Understanding Typical Business Cases
The Identity Provider Proxy feature is designed to be used by two types of users. Administrators configure the SAMLv2 Identity Provider Proxy. End–users access the services provided by service providers that initiate the single sign-on process across different circles of trust.
The following are typical business cases:
-
Single Sign-On, Introduction Cookie not enabled
-
Single Sign-On, Introduction Cookie enabled
-
Single Logout
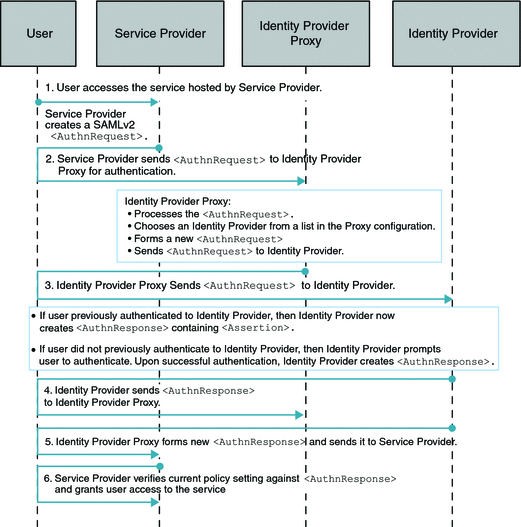
Single Sign-On, Introduction Cookie is Not Enabled
How the Identity Provider Proxy obtains the information about the actual Identity Provider is determined by whether or not the Introduction Cookie is enabled. Introduction Cookie is turned off, the Identity Provider Proxy retrieves an Identity Provider name from a list of pre-configured Identity Providers specified in the configuration.
The following figure illustrates the process for this use case. In this example, persistent federation is in place. In the transient federation mode, the Identity Provider Proxy does not contain any user information. The Identity Provider Proxy is used for proxying. The user information is only stored in the actual Identity Provider. The following figure illustrates the process flow for this use case.
Figure 7–2 Process Flow for Single Sign-On When Introduction Cookie is Not Enabled
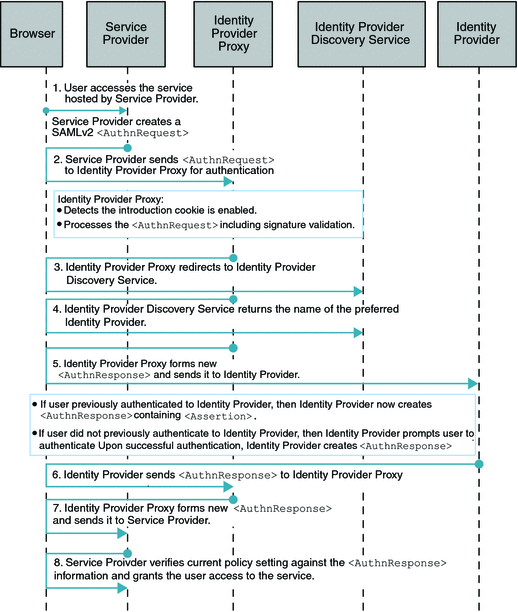
Single Sign-On (SSO) with Introduction Cookie Enabled
When the Introduction Cookie is enabled at the Service Provider, the Identity Provider Proxy relies on the com.sun.identity.SAMLv2.profile.SAMLv2IDPProxy plug-in to determine the preferred Identity Provider to proxy the authentication request to. The default implementation of this plug-in interface in OpenSSO Enterprise 8.0 is to consult the Identity Provider Discovery Service to get the information about the preferred Identity Provider . The following figure illustrates the process flow for this use case.
Figure 7–3 Process Flow for Single Sign-On (SSO) with Introduction Cookie Enabled
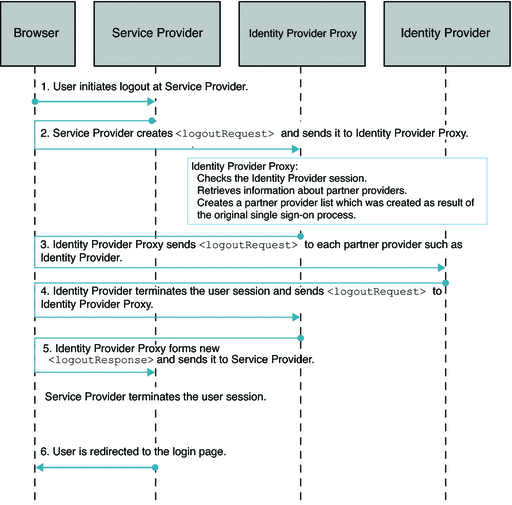
Single SAMLv2 Identity Provider Proxy Logout
The following figure illustrates the process for this use case.
Figure 7–4 Process Flow for Single Logout
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
