Sun Common SCSI Architecture Overview
The Sun Common SCSI Architecture (SCSA) is the Solaris DDI/DKI programming interface for the transmission of SCSI commands from a target driver to a host bus adapter driver. This interface is independent of the type of host bus adapter hardware, the platform, the processor architecture, and the SCSI command being transported across the interface.
By conforming to the SCSA, the target driver can pass any SCSI command to a target device without knowledge of the hardware implementation of the host bus adapter.
The SCSA conceptually separates building the SCSI command (by the target driver) from transporting the SCSI command and data across the SCSI bus. The architecture defines the software interface between high-level and low-level software components. The higher level software component consists of one or more SCSI target drivers, which translate I/O requests into SCSI commands appropriate for the peripheral device. Figure 14–1 illustrates the SCSI architecture.
Figure 14–1 SCSA Block Diagram
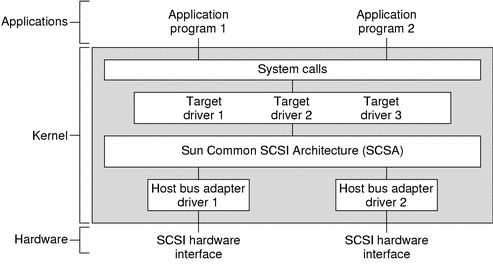
The lower-level software component consists of a SCSA interface layer and one or more host bus adapter drivers. The target driver is responsible for the generation of the proper SCSI commands required to execute the desired function and for processing the results.
General Flow of Control
Assuming no transport errors occur, the following steps describe the general flow of control for a read or write request.
-
The target driver's read(9E) or write(9E) entry point is invoked. physio(9F) is used to lock down memory, prepare a buf structure, and call the strategy routine.
-
The target driver's strategy(9E) routine checks the request and allocates a scsi_pkt(9S) using scsi_init_pkt(9F). The target driver initializes the packet and sets the SCSI command descriptor block (CDB) using the scsi_setup_cdb(9F) function. The target driver also specifies a timeout and provides a pointer to a callback function, which is called by the host bus adapter driver on completion of the command. The buf(9S) pointer should be saved in the SCSI packet's target-private space.
-
The target driver submits the packet to the host bus adapter driver using scsi_transport(9F). The target driver is then free to accept other requests. The target driver should not access the packet while it is in transport. If either the host bus adapter driver or the target supports queueing, new requests can be submitted while the packet is in transport.
-
As soon as the SCSI bus is free and the target not busy, the host bus adapter driver selects the target and passes the CDB. The target executes the command and performs the requested data transfers.
-
After the target sends completion status and the command completes, the host bus adapter driver notifies the target driver by calling the completion function that was specified in the SCSI packet. At this time the host bus adapter driver is no longer responsible for the packet, and the target driver has regained ownership of the packet.
-
The SCSI packet's completion routine analyzes the returned information and determines whether the SCSI operation was successful. If a failure has occurred, the target driver retries the command by calling scsi_transport(9F) again. If the host bus adapter driver does not support auto request sense, the target driver must submit a request sense packet to retrieve the sense data in the event of a check condition.
-
If either the command was completed successfully or cannot be retried, the target driver calls scsi_destroy_pkt(9F), which synchronizes the data and frees the packet. If the target driver needs to access the data before freeing the packet, it calls scsi_sync_pkt(9F).
-
Finally, the target driver notifies the application program that originally requested the read or write that the transaction is complete, either by returning from the read(9E) entry point in the driver (for a character device) or indirectly through biodone(9F).
SCSA allows the execution of many of such operations, both overlapped and queued, at various points in the process. The model places the management of system resources on the host bus adapter driver. The software interface enables the execution of target driver functions on host bus adapter drivers using SCSI bus adapters of varying degrees of sophistication.
SCSA Functions
SCSA defines functions to manage the allocation and freeing of resources, the sensing and setting of control states, and the transport of SCSI commands. These functions are listed in Table 14–1.
Table 14–1 Standard SCSA Functions|
Function Name |
Category |
|---|---|
|
Resource management |
|
|
|
|
|
scsi_dmafree(9F) |
|
|
|
|
|
scsi_alloc_consistent_buf(9F) |
|
|
scsi_free_consistent_buf(9F) |
|
|
Command transport |
|
|
Transport information and control |
|
|
scsi_ifsetcap(9F) |
|
|
scsi_abort(9F) |
Error handling |
|
scsi_reset(9F) |
|
|
scsi_poll(9F) |
Polled I/O |
|
scsi_probe(9F) |
Probe functions |
|
scsi_unprobe(9F) |
|
|
scsi_setup_cdb(9F) |
CDB initialization function |
Note –
If your driver needs to work with a SCSI-1 device, use the makecom(9F) function.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
