Chapter 27 Installing With Custom JumpStart (Examples)
This chapter provides an example of setting up and installing Solaris software on both SPARC based and x86 based systems by using a custom JumpStart installation.
-
SPARC: Set Up Engineering Systems to Install From the Network
-
SPARC: Boot the Engineering Systems and Install Solaris 9 Software
-
x86: Boot the Marketing Systems and Install Solaris 9 Software
Sample Site Setup
Figure 27–1 shows the site setup for this example.
Figure 27–1 Sample Site Setup
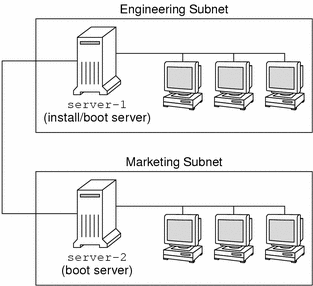
At this sample site, the conditions are as follows:
-
SPARC: The engineering group is located on its own subnet. This group uses SPARCstationTM systems for software development.
-
x86: The marketing group is located on its own subnet. This group uses x86 based systems for running word processors, spreadsheets, and other office productivity tools.
-
The site uses NIS. The Ethernet addresses, IP addresses, and host names of the systems are preconfigured in the NIS maps. The subnet mask, date and time, and geographic region for the site are also preconfigured in the NIS maps.
Note –
The peripheral devices for the marketing systems are preconfigured in the sysidcfg file.
-
Both the engineering and marketing systems are to be installed with Solaris 9 software from the network.
Create an Install Server
Because the groups need to install Solaris 9 software from the network, you make server-1 an install server for both groups. You use the setup_install_server(1M) command to copy the images to the server-1 local disk (in the /export/install directory). Copy the images from the Solaris 9 Software CDs and the Solaris 9 Languages CD or from the Solaris 9 DVD.
You must copy the image from the disc to an empty directory, in these examples the sparc_9and x86_9 directories.
Example 27–1 SPARC: Copying the Solaris 9 CDs
Insert the Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 SPARC Platform Edition CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# mkdir -p /export/install/sparc_9 server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./setup_install_server /export/install/sparc_9 |
Insert the Solaris 9 Software 2 of 2 SPARC Platform Edition CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./add_to_install_server /export/install/sparc_9 |
Insert the Solaris 9 SPARC Platform Edition Languages CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./add_to_install_server /export/install/sparc_9 |
Example 27–2 x86: Copying the Solaris 9 CDs
Insert the Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 x86 Platform Edition CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# mkdir -p /export/install/x86_9 server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./setup_install_server /export/install/x86_9 |
Insert the Solaris 9 Software 2 of 2 x86 Platform Edition CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./add_to_install_server /export/install/x86_9 |
Insert the Solaris 9 x86 Platform Edition Languages CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./add_to_install_server /export/install/x86_9 |
Example 27–3 SPARC: Copying the Solaris 9 DVD
Insert the Solaris 9 SPARC Platform Edition DVD in the DVD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# mkdir -p /export/install/sparc_9 server-1# cd /DVD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./setup_install_server /export/install/sparc_9 |
Example 27–4 x86: Copying the Solaris 9 DVD
Insert the Solaris 9 x86 Platform Edition DVD in the DVD-ROM drive that is attached to server-1 and type the following commands:
server-1# mkdir -p /export/install/x86_9 server-1# cd /DVD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./setup_install_server /export/install/x86_9 |
x86: Create a Boot Server for Marketing Systems
Systems cannot boot from an install server on a different subnet, so you make server-2 a boot server on the marketing group's subnet. You use the setup_install_server(1M) command to copy the boot software from the Solaris 9 x86 Platform Edition DVD or the Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 x86 Platform Edition CD to the server-2 local disk (in the /export/boot directory).
If you insert the Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 x86 Platform Edition CD in the CD-ROM drive that is attached to server-2, type the following command:
server-2# cd /CD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-2# ./setup_install_server -b /export/boot |
If you insert the Solaris 9 x86 Platform Edition DVD in the DVD-ROM drive that is attached to server-2, type the following command:
server-2# cd /DVD_mount_point/Solaris_9/Tools server-2# ./setup_install_server -b /export/boot |
In the setup_install_server command, -b specifies that setup_install_server is to copy the boot information to the directory that is named /export/boot.
Create a JumpStart Directory
Now that you have the install server and boot server set up, you create a JumpStart directory on server-1. You can use any system on the network. This directory holds files that are required for a custom JumpStart installation of Solaris software. You set up this directory by copying the sample directory from the Solaris 9 DVD image or from the Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 CD image that has been copied to /export/install:
server-1# mkdir /jumpstart server-1# cp -r /export/install/sparc_9/Solaris_9/Misc/jumpstart_sample /jumpstart |
Share the JumpStart Directory
To make the rules file and profiles accessible to systems on the network, you share the /jumpstart directory. To enable the sharing of a directory, you add the following line to the /etc/dfs/dfstab file:
share -F nfs -o ro,anon=0 /jumpstart |
Then, at the command line, you type the shareall command:
server-1# shareall |
SPARC: Create the Engineering Group's Profile
For the engineering systems, you create a file that is named eng_prof in the /jumpstart directory. The eng_prof file contains the following entries, which define the Solaris 9 software to be installed on systems in the engineering group:
install_type initial_install1 system_type standalone2 partitioning default3 cluster SUNWCprog4 filesys any 512 swap5
-
Specifies that the installation is to be treated as an initial installation, as opposed to an upgrade.
-
Specifies that the engineering systems are standalone systems.
-
Specifies that the JumpStart software uses default disk partitioning for installing Solaris software on the engineering systems.
-
Specifies that the Developer System Support software group is to be installed.
-
Specifies that each system in the engineering group is to have 512 Mbytes of swap space.
x86: Create the Marketing Group's Profile
For the marketing systems, you create a file that is named marketing_prof in the /jumpstart directory. The marketing_prof file contains the following entries, which define the Solaris 9 software to be installed on systems in the marketing group:
install_type initial_install1 system_type standalone2 partitioning default3 cluster SUNWCuser4 package SUNWaudio5
-
Specifies that the installation is to be treated as an initial installation, as opposed to an upgrade.
-
Specifies that the marketing systems are standalone systems.
-
Specifies that the JumpStart software is to use default disk partitioning for installing Solaris on the marketing systems.
-
Specifies that the End User Solaris Software Group is to be installed.
-
Specifies that the audio demo software package is to be added to each system.
Update the rules File
Now you must add rules to the rules file. The Solaris suninstall program uses the rules to select the correct installation (profile) for each system during a custom JumpStart installation.
At this site, each department is located on its own subnet and has its own network address. The engineering department is located on subnet 255.222.43.0. The marketing department is located on 255.222.44.0. You can use this information to control how the engineering and marketing systems are installed with the Solaris 9 software. In the /jumpstart directory, you edit the rules file, delete all of the example rules, and add the following lines to the file:
network 255.222.43.0 - eng_prof - network 255.222.44.0 - marketing_prof - |
Basically, these rules state that systems on the 255.222.43.0 network are to be installed with the Solaris 9 software by using the eng_prof profile. The systems on the 255.222.44.0 network are to be installed with the Solaris 9 software by using the marketing_prof profile.
Note –
You can use the sample rules to use a network address to identify the systems to be installed with the Solaris 9 software by using eng_prof and marketing_prof, respectively. You can also use host names, memory size, or model type as the rule keyword. Table 28–1 contains a complete list of keywords you can use in a rules file.
Validate the rules File
After the rules and profiles are set up, you run the check script to verify that the files are correct:
server-1# cd /jumpstart server-1# ./check |
If the check script does not find any errors, the script creates the rules.ok file.
SPARC: Set Up Engineering Systems to Install From the Network
After setting up the /jumpstart directory and files, you use the add_install_client command on the install server, server-1, to set up the engineering systems to install the Solaris 9 software from the install server. server-1 is also the boot server for the engineering group's subnet.
server-1# cd /export/install/sparc_9/Solaris_9/Tools server-1# ./add_install_client -c server-1:/jumpstart host-eng1 sun4u server-1# ./add_install_client -c server-1:/jumpstart host-eng2 sun4u |
In the add_install_client command, the options that are used have the following meanings:
x86: Set Up Marketing Systems to Install From the Network
Next, you use the add_install_client command on the boot server (server-2). This command sets up the marketing systems to boot from the boot server and install the Solaris 9 software from the install server (server-1):
server-2# cd /marketing/boot-dir/Solaris_9/Tools server-2# ./add_install_client -s server-1:/export/install/x86_9 \ -c server-1:/jumpstart host-mkt1 i86pc server-2# ./add_install_client -s server-1:/export/install/x86_9 \ -c server-1:/jumpstart host-mkt2 i86pc server-2# ./add_install_client -d -s server-1:/export/install/x86_9 \ -c server-1:/jumpstart SUNW.i86pc i86pc |
In the add_install_client command, the options that are used have the following meanings:
SPARC: Boot the Engineering Systems and Install Solaris 9 Software
After setting up the servers and files, you can boot the engineering systems by using the following boot command at the ok (PROM) prompt of each system:
ok boot net - install |
The Solaris operating environment is automatically installed on the engineering group's systems.
x86: Boot the Marketing Systems and Install Solaris 9 Software
You can boot the system from one of the following:
-
Solaris 9 Software 1 of 2 x86 Platform Edition CD
-
Solaris 9 x86 Platform Edition DVD
-
The network by using PXE network boot
-
The profile diskette
-
The Solaris 9 Device Configuration Assistant x86 Platform Edition diskette
Solaris 9 is automatically installed on the marketing group's systems.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
