Installing a Terminal
If you have not added a terminal to your system before, first try installing a terminal in ASCII mode only. For more information, see Solaris System Administration Guide.
Serial Port Interface for Adding Terminals
Serial Ports is available from the Admintool menu to configure serial ports for terminals. Serial Ports provides the easiest method of installing a terminal. Serial Ports is invoked by admintool. For more information on admintool, see Solaris System Administration Guide.
Accessing Serial Ports
-
Become superuser.
system% su
-
Type admintool.
The admintool menu will appear.
system# admintool
-
Select the Serial Ports icon.
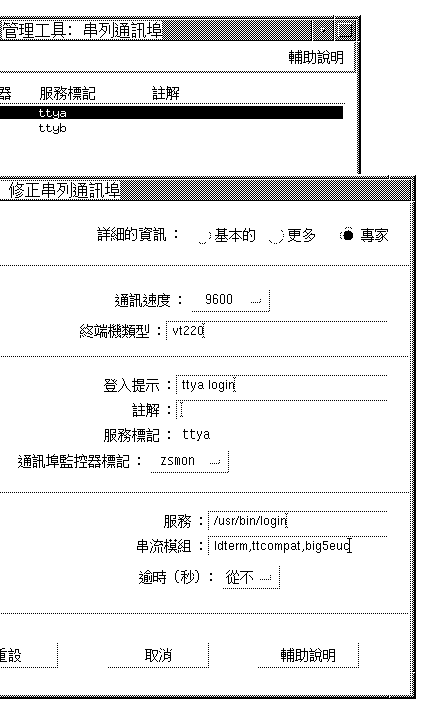
Using Serial Ports Menus
A Chinese terminal that supports CNS 11643 is installed as you would install an ASCII terminal.
-
Select Edit on the Serial Ports menu.
Serial Ports: Modify Service submenu appears.
-
On Admintool: Modify Service submenu select Enabled, Baud Rate 9600, and enter the terminal type.

-
Under Expert Options, select "Create utemp entry" and enter the appropriate module in the Streams Modules field:
Note -To install a terminal that supports Big5 code for the Traditional Chinese Solaris operating environment, add big5euc to the Streams Modules field.
Command Line Interface for Adding Terminals
The following procedure is required to set up a terminal on ttya port via the command line:
-
Determine the port monitor version number.
The port monitor version number will display.
# ttyadm -V
-
Enter the following commands, substituting the port monitor version number for ver.
(For more information on sacadm(1M)and pmadm(1M), see their man pages.)
# pmadm -r -p zsmon -s ttya # sacadm -a -p zsmon -t ttymon -c /usr/lib/saf/ttymon -v ver
-
Use the pmadm command that matches your terminal type to add a login service:
For EUC terminals, use the following command:
# pmadm -a -p zsmon -s ttya -i root -fu -v ver -m " `ttyadm -S y \ -T terminal_type -d /dev/ttya -l 9600 -m ldterm,ttcompat -s \ /usr/bin/login`"
For Big5 code terminals, use the STREAMS module big5euc in the ttyadm command:
# pmadm -a -p zsmon -s ttya -i root -fu -v ver -m "`ttyadm -S y \ -T terminal_type -d /dev/ttya -l 9600 -m big5euc,ldterm,ttcompat -s \ /usr/bin/login`"
-
Turn on the terminal.
Follow the documentation that accompanies the terminal.
-
Log in the terminal.
-
Check the correctness of the installation:
# setenv LANG locale # /bin/stty cs8 -istrip defeucw
Note -These values show that the operating system is set to communicate with the terminal in "8-bit no-parity" mode. Make sure the terminal is set up in "8-bit no-parity" mode. Refer to the terminal's setup manual for the proper way to set terminal options.
Setting a User's TTY
To verify that your TTY is properly set up:
-
Type the /bin/stty command with the -a option:
system% /bin/stty -a
-
If the values from above (cs8, -istrip) are not listed, then use the following command to set them:
system% /bin/stty cs8 -istrip defeucw
This is the last step in setting up a terminal.
Using Big5 TTY With EUC Locale
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
