Proxy MBeans
A proxy MBean is an object which represents a specific MBean instance and makes it easier to access that MBean. A management application instantiates a proxy so that it has a simple handle on a registered MBean, instead of needing to access the MBean server.
The manager may access MBeans by invoking the methods of their proxy object. The proxy formulates the corresponding management request to the MBean server. The operations are those which are possible on an MBean:
-
Getting or setting attributes
-
Invoking operations
-
Registering or deregistering for notifications
Because dynamic MBeans only expose their management interface at runtime, they cannot have a specific proxy MBean. Instead they have a generic proxy whose methods have an extra parameter to specify the attribute or operation name. The following diagram shows management components interacting with both standard and dynamic MBeans through both standard and generic proxies. Notice that a generic proxy may also represent a standard MBean.
Figure 2-1 Binding Proxy MBeans to Local and Remote Servers
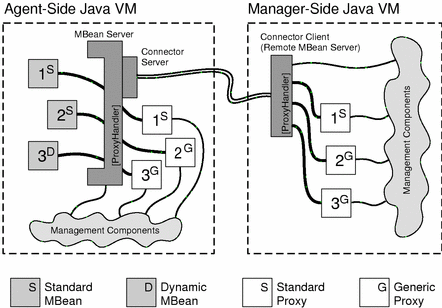
This diagram also shows that proxies may be instantiated either locally in the agent or remotely in the manager. Since the MBean server and the connector client have the same API, management request to either of them are identical. This creates a symmetry that allows the same management components to be instantiated either in the agent or in the manager application. This feature contributes to the scalability of Java Dynamic Management applications.
A standard proxy is generated from a standard MBean by using the proxygen compiler, supplied with the Java Dynamic Management Kit. The resulting class then needs to be loaded wherever the proxy will be instantiated. Generic proxies provide less of an abstraction but do not need to be generated. They are part of the Java Dynamic Management Kit libraries and are thus always available.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
