| C H A P T E R 1 |
|
Sun Remote System Control (RSC) 2.2 Software |
Sun Remote System Control (RSC) 2.2 software is a server management tool that allows you to monitor and control servers over modem lines and over a network. RSC provides remote system administration for geographically distributed or physically inaccessible systems. RSC 2.2 software works with the RSC card included in supported Sun workgroup servers released after 1999 and also with RSC hardware included with Sun Enterprise 250 servers. For information about supported servers, click on Server Types in the RSC graphical user interface.

Online copies of Sun Remote System Control (RSC) 2.2 User's Guide are available in these locations after RSC installation:
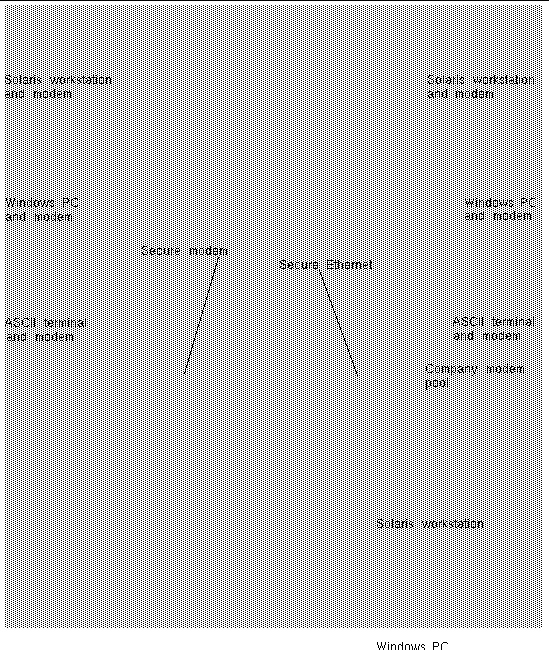
You can access RSC from a workstation running the Solaris, Microsoft Windows 98, Windows 2000, or Windows NT operating environment and Sun's RSC Java application, or from an ASCII terminal or device running ASCII terminal emulation software. FIGURE 1-1 shows remote access paths to RSC.
application, or from an ASCII terminal or device running ASCII terminal emulation software. FIGURE 1-1 shows remote access paths to RSC.
After RSC software is installed and configured to manage your server, you can use it to run diagnostic tests, view diagnostic and error messages, reboot your server, and display environmental status information from a remote console.
The RSC firmware runs independently of the host server, and uses standby power drawn from it. The RSC card also includes a battery that provides approximately 30 minutes of power to RSC in case of a power failure. Therefore, RSC hardware and software continue to be effective when the server operating system goes offline, and can send notification of hardware failures or other events that may be occurring on your server. Use of an uninterruptible power supply extends this capability.
|
Note - RSC hardware for Sun Enterprise 250 servers does not include a backup battery. |

The server can boot and operate normally when RSC software is not enabled, and Sun console features continue to be available on standard RS232 ports.
RSC has the following features:
 Diagnostics
Diagnostics
|
Note - RSC hardware for Sun Enterprise 250 servers does not include a backup battery or PCMCIA modem; you can connect a modem to the RSC serial port. |

RSC complements existing Sun monitoring and diagnostics tools such as Solstice Sun Management Center, SunVTS
Sun Management Center, SunVTS , the kadb kernel debugger, OpenBoot PROM, and OpenBoot Diagnostics. Sun Management Center operation remains unchanged, and it continues to be the main tool for observing system operation and performance while the server operating system is running.
, the kadb kernel debugger, OpenBoot PROM, and OpenBoot Diagnostics. Sun Management Center operation remains unchanged, and it continues to be the main tool for observing system operation and performance while the server operating system is running.
After installing and configuring Sun Remote System Control software on the server and client systems, you may use an OpenBoot PROM command and set OpenBoot PROM variables to redirect the console output to RSC.
Part of RSC configuration defines and enables alert mechanisms. Alerts provide remote notification of system problems and can be sent to pagers or an email address. RSC also sends alerts to any clients that are currently logged in to RSC.
|
Note - For sending pager alerts, RSC is designed to operate with any modem paging service that complies with the Telocator Alphanumeric Protocol (TAP). |
RSC sends an alert message whenever any of the following occurs:
|
Note - RSC hardware for Sun Enterprise 250 servers does not include a backup battery. |

Each alert message includes the server name and other important details, including time, date, and a description of the event. RSC configuration controls whether an alert is sent to an email address, to pagers, or to both. In addition, an alert is always sent to any clients currently logged in to RSC accounts for that server, and to the RSC event log. FIGURE 1-2 shows RSC remote alert paths.
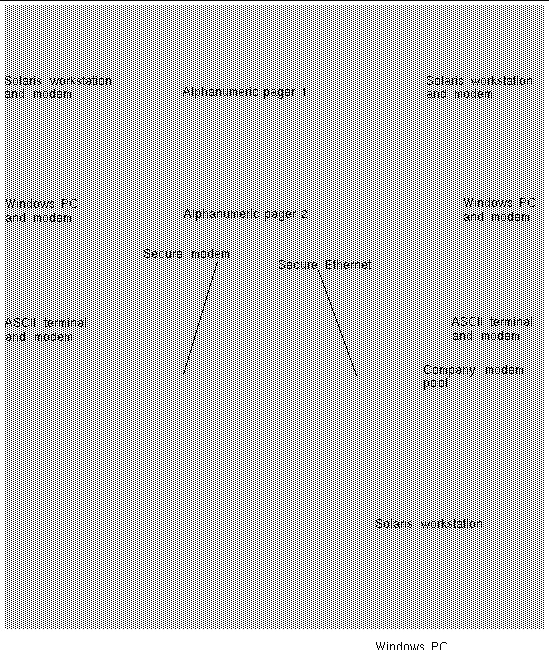
After receiving an alert message, you can connect to your RSC account for the server that caused the alert. Then you can check console messages to determine whether the server has recovered and is running, or whether the server operating system is down.
If the server is running, you can log in to it and debug the system using UNIX system administration tools such as SunVTS and Sun Management Center. If the server is not running, or if UNIX system administration tools are not available, you can use the RSC remote console feature to debug the server. After diagnosing a problem, you can schedule server downtime and service, if necessary.
RSC provides the following capabilities for remotely monitoring and controlling supported Sun workgroup servers.
You can control RSC configuration settings for:

After installation, you run a script file that guides you through basic configuration. See Chapter 2.
You can extend the amount of time you can use RSC beyond the RSC battery life by using a UPS (recommended). See Appendix A.
|
Note - RSC hardware for Sun Enterprise 250 servers does not include a backup battery. |

RSC supports a total of four concurrent telnet sessions per server, including command-line interface sessions and a graphical user interface (GUI) connection to the server console (Open Console). In addition, RSC supports up to four active concurrent RSC GUI sessions.
|
Note - Sun Enterprise 250 servers support two concurrent telnet sessions and three active concurrent RSC GUI sessions. |

The hardware and process required for you to log in to an RSC account on a managed server depend on company security practices, and whether the serial port, Ethernet, or modem dial-in are used. Further security is provided by RSC accounts, individual account access rights, and passwords. In addition, RSC records all logins and sends an alert if it detects more than five login failures within five minutes.
Characteristics of the modem settings and phone line connection to RSC determine access security for modem connections. For instance, use of a dial-back option or a phone line that supports dial-out only can increase security.
To use the RSC graphical user interface, a client must have Sun's RSC Java application installed; this is provided during installation. To use the RSC command shell, a client must be an ASCII character terminal or have ASCII character terminal emulation software installed.
Copyright © 2004, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All Rights Reserved.