HTTP Security Agent
The HTTP security agent protects the endpoints of a web service that uses HTTP for communication. After the HTTP agent is deployed in a web container on the WSP side, all HTTP requests for access to web services protected by it are redirected to the login and authentication URLs defined in the OpenSSO Enterprise configuration data on the WSC side. The configurable properties are:
-
com.sun.identity.loginurl=ossoserver_protocol://ossoserver_host:ossoserver_port/ossoserver/UI/Login
-
com.sun.identity.liberty.authnsvc.url=ossoserver_protocol://ossoserver_host:ossoserver_port/ossoserver/Liberty/authnsvc
Note –
For this release, the HTTP security agents are used primarily for bootstrapping. Future releases will protect web applications.
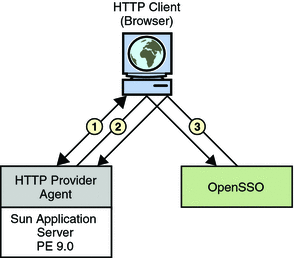
Figure 14–7 illustrates the interactions described in the procedure below it.
Figure 14–7 HTTP Security Agent Process
-
A WSC (user with a browser) makes a request to access a web service protected by an HTTP security agent.
-
The security agent intercepts the request and redirects it (via the browser) to OpenSSO Enterprise for authentication.
-
Upon successful authentication, a response is returned to the web service, carrying a token as part of the Java EE Subject.
This token is used to bootstrap the appropriate Liberty ID-WSF security profile. If the response is successfully authenticated, the request is granted.
Note –
The functionality of the HTTP security agent is similar to that of the Java EE policy agent when used in SSO ONLY mode. This is a non restrictive mode that uses only the OpenSSO Enterprise Authentication Service to authenticate users attempting access. For more information on Java EE policy agents, see the Sun OpenSSO Enterprise Policy Agent 3.0 User’s Guide for J2EE Agents.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
