Configuration Examples
This section contains some examples of configuration files, based on the "Configuration Planning Example".
-
"IP-Transparent Mode Interface Configuration" shows an IP-transparent configuration.
-
"Server Mode Interface Configuration" shows the configurations for two interfaces, each configured in server mode.
-
"Logical Interfaces" shows the configuration for one interface that is configured as one logical interface at the IP level, using classes to divide the traffic by subnet.
-
"Complete Configuration" shows a complete configuration for the Paris site, including the standard service definitions.
IP-Transparent Mode Interface Configuration
Figure 4-1 IP-Transparent Configuration at London Site
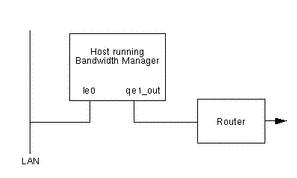
In IP-transparent mode, the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager sits between the traffic source (usually a LAN) and the router. On the host shown in Figure 4-1, you configure the qe1_out interface for Solaris Bandwidth Manager, giving le0 as the network device. For example:
interface qe0_out
rate 512000
activate enabled
router_addr 123.xxx.yyy.1
network le0
router_mac 809xxxxx
multicast all
In addition to the configuration shown above, you must configure a standard IP interface for the network interface to the LAN. This is necessary for the interface to be inserted into the IP stack at boot time. Create the file /etc/hostname.interfacename with a reference to the IP address of the interface.
Note -
Do not configure the network interface on the WAN side. Run ifconfig -a and check that there is no reference to this interface.
Server Mode Interface Configuration
Figure 4-2 Interfaces Configuration at Paris Site
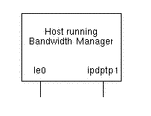
In this example, the host running Solaris Bandwidth Manager is acting as a router and there are two interfaces. le0 is the interface used when sending network traffic to London, and ipdptp1 is a PPP interface used when sending network traffic to Bonn. The configurations for both interfaces are normal server mode configurations. For example:
interface le0_out
rate 263144
activate enabled
interface ipdptp1_in
rate 65536
activate enabled
Logical Interfaces
Figure 4-3 Configuring Logical Interfaces
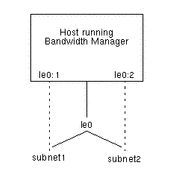
Solaris Bandwidth Manager operates at the level of the physical interface (le0) and does not recognize logical interfaces (le0:1 and le0:2, for example). If your IP configuration includes logical interfaces, you can use the class hierarchy to subdivide network traffic according to the destination subnet, and then manage the traffic for each subnet separately. Figure 4-3 shows a configuration with two logical interfaces. The configuration file contains a definition for the le0 interface, and filter and class definitions for the subnet1 and subnet2 classes. For example:
filter subnet1
remote
type subnet
address 123.xxx.yyy.0
mask 255.255.255.0
filter subnet2
remote
type subnet
address 123.xxx.zzz.0
mask 255.255.255.0
interface le0
rate 263144
activate enabled
class subnet1
parent root
interface le0_in
bandwidth 60
priority 3
max_bandwidth 100
filter subnet1
class subnet2
parent root
interface le0_in
bandwidth 40
priority 3
max_bandwidth 100
filter subnet2
Complete Configuration
The following file implements the configuration described for the Paris server in "Configuration Planning Example". Note that two filters, imap and smtp, have been used to define the class email.
# Sample configuration file for Paris site
version 1.6
timeout 30
#Subnet Group definitions
subnet_group bonn
address 129.xxx.xxx, 129.xxx.yyy
mask 225.225.225.0
subnet_group paris
address 129.yyy.xxx, 129.yyy.yyy, 129.yyy.zzz
mask 225.225.225.0
subnet_group london
address 129.zzz.xxx, 129.zzz.yyy
mask 225.225.225.0
#Filter definitions
filter http_to_london
local
type subnet_group
name paris
remote
type subnet_group
name london
service http
filter telnet
service telnet
filter imap
service imap
filter http_to_bonn
local
type subnet_group
name paris
remote
type subnet_group
name bonn
service http
filter snmp
service snmp
filter http
service http
filter ftp
service ftp
filter smtp
service smtp
#Interface defintions for qe0_out
interface qe0_out
rate 128000
activate enabled
#Class definitions for interface qe0_out
class ftp
interface qe0_out
parent root
filter ftp
bandwidth 15
priority 7
max_bandwidth 15
class email
interface qe0_out
parent root
filter imap, smtp
bandwidth 20
priority 7
max_bandwidth 20
class snmp
interface qe0_out
parent root
filter telnet
bandwidth 5
priority 1
max_bandwidth 5
class telnet
interface qe0_out
parent root
filter telnet
bandwidth 30
priority 1
max_bandwidth 30
class http
interface qe0_out
parent root
filter http
bandwidth 20
priority 5
max_bandwidth 20
class http_bonn
interface qe0_out
parent http
filter http_to_bonn
bandwidth 5
priority 3
max_bandwidth 5
class http_london
interface qe0_out
parent http
filter http_to_london
bandwidth 10
priority 3
max_bandwidth 10
class default
interface qe0_out
bandwidth 0
priority 7
max_bandwidth 0
#Interface definition for qe0_in
interface qe0_in
rate 128000
activate enabled
#Class definition for interface qe0_in
class default
interface qe0_in
bandwidth 100
priority 7
max_bandwidth 100
|
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
