LDAP Data Views
An LDAP data view exposes data in an LDAP server to a client request and specifies the data source pool that responds to the request. By defining LDAP data views, you can perform the following tasks:
-
Expose a whole database in a single view
-
Provide different views for different subtrees in a database
-
Provide a unified view of different databases
There are additional types of data views but distribution can only be done with LDAP data views. For more information about other types of data views, see Chapter 18, Directory Proxy Server Virtualization.
LDAP Data View Features
A simple LDAP data view is defined primarily by the base DN of the data view. In a simple data view all of the entries in the subtree are encompassed by the data view. Data views can exist in hierarchy, with a superior data view and a subordinate data view. A subordinate data view is a data view whose base DN is inferior to the base DN of a superior data view. The entries in a subordinate data view are excluded from the superior data view.
For information about the features of a data view, see the following sections.
Excluding a Subtree From a Data View
When a subordinate data view is created, Directory Proxy Server automatically excludes the subordinate data view from the superior data view. When a request targets the subordinate data view, the request is sent to the subordinate data view instead of the superior data view.
By default, Directory Proxy Server automatically configures the excluded-subtrees parameter in the superior data view to exclude subordinate data views. For information about how to disable the automatic configuration, see To Manually Configure the excluded-subtrees and alternate-search-base-dn Properties in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
The following subtrees are excluded by default from all data views: cn=config, cn=monitor, and cn=proxy manager.
Performing a Search Directed at a Superior Data View on an Excluded, Subordinate Data View
When an alternate search base is specified in a subordinate data view, search operations targeted at the superior data view are also performed in the subordinate data view.
By default, Directory Proxy Server automatically configures the alternateSearchBase parameter in the subordinate data view. For information about how to disable the automatic configuration, see To Manually Configure the excluded-subtrees and alternate-search-base-dn Properties in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
Attribute Renaming and DN Renaming
Each entry in a directory is identified by a DN and a set of attributes and their values. Often, the DN and the attributes defined on the client side do not map to the DN and the attributes defined on the server side.
Data views can be defined to rename DNs and attributes to values that match the server side. When a client makes a request, the DNs and attributes are renamed to match the server side. When the result is returned to a client, the DN and attributes are changed back to match the client side.
Attribute Renaming
The following figure illustrates how attribute renaming is performed by Directory Proxy Server.
Figure 17–1 Attribute Renaming
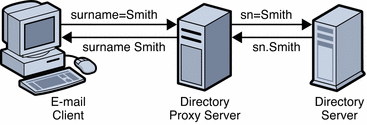
In Figure 17–1, the email client expects the last names to be specified by the attribute surname However, in the LDAP server, last names are specified by the attribute sn. When attributes are renamed, only the name of the attribute is affected — the value of the attribute is not changed. However, when attributes are renamed all entries with that name are renamed.
For information about how to configure attribute renaming, see To Configure Attribute Renaming in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
DN Renaming
The following figure illustrates how DN renaming is performed by Directory Proxy Server.
Figure 17–2 DN Renaming
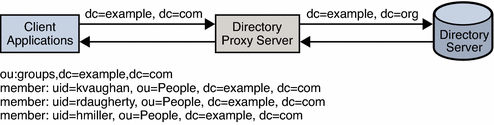
In Figure 17–2, the client contains the dc=example, dc=com database. The LDAP server contains the dc=example, dc=org database. The Directory Proxy Server renames the DNs.
Attributes that contain DNs must also be renamed if those DNs are in the portion of the DIT that is affected by the original DN renaming. In Figure 17–2, the group attribute contains a list of the DNs of group members. When dc=example, dc=com is renamed to dc=example, dc=org, the DNs in the group attribute must also be renamed.
For information about how to configure DN renaming, see To Configure DN Renaming in Sun Java System Directory Server Enterprise Edition 6.1 Administration Guide.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
