Logical Interfaces
Figure 4-3 Configuring Logical Interfaces
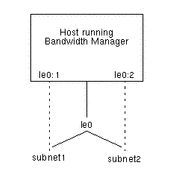
Solaris Bandwidth Manager operates at the level of the physical interface (le0) and does not recognize logical interfaces (le0:1 and le0:2, for example). If your IP configuration includes logical interfaces, you can use the class hierarchy to subdivide network traffic according to the destination subnet, and then manage the traffic for each subnet separately. Figure 4-3 shows a configuration with two logical interfaces. The configuration file contains a definition for the le0 interface, and filter and class definitions for the subnet1 and subnet2 classes. For example:
filter subnet1
remote
type subnet
address 123.xxx.yyy.0
mask 255.255.255.0
filter subnet2
remote
type subnet
address 123.xxx.zzz.0
mask 255.255.255.0
interface le0
rate 263144
activate enabled
class subnet1
parent root
interface le0_in
bandwidth 60
priority 3
max_bandwidth 100
filter subnet1
class subnet2
parent root
interface le0_in
bandwidth 40
priority 3
max_bandwidth 100
filter subnet2
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
