Chapter 1 Sun Remote System Control (RSC) Software
Sun Remote System Control (RSC) is a server management tool that allows you to monitor and control your server over modem lines and over a network. RSC provides remote system administration for geographically distributed or physically inaccessible systems. The RSC software works with the System Service Processor (SSP) on the Sun(TM) Enterprise(TM) 250 main logic board. RSC and the SSP support both serial and Ethernet connections to a remote console.
RSC Access
You can access RSC from a workstation running the Solaris, Windows 95, Windows 98, or Windows NT operating environment and Sun's RSC Java(TM) application, or from an ASCII terminal or device running ASCII terminal emulation software. Figure 1-1 shows remote access paths to RSC.
Figure 1-1 RSC Remote Access Paths
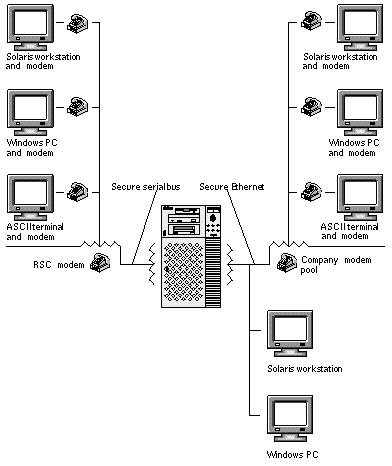
Once RSC software is installed and configured to manage your server, you can use it to run diagnostic tests, view diagnostic and error messages, reboot your server, and display environmental status information from a remote console.
The RSC firmware on the SSP runs independently, and uses standby power from the server. Therefore, SSP hardware and RSC software continue to be effective when the server operating system goes offline, and can send notification of hardware failures or other events that may be occurring on your server.
The server can boot and operate normally when RSC software is not enabled, and Sun console features continue to be available on standard RS232 ports.
RSC Features
RSC has the following features:
-
Remote system monitoring and error reporting, including output from power-on self-test (POST) and OpenBoot(TM) Diagnostics (OBDiag)
-
Remote server reboot, power-on, and power-off on demand
-
Ability to monitor the CPU temperature and fan sensors without being near the managed server, even when the server is offline
-
Ability to run diagnostic tests from a remote console
-
Remote event notification of server problems
-
A detailed log of RSC events
-
Remote console functions on both the serial and Ethernet ports
RSC complements existing Sun monitoring and diagnostics tools such as Solstice(TM) SyMON(TM), SunVTS(TM), the kadb kernel debugger, OpenBoot PROM (OBP), and OpenBoot Diagnostics (OBDiag). Solstice SyMON operation remains unchanged, and it continues to be the main tool for observing system operation behavior and performance while the server operating system is up and running.
RSC Use
After installing and configuring Sun Remote System Control software on the server and client systems, you use an OpenBoot command and set OpenBoot variables that redirect the console output to RSC.
Part of RSC configuration defines and enables alert mechanisms. Alerts provide remote notification of system problems, and can be sent to pagers or an email address; RSC also sends alerts to any clients that are currently logged in to RSC.
RSC sends an alert message whenever any of the following occurs:
-
The server system resets.
-
Server temperature crosses the lower-fault (high-temperature warning) limit.
-
Server temperature crosses the upper-fault (high-temperature shutdown) limit.
-
A server redundant power supply fails.
-
A power outage occurs at the server site, if an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is in use and it is configured to send an alert to RSC (see Appendix A, Installing and Configuring an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)).
-
RSC receives a server-generated alert.
-
The server undergoes a hardware watchdog reset.
-
RSC detects five unsuccessful RSC login attempts within five minutes.
Each alert message includes the server name and other important details. RSC configuration controls whether an alert is sent to an email address, to pagers, or to both. In addition, an alert is always sent to any clients currently logged in to RSC accounts for that server. Figure 1-2 shows RSC remote alert paths.
Figure 1-2 RSC Remote Alert Paths
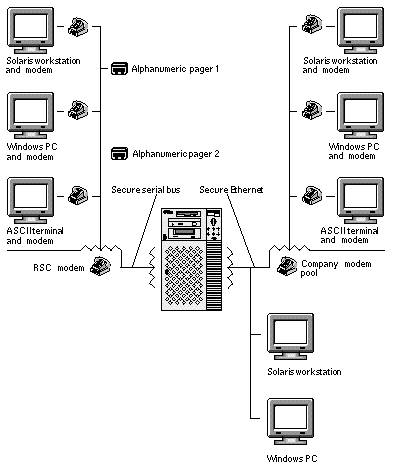
After receiving an alert message, you can connect to your RSC account for the server that caused the alert. Then you can check console messages to determine whether the server has recovered and is running, or whether the server operating system is down.
If the server is running, you can log in to it using a separate connection and debug the system using UNIX system administration tools such as SunVTS and Solstice SyMON. If the client is not running the Solaris operating system, these tools may be available through X windows.
If the server is not running, or if UNIX system administration tools are not available, you can use the RSC remote console feature to debug the server.
You can also debug the server by using RSC to:
-
Show environmental information
-
Put the server into debug mode
-
Control server firmware behavior
-
Turn server power off and then on, if the server is hung
After diagnosing a problem, you can schedule server downtime and service, if necessary.
RSC Capabilities
Sun Remote System Control provides the following capabilities for remotely monitoring and controlling Sun Enterprise 250 servers.
Server Status and Control
-
Show server environmental status.
-
Access a console that includes all UNIX console functions.
-
Send a break to put the server into debug mode.
-
Control the diagnostics level for a server reboot.
-
Reset the server on demand. When the system is not responding, you can issue a cold reset to bring the server back online.
-
Turn server power off and on.
View Logs
-
Display a detailed log of RSC errors, events, and RSC command history.
-
Display and reset server console logs.
RSC Configuration
You can control RSC configuration settings for:
-
Alerts
-
Ethernet port
-
Serial port
-
RSC date and time
-
Your RSC password
-
RSC user accounts
After installation, you run a script file that guides you through basic configuration. See the Sun Remote System Control (RSC) Installation Guide.
If you want to be able to use RSC in case of a complete power failure, you should install and configure an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) for the server. See Appendix A, Installing and Configuring an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS).
If you plan to use a modem on the RSC serial port, you must configure the modem properly. See Appendix B, Configuring the RSC Serial Port Modem.
User Interfaces
RSC user interfaces include:
-
A graphical interface that runs using Sun's RSC Java application
-
A command-line interface you can access using standard telnet to the RSC Ethernet port, and to the RSC serial port using point-to-point protocol (PPP)
-
A command-line interface you can access by connecting an ASCII character terminal directly to the RSC serial port
RSC supports a maximum of two concurrent telnet connections per server. These connections can be command-line interface sessions or RSC GUI connections to the server console (Open Console). In addition, RSC supports up to three concurrent RSC GUI sessions.
RSC Security
The hardware and process required to log in to an RSC account on a managed server depend on company security practices, and whether Ethernet or modem dial-in is used. Further security is provided by RSC accounts, individual account access rights, and passwords. In addition, RSC records all logins, and sends an alert if it detects five login failures within five minutes.
Characteristics of the modem and phone line that are connected to the RSC serial port also determine access security for remote serial port connections, for instance, use of a dialback option or a phone line that supports dial-out only. You can set RSC to disconnect a session connected to the serial port after ten minutes of inactivity; see "serial_hw_handshake".
As for any computer session, do not leave your session unattended. Always use the RSC logout command before disconnecting your session. In addition, before logging out of RSC, take care to log out of any server sessions you initiate while using the RSC console.
RSC Client Requirements
To use the RSC graphical user interface, a client must have Sun's RSC Java application installed. To use the RSC command shell, a client must be an ASCII character terminal or have ASCII character terminal emulation software installed.
Note -
To run the RSC GUI Java application on a Solaris client machine, the client machine must have the Java Development Kit for Solaris version 1.1.5 or a subsequent compatible version installed. This software is included on the Sun Enterprise 250 Supplement CD-ROM and can be installed along with the RSC software from the CD-ROM. If you install RSC software from the Web, you must download the Java Development Kit from the following location: http://www.sun.com/solaris/java/
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
