RSC Use
After installing and configuring Sun Remote System Control software on the server and client systems, you use an OpenBoot command and set OpenBoot variables that redirect the console output to RSC.
Part of RSC configuration defines and enables alert mechanisms. Alerts provide remote notification of system problems, and can be sent to pagers or an email address; RSC also sends alerts to any clients that are currently logged in to RSC.
RSC sends an alert message whenever any of the following occurs:
-
The server system resets.
-
Server temperature crosses the lower-fault (high-temperature warning) limit.
-
Server temperature crosses the upper-fault (high-temperature shutdown) limit.
-
A server redundant power supply fails.
-
A power outage occurs at the server site, if an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) is in use and it is configured to send an alert to RSC (see Appendix A, Installing and Configuring an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS)).
-
RSC receives a server-generated alert.
-
The server undergoes a hardware watchdog reset.
-
RSC detects five unsuccessful RSC login attempts within five minutes.
Each alert message includes the server name and other important details. RSC configuration controls whether an alert is sent to an email address, to pagers, or to both. In addition, an alert is always sent to any clients currently logged in to RSC accounts for that server. Figure 1-2 shows RSC remote alert paths.
Figure 1-2 RSC Remote Alert Paths
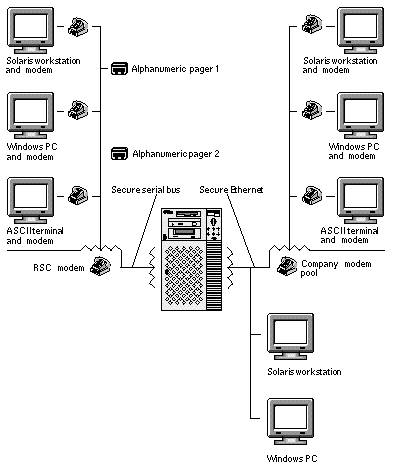
After receiving an alert message, you can connect to your RSC account for the server that caused the alert. Then you can check console messages to determine whether the server has recovered and is running, or whether the server operating system is down.
If the server is running, you can log in to it using a separate connection and debug the system using UNIX system administration tools such as SunVTS and Solstice SyMON. If the client is not running the Solaris operating system, these tools may be available through X windows.
If the server is not running, or if UNIX system administration tools are not available, you can use the RSC remote console feature to debug the server.
You can also debug the server by using RSC to:
-
Show environmental information
-
Put the server into debug mode
-
Control server firmware behavior
-
Turn server power off and then on, if the server is hung
After diagnosing a problem, you can schedule server downtime and service, if necessary.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
