Access Control Lists
ACLs enable you to define file or folder permissions for the owner, owner's group, others, and specific users and groups, and default permissions for each of these categories. You can set up only one ACL per file or folder. An ACL consists of ACL entries. Each entry has a user type associated with it, much as basic permissions have Owner, Group, or Other associated with them.
If you want to grant file or folder access to a particular user or group, use the User or Group type ACL entry, respectively. You must specify the name of the user or group when you create the ACL entry. For example, you can use an ACL to grant a friend read permission on your resume, while protecting it from being read by the rest of the world (besides yourself).
To create, modify, or view ACLs on a file or folder, it must reside on a server or system running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible versions, and you must be running Solaris 2.5 Operating Environment or compatible versions. Such files and folders are called ACL-enabled. To set, modify, and view basic permissions and ACLs using the Properties Graphical User Interface (GUI), you must be running CDE 1.1 or later.
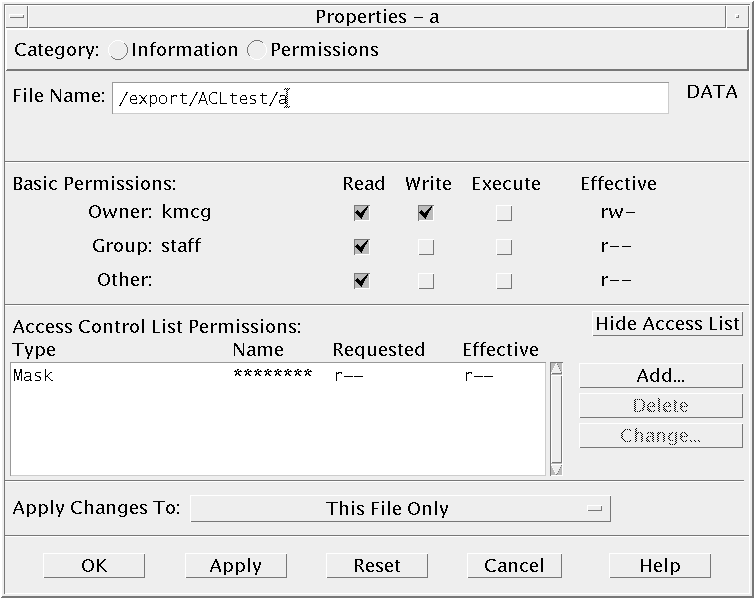
You must be the owner of the file or folder to create or modify basic permissions or ACLs for that file or folder. If you are not the owner, all fields in the Properties dialog box are displayed as read-only.
Note –
ACL terminology in this section refers to terminology used in the Properties GUI. Command-line terminology may be slightly different.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
