detailed instructions on performing the preceding tasks, see the following sections:
Installing and Configuring the Cluster Hardware and Network Topology
Installing and Configuring the Installation Server Hardware and Software
Installing the OS and the Netra HA Suite Software on the Cluster
Note - Wherever possible, URLs are provided to relevant online documentation. Where no URL is provided, see the documentation that is provided with the hardware. |
The nhinstall tool enables you to install and configure the Foundation Services on the cluster. This tool must be installed on an installation server. The installation server must be connected to your cluster. For details on how to connect nodes of the cluster and the installation server, see Connecting the Cluster and the Installation Server.
The nhinstall tool, running on the installation server, installs the Solaris Operating System (Solaris OS), Wind River Carrier Grade Linux (CGL)
The following table lists the tasks for installing the software with the nhinstall tool. Perform the tasks in the order shown.
| Task | For Instructions | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Install the cluster and installation server hardware. | Installing and Configuring the Cluster Hardware and Network Topology and Installing and Configuring the Installation Server Hardware and Software |
| 2. | Connect the cluster to the installation server. | Connecting the Cluster and the Installation Server |
| 3. | Install an OS on the installation server. | Installing and Configuring the Installation Server Hardware and Software |
| 4. | Choose the OS distribution you want to install on the cluster. | Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Getting Started Guide |
| 5. | Prepare the installation environment on the installation server. | Preparing the Installation Environment on a Solaris OS Installation Server or Preparing the Installation Environment on a Linux SLES9 Installation Server depending on the OS you have installed on the installation server. |
| 6. | Install the nhinstall tool on the installation server. | Installing the nhinstall Tool |
| 7. | Configure the nhinstall tool. | Configuring the nhinstall Tool.
Note that env_installation.conf and cluster_definition.conf are the only required configuration files. See examples of configurations that can be used for evaluation purposes in the versions of these files that are included in the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Reference Manual. |
| 8. | Install the software using the nhinstall tool. | Chapter 3 |
| 9. | Verify that the cluster is configured correctly. | Verifying the Installation |
The following sections describe how to install and configure the cluster hardware and network topology.
To install rackmounted server hardware, see the documentation that is provided with the hardware or go to the following web site for more information:
http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/docs/CPU_Boards/
When using rackmounted server hardware as the master-eligible or master-ineligible nodes of your cluster, you must connect them to a terminal server and Ethernet switches.
A terminal server is a console access device that connects the console ports of several nodes to a TCP/IP network. This enables you to access the console of a node from a workstation that is connected to the TCP/IP network, which is connected to the terminal server.
Note - Terminal servers are also called remote terminal servers (RTS), system console servers, or access servers. |
For the Foundation Services, each cluster must have one terminal server. You can use any terminal server with your cluster. You can share a terminal server across clusters, where the number of nodes you can have per terminal server depends on the server model. Install your terminal server using the documentation that is provided with your terminal server.
Netra HA Suite software has been tested on clusters that use terminal servers such as the Cisco 2511 Access Server, the Annex, and the PERL CS9000. The examples in this section are for the Cisco 2511 Access Server. The documentation for this terminal server is located at:
http://cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_fix/cis2500/
Turn on the power for the Cisco 2511 Access Server, and connect to it by using a terminal console window.
Startup information is displayed in the console window.
14336K/2048K bytes of memory. Processor board ID 21448610, with hardware revision 00000000 Bridging software. X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant. 1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s) 2 Serial network interface(s) 16 terminal line(s) 32K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory. 8192K bytes of processor board System flash (Read ONLY) ... Default settings are in square brackets '[]'. Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]: |
When asked if you want to enter the initial configuration dialog, type No.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes]: No |
Enter the configuration mode to modify the configuration on the terminal server:
router> enable |
When you are in the configuration mode, the prompt changes to router#.
Display the running-config configuration file for the terminal server:
router# show running-config |
Copy and paste the entire configuration file into a text editor.
In the text editor, customize the configuration file for your network.
Change the parameters that are marked in italics in the following example:
! version 11.2 no service password-encryption no service udp-small-server no service tcp-small-servers ! hostname machine-hostname ! enable password access-password ! no ip routing ip domain-name IP-domain-name ip name-server IP-name-server ! interface Ethernet0 ip address IP-address 255.255.255.0 no shutdown ! interface Serial0 no ip address no ip route-cache shutdown ! ip default-gateway IP-default-gateway ip classless ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 IP-default-gateway snmp-server community public R0 snmp-server trap-authentication snmp-server location snmp-server-location snmp-server contact contact-email-address ! line con 0 transport preferred none line 1 16 no exec exec-timeout 0 0 transport preferred none transport input all stopbits 1 line aux 0 line vty 0 4 no login ! |
Enable the configuration file to be modified from the console window:
router# config terminal |
Copy and paste the modified configuration file into the console window.
router(config)# end |
Verify that the configuration file has been modified:
router# show running-config |
Verify that the output contains the configuration information that you specified in Step 6.
Save the configuration as the startup configuration file:
router# copy running-config startup-config |
Press Return to confirm and to save the changes to the configuration.
The terminal server, the Cisco 2511 Access Server, is now configured to be used by your cluster. You can access a console window to the terminal server on a port using telnet as follows:
% telnet terminal-concentrator-hostname 20port-number |
A Foundation Services cluster must have a redundant network: that is, two network interfaces that back each other up. To make a network redundant, a cluster requires two Ethernet switches. Netra HA Suite software has been validated on Cisco Catalyst 29x0 Desktop switches.
If you use other switches, check that the switches support the following:
The documentation for Cisco Catalyst 29x0 Desktop Switches is located at:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/lan/cat2900/
If IP addresses are not assigned manually to the Cisco 29x0 switches, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) attempts to assign IP addresses, which might result in errors.
Type the following series of commands on the console window:
switch1>enable switch1#config term Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#ip address IP-address 255.255.255.0 switch1(config)#interface VLAN1 switch1(config-if)#hostname switch-hostnameswitch1(config)#end switch1#copy run start Destination filename [startup-config]? |
switch-hostname is the host name that you assign to the switch
IP-address is the IP address that you associate with the host name. This address should be an IP address on your company’s network.
Press Return to confirm these commands and that the configuration file is startup-config.
Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for the other switch to assign the second IP address.
|
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) ensures that a loop occurs when you have redundant paths in your network. There should be no loops between the redundant networks in the Foundation Services cluster network because such networks are completely separate. There should be no crossover link between the two redundant switches. Therefore, you must disable the STP.
To disable the STP, see the documentation that is supplied with your Ethernet switch. The STP should also be disabled for any additional virtual local area networks (VLANs) used in your cluster. An example of the commands that you can use is as follows:
Type the following series of commands on the console window of the switch:
switch1>enable switch1#config term Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. switch1(config)#no spanning-tree vlan 1 switch1(config)#end switch1#copy run start Destination filename [startup-config]? |
Press Return to confirm that the STP has been disabled and that the configuration file is startup-config.
Repeat Step 1 through Step 3 for the other switch to disable the STP.
To install ATCA blade server hardware (either a Sun Netra CT 900 chassis or a chassis from a third-party provider), see the documentation that is provided with the hardware or go to the following web site for more information:
http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/docs
To install ATCA blades (Netra CP3010, Netra CP3020, or Netra CP3060) in your chassis, see the documentation provided with the blade or go to the site referenced above.
When using ATCA blade servers, you can access the consoles of each blade through either direct serial links to each blade or through the shelf manager blades delivered with the chassis. In the prior case, you need to connect the serial links to a terminal server (see Installing and Configuring the Terminal Server). In the latter case, there is no need for a terminal server because you can access the consoles of the blades from a PC or workstation connected through Ethernet to the shelf managers.
Regarding switches, there is no need for external switches to be installed. However, blades must be connected to the fabrics (switches) provided with the chassis (either base or extended fabrics).
For information about configuring ATCA switches, refer to the documentation that is delivered with the ATCA blade server hardware.
To install and configure the installation server hardware, see the documentation that is provided with the hardware or go to the following web site for more information:
http://www.sun.com/products-n-solutions/hardware/docs
After installing and configuring the installation server hardware, install either the Solaris OS or a Linux distribution. It is not required that you install the same version of the Solaris OS on the installation server as you are going to install on your cluster. However, if you choose to install a Linux distribution on the installation server, you must also install the Linux OS on your cluster.
At the time of this release, the only Linux distribution that you can install on your installation server is a SuSe 9 distribution. Installing the Solaris OS on your installation server (at least Solaris 8 2/02, Solaris 9, or 10) enables you to install either the Solaris OS or a Linux distribution on your cluster.
For the final step involved in preparing the installation server (installing the software on the cluster), you must copy the Solaris or Linux packages, as well as the Netra HA Suite packages, that you want to install on your cluster.
The nodes of your cluster are connected to each other through switches. You can connect the console of each node to the terminal server to provide access to the console of the node. To install the software on the cluster, connect the installation server to the cluster network through a switch. For more information, see To Connect the Installation Server to the Cluster Network.
The following figure provides an example for connecting the cluster hardware and the installation hardware.
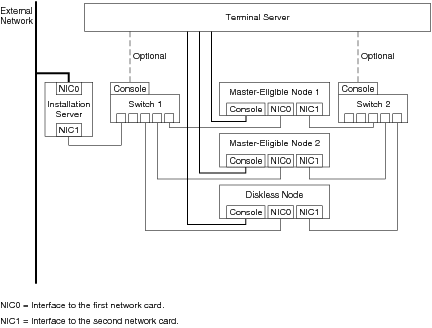
In addition, you can directly connect the serial ports of the master-eligible nodes. This connection prevents a split brain situation, where there are two master nodes in the cluster because the network between the master node and the vice-master node fails. The direct link between the master-eligible nodes must then be configured as described in the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Manual Installation Guide for the Solaris OS.
The cluster nodes must not be on the same physical wire as the nodes of another cluster. When a diskless node boots, it sends a broadcast message to find the master node. If two clusters share the same wire, the diskless node could receive messages from the wrong master node.
Connect the installation server's second interface, NIC1, to the Ethernet switch connecting the NIC0 interfaces of the nodes.
Create the file /etc/hostname.cluster-network-interface-name (hme0 in this procedure) on the installation server:
# touch /etc/hostname.hme0 |
Edit the /etc/hostname.hme0 file to add the host name of the installation server, for example, installation-server-cluster.
Choose an IP address for the network interface that is connected to the cluster, for example, 10.250.1.100.
Edit the /etc/hosts file on the installation server to add the IP address that you chose in Step 5.
Set the netmask of the cluster network in the /etc/netmasks file:
10.250.1.0 255.255.255.0 |
When the cluster hardware and installation server (hardware and OS) have been installed, configured, and connected, you are ready to install the OS and the Netra HA Suite software on the cluster. Use the installation method of your choice to install the software.
If you use the nhinstall tool to install the OS and Netra HA Suite software, follow the instructions in this document to install the software. If you decide, instead, to install the software manually, refer to the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Manual Installation Guide for the Solaris OS for this information. If you want to install a NHAS cluster on a HW supporting virtualization and the logical domain (LDoms) technology, see Installing Netra HA Suite Software on LDoms.
The LDoms installation process involves checking and updating firmware, checking operating system revisions, and installing the Logical Domains Manager and associated packages. Refer to the Logical Domains (LDoms) Administration Guide for general information about installing, configuring, and using LDoms. You can find LDoms documentation here:
http://docs.sun.com/app/docs/prod/ldoms.mgr
This section describes how to create a four-node cluster using only two Netra CP3060 blades or two Netra T2000 servers with logical domains. Most of the steps shown here require superuser access to the Solaris Operating System.
In this example, each of the two Netra CP3060 blades or Netra T2000 servers are configured to run the following three logical domains:
With this configuration, you can create a four-node cluster using only two physical machines. The cluster will be configured for running CGTP. The following example shows how network interfaces and disk drives are configured for each domain.
Installing LDoms in an environment that is running the Netra HA Suite software involves the following tasks:
Download the LDoms software from the Sun Software Download Center from the following website: http://www.sun.com/download
Download the Solaris 10 11/06 OS SPARC or newer from the following website: http://www.sun.com/software/solaris
Download the following Solaris patches from SunSolve at: http://sunsolve.sun.com
at: http://sunsolve.sun.com
Download the Sun system
firmware version 6.4.4 or newer from SunSolve at: http://sunsolve.sun.com
system
firmware version 6.4.4 or newer from SunSolve at: http://sunsolve.sun.com
Install the Solaris 10 11/06 OS as usual on two systems.
To enable CGTP, the systems must be configured to use two network interfaces. On the first system, use 10.130.1.10 as the IP-address on the e1000g0 interface, and 10.130.2.10 as the IP-address on the e1000g1 interface.
For the second system, use IP-address 10.130.1.20 and 10.130.2.20 for network interface e1000g0 and e1000g1, respectively.
Refer to the Solaris Installation Guide for details on how to install the Solaris OS.
Copy the LDoms software package to the machine where it will be installed and unpack the software.
On the Netra HA Suite installation server, copy the software as follows:
# rcp LDoms_Manager-1_0-RR.zip 10.130.1.10:/var/tmp/ # rcp 118833-36.zip 10.130.1.10:/var/tmp/ # rcp 125043-01.zip 10.130.1.10:/var/tmp/ # rcp 124921-02.zip 10.130.1.10:/var/tmp/ |
On the console of the systems that will run LDoms (for example, on 10.130.1.10 and 10.130.1.20), unzip the software as follows:
# cd /var/tmp # unzip LDoms_Manager-1_0-RR.zip # unzip 118833-36.zip # unzip 125043-01.zip # unzip 124921-02.zip |
Patch the Solaris to include the latest Logical Domains updates.
Login on the console and apply the patches in single-user mode as follows:
# init S # cd /var/tmp/ # patchadd 118833-36 # touch /reconfigure # shutdown -i6 -g0 -y |
Install patches for virtual console and LDoms drivers and utilities when the system has rebooted:
# cd /var/tmp/ # patchadd 125043-01 # patchadd 124921-02 |
Ensure that the system firmware version on your system is up to date. LDoms 1.0 software requires system firmware 6.4.4 or newer for Netra CP3060 blades or Netra T2000 servers.
To check which firmware is present on your system, connect to the system controller (ALOM) on your Netra CP3060 or Netra T2000 server and run the following command:
sc> showhost System Firmware 6.4.4 Netra CP3060 2007/04/20 10:15 Host flash versions: Hypervisor 1.4.1 2007/04/02 16:37 OBP 4.26.1 2007/04/02 16:25 Netra[TM] CP3060 POST 4.26.0 2007/03/26 16:47 sc> |
The instructions, binary files, and tools needed to perform a firmware upgrade are located in the patch package, as shown in the following code example.
# rcp 126402-01.zip 10.130.1.10:/var/tmp # cd /var/tmp # unzip 126402-01.zip # more /var/tmp/126402-01/sysfwdownload.README |
Install the LDoms Manager software.
# cd /var/tmp/LDoms_Manager-1_0-RR # ./Install/install-ldm |
When prompted, select the recommended settings for the Solaris Security Toolkit.
Reboot the system to activate the patches and to start the LDoms Manager software.
# shutdown -i6 -g0 -y |
After the reboot, LDoms will be active with one logical domain named ’primary’ running on the system. This domain is the control domain.
The control domain can be accessed through the serial console,
or by using Secure Shell. All other ports have been disabled by
the Solaris Security Toolkit to
ensure that the control domain is as secure as possible.
Security Toolkit to
ensure that the control domain is as secure as possible.
Log in on the control domain and set the path to access the LDoms Manager command line tool:
# ssh 10.130.1.10 # export PATH=/opt/SUNWldm/bin:$PATH |
Set up virtual services in control domain.
These services provide console, disk, and network access for the guest domains.
# ldm add-vdiskserver primary-vds0 primary |
For the virtual console server:
# ldm add-vconscon port-range=5000-5100 primary-vcc0 primary |
Configure two virtual network switches to enable CGTP:
# ldm add-vswitch net-dev=e1000g0 primary-vsw0 primary # ldm add-vswitch net-dev=e1000g1 primary-vsw1 primary |
Set the resources available to the control domain to limit the resources used by the control domain so that they are free to be used by the guest domains.
# ldm set-mau 2 primary # ldm set-vcpu 8 primary # ldm set-memory 2G primary |
# ldm add-config nhas |
# shutdown -i6 -g0 -y |
After rebooting the system, start up the virtual console service:
# svcadm enable vntsd |
Create a guest domain named men15. This domain will be a master-eligible node in the Netra HA Suite cluster.
# ldm create men15 # ldm set-mau 2 men15 # ldm set-vcpu 8 men15 # ldm set-memory 2G men15 # ldm ldm add-vnet vnet0 primary-vsw0 men15 # ldm add-vnet vnet1 primary-vsw1 men15 |
Create the disk image that will be used as the virtual disk for the master-eligible node.
The virtual disk is mapped to normal file in the control domain.
# mkfile 16G /test1/bootdisk_men15.img # ldm add-vdiskserverdevice /test1/bootdisk_men15.img vol1@primary-vds0 # ldm add-vdisk vdisk1 vol1@primary-vds0 men15 # ldm set-variable auto-boot\?=false men15 # ldm bind-domain men15 |
Create a guest domain named nmen35. This domain will be a non-master eligible node.
# ldm create nmen35 # ldm set-mau 2 nmen35 # ldm set-vcpu 8 nmen35 # ldm set-memory 2G nmen35 # ldm add-vnet vnet0 primary-vsw0 nmen35 # ldm add-vnet vnet1 primary-vsw1 nmen35 # ldm set-variable auto-boot\?=false nmen35 # ldm bind-domain nmen35 |
Create the virtual disk for the node.
Note that this non-master eligible node will be a dataless node. To create a diskless node instead of a dataless node, do not perform the following tasks:
# mkfile 4G /test1/bootdisk_nmen35.img # ldm add-vdiskserverdevice /test1/bootdisk_nmen35.img vol2@primary-vds0 # ldm add-vdisk vdisk1 vol2@primary-vds0 nmen35 |
# ldm start men15 # ldm start nmen35 |
The virtual console of the guest domains are only accessible through the control domain.
Use the following commands to access the consoles of the guest domains from outside the control domain:
men15: ssh 10.130.1.10 telnet localhost 5000 nmen35: ssh 10.130.1.10 telnet localhost 5001 |
Repeat and to set up the second Netra CP3060 or Netra T2000 system so a four-node cluster is ready to install Netra HA Suite.
Using the nhinstall tool, install Netra HA Suite as described in this guide, using the IP-addresses and names listed in EXAMPLE 1-1, with the following changes:
In cluster_definition.conf, use vnet0 and vnet1 as network interfaces for all nodes. Use the ldm ls-bindings command in the control domain to get the MAC addresses for vnet0 and vnet1 in each domain:
MEN_INTERFACES=vnet0 vnet1 NMEN_INTERFACES=vnet0 vnet1 |
Use c0d0s0, c0d0s1, and the like as disk slice names:
SLICE=c0d0s0 3072 / - logging MEN,DATALESS SLICE=c0d0s3 128 unnamed - - MEN SLICE=c0d0s4 128 unnamed - - MEN SLICE=c0d0s5 2048 /SUNWcgha/local c0d0s3 logging MEN SLICE=c0d0s6 8192 /export c0d0s4 logging MEN SLICE=c0d0s1 free swap - - MEN,DATALESS |
Add the patches required by LDoms to addon.conf:
SMOSSERVICEPATCH=118833-36 <path to patch directory> - I USR_SPECIFIC Y Y Y PATCH_WITH_PKGADDPATCH=118833-36 <path to patch directory> - S LOCAL N Y N PATCH=125043-01 <path to patch directory> - I LOCAL Y Y Y SMOSSERVICE PATCH=T124921-02 <path to patch directory> - I LOCAL Y N Y SMOSSERVICE |
Use the following command to jump-start the nodes instead of using the more commonly used boot net - install command:
ok boot /virtual-devices@100/channel-devices@200/network@0 - install |
Use the following command to boot the diskless nodes after the master-eligible nodes are installed:
ok ldm set-variable boot-device=\ "/virtual-devices@100/channel-devices@200/network@0:dhcp,,,,,5 \ /virtual-devices@100/channel-devices@200/network@1:dhcp,,,,,5" nmen35 ok boot |
In the control domain,
update the OpenBoot PROM
variables to make the nodes boot automatically.
PROM
variables to make the nodes boot automatically.
For diskless nodes, type the following:
# ldm set-variable \ boot-device=/virtual-devices@100/channel-devices@200/disk@0 men15 # ldm set-variable auto-boot\?=true men15 |
For dataless nodes, type the following:
# ldm set-variable \ boot-device=/virtual-devices@100/channel-devices@200/disk@0 nmen35 # ldm set-variable auto-boot\?=true nmen35 |
Installing a development host is not required, however, if you choose to do so, you can use the installation server, or you can install a server that is separate from the installation server. Refer to the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Getting Started Guide for information about choosing hardware and for development host software requirements.
After choosing the hardware to use for a development host, install it as described in the documentation that accompanied the product you selected.
After you have installed a development host, install software on it as described in the Netra High Availability Suite 3.0 1/08 Foundation Services Getting Started Guide.
After you have installed the software on the development host, connect it as described in Connecting the Cluster and the Installation Server.
Copyright © 2008, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.