|
|
| Sun ONE Connector Builder 2.0 Installation and Getting Started Guide |
Lessons for Creating a COTS Sample Resource AdapterThis module describes how to create the COTS sample resource adapter. The following lessons are described in this module .
- Lesson 1 - Mount the COTS EIS API and a Working Directory
- Lesson 2 - Define the Resource Adapter
- Lesson 3- Generate the COTS Resource Adapter
- Lesson 4- Customize the Generated Code for the COTS Adapter
- Lesson 5 - Copy the EIS Client Files
- Lesson 6 - Build and Package the Resource Adapter
- Lesson 7- Generate SOAP Services for the Connector Builder COTS Resource Adapter (optional)
All the files required for generating the sample resource adapter are included with the Connector Builder software.
Lesson 1 - Mount the COTS EIS API and a Working Directory
The COTS EIS Java API must be mounted correctly in the IDE file system. The COTS EIS API can be in one of the following forms
- .jar file
- .class file
- .java file of a class
- an interface of the COTS EIS API.
Mounting is required so that you can browse the classes to identify the COTS EIS API to the Wizard.
To Mount the COTS API and a Working Directory
- Start IDE.
- Select File > Mount Filesystem > Local Directory.
- Click Next.
- Browse to the location where the EIS API is located.
- Select the parent directory of the package you want to use.
For example, if a class COTSAPI is located in the package com.sun.appinteg.samples.eis
and the complete directory path is <connector_builder_install_root>/samples/cots/eissystem/src/com/sun/ appinteg/samples/eis
mount the directory: <connector_builder_install_root>/samples/cots/eissystem/src.
- Click Finish.
- Select File > Mount Filesystem > Local Directory.
Mount a local working directory where you want to generate the resource adapter. For the sample resource adapter we created and mounted a directory named "C:\COTS_location".
- Click Next.
- Select a local working directory where you want to generate the resource adapter.
For the sample resource adapter we created and mounted a directory named "C:\COTS_location".
- Click Finish."
Lesson 2 - Define the Resource Adapter
The Connector Builder Wizard is used to define the resource adapter.
The process consists of the following nine steps:
- Step 1 - Choose Template
- Step 2 - Specifying Adapter Location Information
- Step 3 - Entering Adapter General Information
- Step 4 - Mapping the EIS API
- Step 5 - Customizing Interaction Specs
- Step 6 - Specifying Configuration Properties
- Step 7 - Choosing Authentication and Transactional Support
- Step 8 - Enter Licensing Information (Optional)
- Step 9 - Set Adapter Icons (Optional)
There are two ways to run the Connector Builder Wizard:
- via the IDE Explorer
- via the File menu
Step 1 - Choose Template
You can choose the template using one of the following methods:
From the IDE main menu
- Select File > New.
The following screen is displayed.
Choose Template Page
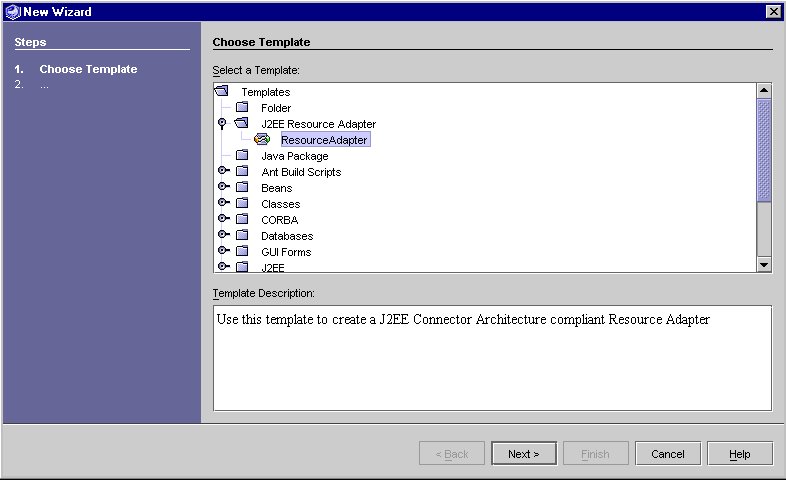
- From the list of templates displayed, select J2EE Resource Adapter > Resource Adapter.
- Click Next.
From the IDE Explorer Area
- In the IDE Explorer, right-click the folder where you want to generate the resource adapter.
- Select New > J2EE Resource Adapter > ResourceAdapter from the pop-up menu.
The Adapter Location Information Page is displayed.
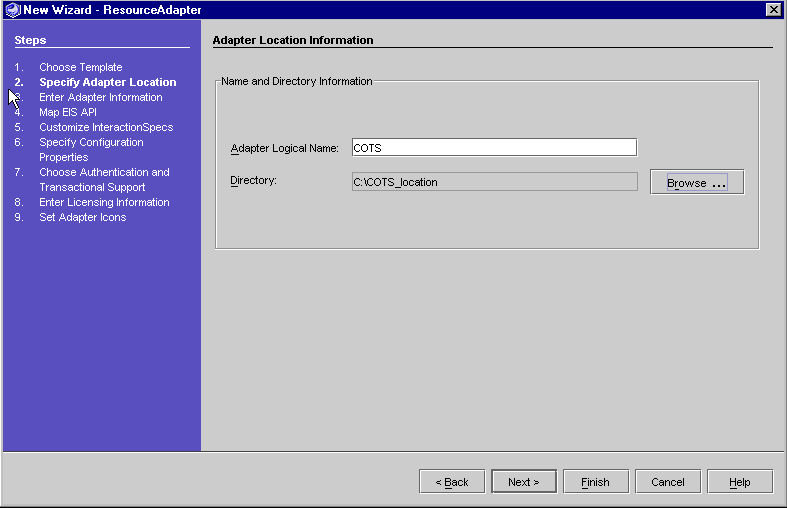
Step 2 - Specifying Adapter Location Information
- Browse to select the directory where you want the adapter files to be generated.
For the sample resource adapter we created and mounted a directory named "C:\COTS_location".
This field can be modified using the Browse button. The adapter files are generated in a folder named <Adapter Logical Name> created within this directory. You cannot have two adapters with the same logical name in the same directory.
- Enter the Adapter Logical Name. For the sample resource adapter, enter the name "COTS".
This field is required. The Adapter Logical Name is used to create the names of classes and files in the generated adapter. After you specify the adapter logical name field and press tab, the Wizard checks that the logical name is correct and unique in the specified directory. If both conditions are met, the Next button is enabled.
- Click Next. The "Adapter General Information Page" is displayed.
Adapter Location Information Page
Step 3 - Entering Adapter General Information
The Wizard uses the Adapter Logical Name entered on the Adapter Location Information page to create defaults for the required fields.
Adapter General Information Page
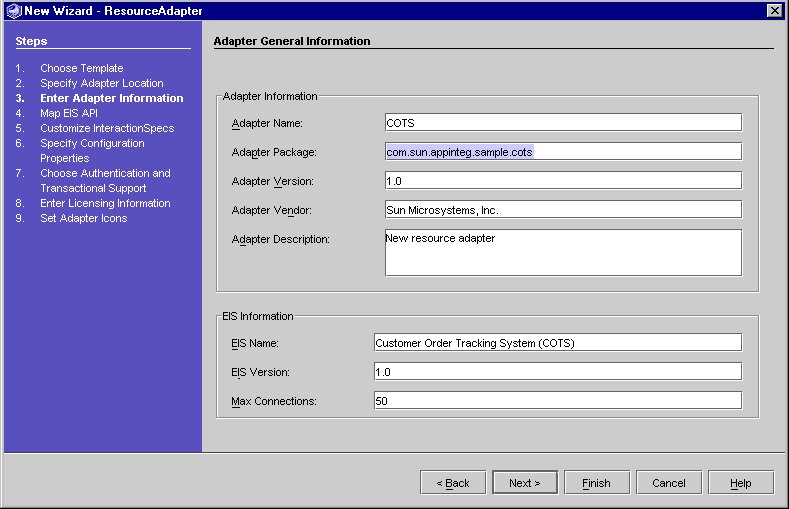
The following table lists the fields in the Adapter. The left column lists the attribute and the right column provides the attribute value for the Connector Builder COTS sample.
The Wizard creates default values of 1.0 for the Adapter Version and EIS Version. For a description of each field please see the Adapter General Information Fields table.
You can modify any field in the Adapter General Information page.
- Click Next. The "Adapter EIS API Mapping Page" is displayed.
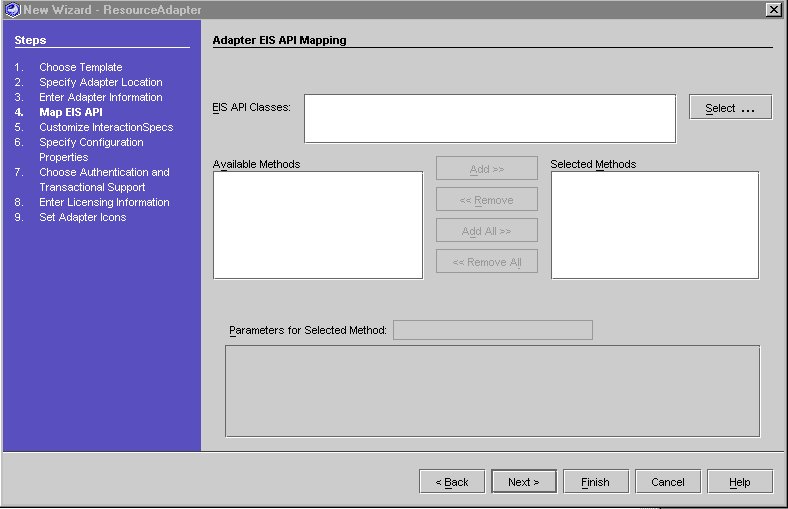
Step 4 - Mapping the EIS API
- In the "Adapter EIS API Mapping Page", click Select and navigate to the location of the COTS EIS API. See "Select a EIS API Class".
- Select the COTSAPI from /com/sun/appinteg/samples/eis directory.
Adapter EIS API Mapping Page
Select a EIS API Class
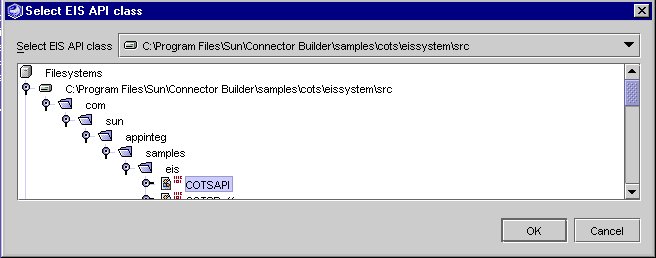
- Select the .java or .class file of a class or interface of the EIS API.
Note In our example, navigate to the following directory: <connector_builder_install_root>/samples/cots/eissystem/src/com/sun/appinteg/samples/eis and select COTSAPI.
- Click OK.
The class' public methods are displayed in the Available Methods as seen in the following screen.
Adapter EIS API Mapping Information Screen
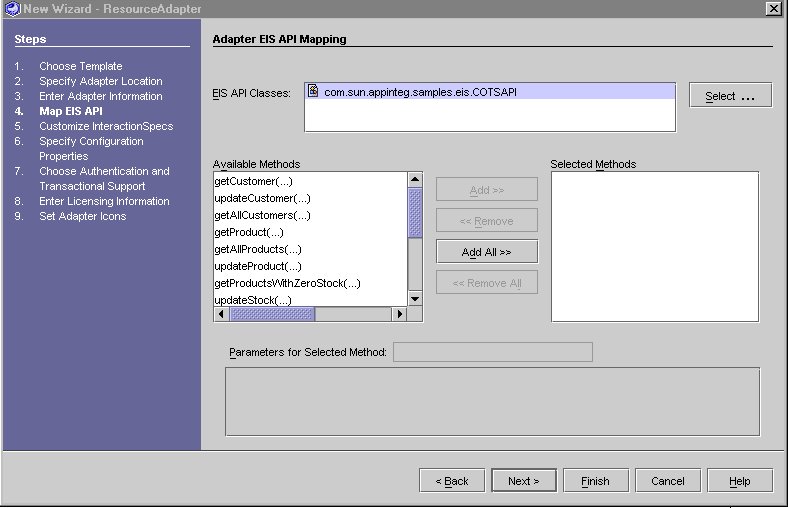
The methods of the EIS API that are to be exposed via the Adapter need to be added to the Selected Methods.
- Select one or more methods in the Available Methods and use Add to move methods to the Selected Methods.
For the COTS sample resource adapter, choose the following three methods:
- getCustomer
- updateCustomer
- getAllCustomer
and add them to the Selected methods as shown in the following screen.
Customize Parameter for EIS API Mappings
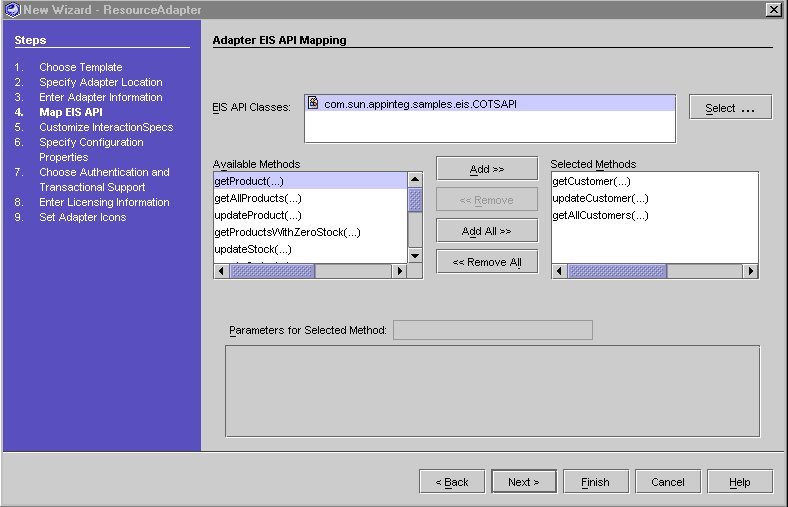
- Select a method from the Selected method. The Parameters for Selected Method table displays the parameters.
Adapter EIS API Mapping Screen
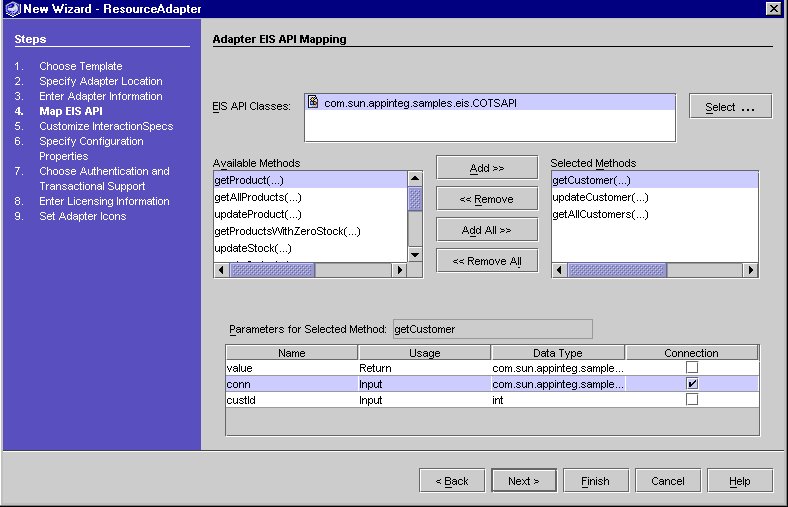
The information displayed for each parameter includes:
Name - must be a valid Java identifier. There may be no duplicate names within the same method.
Usage - displays whether the parameter is the method's return value or an input parameter.
Data Type - displays the fully qualified calss or scalar data type name
Connection - must be a class, input parameter. Only one is allowed per method. Primitive types and arrays are not allowed.
Name and Connection are the only editable columns.
Identifying Connection Objects
Many EIS APIs use a Java object to represent information about the physical connection between the Java application and the EIS. The EIS API documentation might refer to these objects as a "context" object, a connection object, or some other name. Often, one method in the EIS API accepts a username and password as parameters and, if they are valid in the EIS, return a connection object representing the newly-established physical link to the EIS. Other methods in the API accept this connection as a parameter along with other parameters specific to that method's purpose.
The Connector Builder run-time system and the container in which the resource adapter runs optimize the use of physical connections and enforce security for them. It is important that Java applications that use Connector Builder resource adapters be prevented from manipulating these connection objects; yet some of the EIS API methods require the connection object as a parameter.
The Connector Builder handles this situation by providing special treatment for parameters that are connection objects. For these parameters, the Connector Builder generates code that automatically retrieves that connection object from inside the resource adapter and passes it to the EIS API method. The application neither receives nor provides the connection object itself.
Note This step must be repeated for each Connection Object in each method in the COTS EIS API.
To Specify Connection Parameters to Connector Builder
- Select the method that is to be customized in the Selected Methods.
The method's parameters are displayed in the Parameters table.
- Select the Connection checkbox for the EIS Connector type, as shown.
For the COTS API EIS example select the "Connection" checkbox for each "Conn" parameter name for each method.
- Click Next.
Step 5 - Customizing Interaction Specs
For each EIS API method selected, Connector Builder generates a corresponding InteractionSpec class, as described in the J2EE Connector Architecture. An InteractionSpec represents the way an EIS API method can be called from a resource adapter. An application that uses the CCI programming model can establish a connection to the EIS and then use InteractionSpec objects to invoke methods in the EIS API. The Connector Builder Wizard allows you to modify the names of these classes using the following screen.
EIS API Mapped Interaction Specs
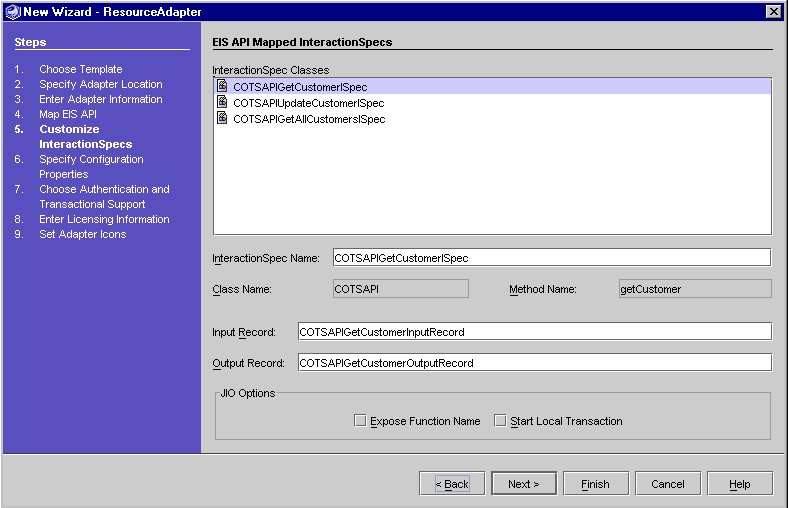
As a further convenience, Connector Builder also generates a Java Interaction Object (JIO) with each generated InteractionSpec. The application can use a JIO simply and easily to invoke the corresponding EIS API method. The JIO automatically obtains a connection to the EIS if necessary and can even start a transaction in the EIS before invoking the method. In addition, the JIO can accept an additional parameter - the name of a function to be performed - which allows the JIO to be used with general-purpose EIS API methods.
The InteractionSpec classes list displays the names of the InteractionSpec classes that are generated for the Selected methods from the previous panel.
When you highlight an item in the list, the fields in the panel display the relevant information for that InteractionSpec. The InteractionSpec Name, Input Record and Output Record are required for each InteractionSpec. They can be modified but must contain only valid Java identifiers and must be unique.
The Output Record is a class that corresponds to the return value for the method that the InteractionSpec class is based on. The Input record corresponds to the input parameters for the method.
Validations are performed when you exit each field.
No customizations are required in this example.
To Continue Building a Connector Without Customizing Interaction Spec
- Click Next.
Step 6 - Specifying Configuration Properties
The configuration properties are used at run-time to create a connection with the EIS. The J2EE Connector Architecture specification describes two types of configuration properties. A property of the first type has a value that applies to all physical connections to a given EIS, regardless of the client that needs to use the physical connection. Common examples of this type of property include a URL, or host name and port number. The resource adapter always connects to the configured URL (or host and port number) to establish physical links to the EIS.
In contrast, the value of a property of the second type can change from one client's request for a physical connection to the next. Connections to a single EIS on behalf of two different users, for instance, would use different username and password values but the same URL value. The Connector Builder considers properties in this second category as "client properties." You can specify a value for such a property on the Configuration Properties page (see "Configuration Properties Editor"), but the resource adapter can override that default value at run-time when it requests a connection on behalf of a particular client application.
The Connector Builder generates certain classes differently depending on which properties are client properties and which are not. You indicate which properties should be treated as client properties by selecting the Client Can Override checkbox in the Properties Table on the Configuration Parameters page.
Configuration Properties Editor
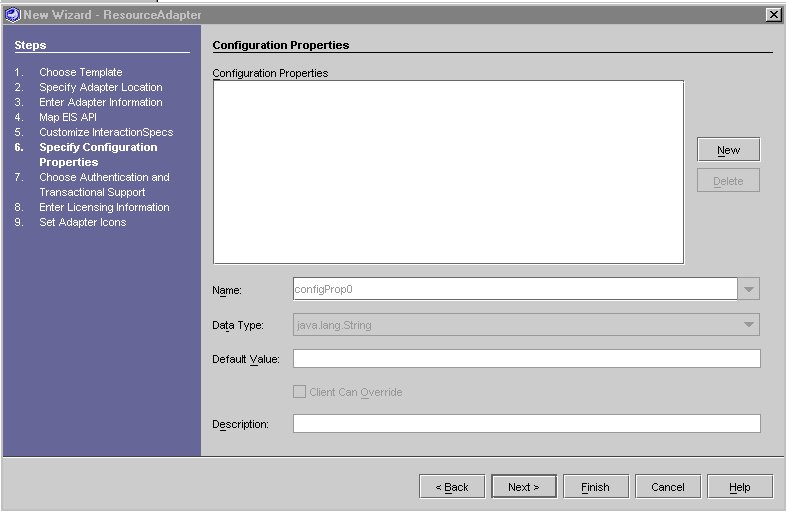
To Edit or Add a Configuration Property
- In the "Configuration Property Editor" click New.
Configuration Property Editor
When you click New, the name of a new property appears in the list. By default, the name of the new property is configProp0, configProp1, configProp2.... (depending on how many properties are in your current list).
- Fill in the fields as described in the following table.
(Repeat steps 1 and 2 for each property that you want to add.)
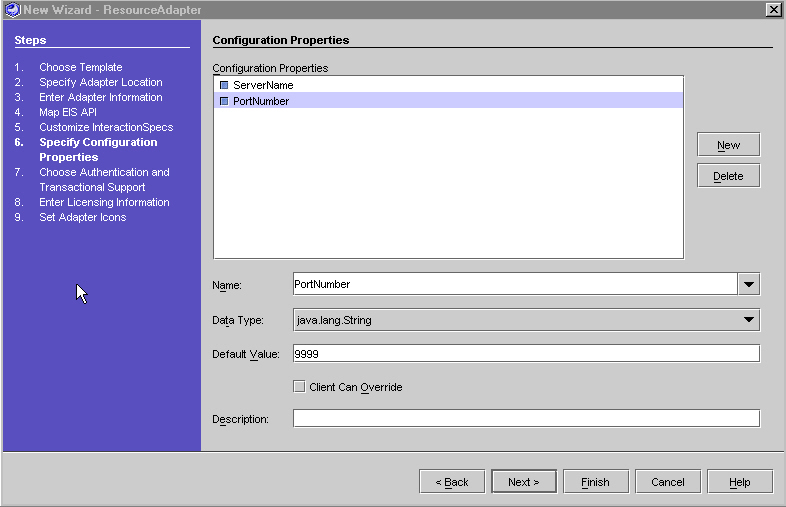
The "Configuration Properties Parameters" table lists the configuration properties. The left column lists the parameter. The right column provides a description.
For the COTS sample resource adapter the following two configuration properties need to be entered:
ServerName and PortNumber
- Click Next.
Step 7 - Choosing Authentication and Transactional Support
- Select Basic Password.
Basic Password - user-password based authentication mechanism that is specific to an EIS.
Authentication and Transactional Support Panel
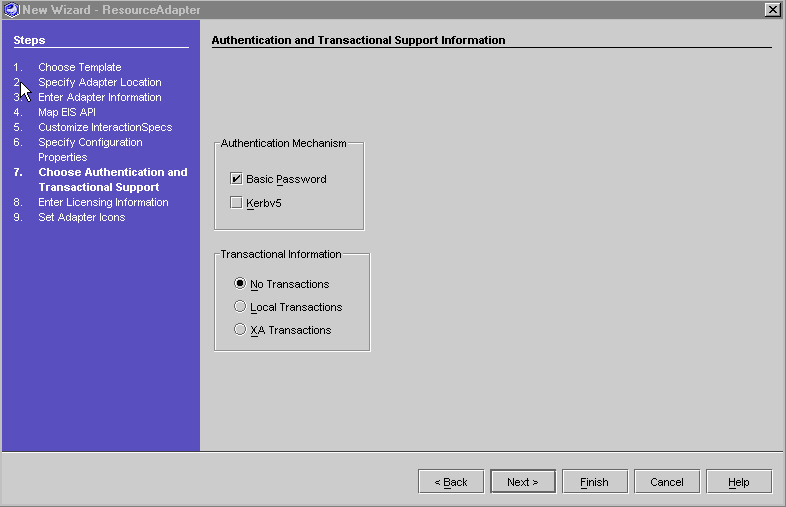
- Select No Transactions (default) - the resource adapter supports neither Local nor XA Transactions.
At this point you may choose to generate the resource adapter, see Lesson 3- Generate the COTS Resource Adapter or continue on with optional steps 8 and 9. For a more detailed description about steps 8 and 9 refer to Chapter 3 in the Sun ONE Connector Builder Developer's Guide.
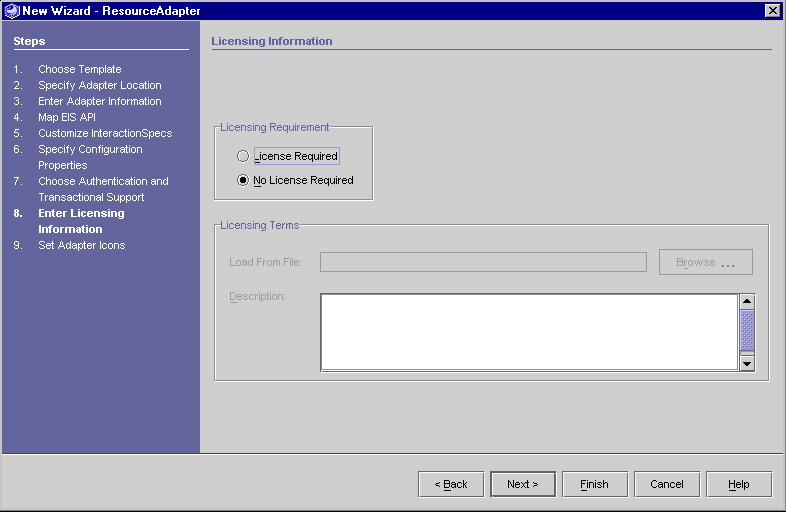
Step 8 - Enter Licensing Information (Optional)
The "Licensing Panel" is used to collect licensing information about the resource adapter. No action is required on this panel.
- Select No License Required (default).
- Click Next.
Licensing Panel
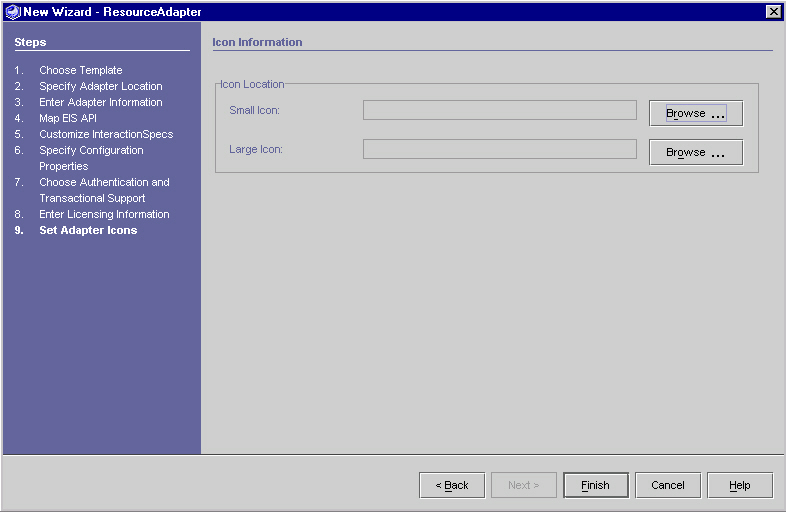
Step 9 - Set Adapter Icons (Optional)
The icons are used to represent the generated resource adapter. No action is required on this panel.
The "Set Adapter Icons Panel" displays the icon information.
Set Adapter Icons Panel
Lesson 3- Generate the COTS Resource Adapter
- Click Finish to generate the Resource Adapter.
When you click Finish, the adapter and JIO generators are invoked. Status messages are displayed in the status text area of IDE, indicating progress of the adapter generation. The messages displayed are "Generating Adapter...", "Generating Java Interaction Objects ..." and then "Adapter Generation is complete". The resource adapter is generated at this point. The IDE output window displays a list of all the files generated and other notes about the generation process. In particular, special notes list the mandatory customizations that you must implement to make the generated resource adapter work correctly with your EIS API.
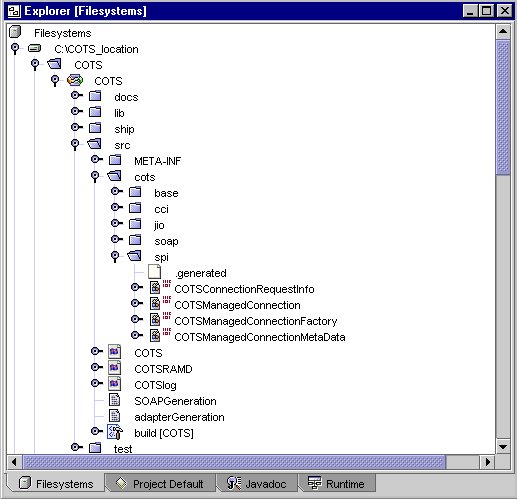
Once the adapter generation is complete, the adapter's root directory (which was specified as the Directory in Step 2 - Specifying Adapter Location Information) is mounted as an IDE filesystem, and appears within the Explorer area of IDE. If you expand this directory, you can see a "node" (COTS) which represents the newly created adapter. The adapter node can also be expanded to show subdirectories of the adapter.
One of these subdirectories is src. After the Connector Builder generated the resource adapter, the src directory should contain a text file named adapterGeneration.txt which describes the results of the generation. It lists the files created and also highlights special steps you should perform - such as certain mandatory customizations to the generated Java code - in order to complete the resource adapter.
The directory is as follows:
Generated Resource Adapter Directory Structure
Lesson 4- Customize the Generated Code for the COTS Adapter
Customize the Methods for the COTS Adapter
Two classes need to be customized for the COTS sample resource adapter.
COTSManagedConnectionFactory.java
Select the COTSManagedConnectionFactory.java class from .../src/com/sun/appinteg/samples/cots/spi directory. You need to customize/add the matchConnection method in this class.
matchConnection
The Connector Builder framework uses this method in its implementation of ManagedConnectionFactory matchConnection, when it is trying to find an existing managed connection that is compatible with the user and password of a new request for a connection.
Currently the COTS EIS server does not support any authentication mechanism, so, there is no need to check connection against security information. You can simply return true.
To Customize the ManagedConnectionFactory Method
- Add the implementation code provided below.
The following is the implementation code for the matchConnectionFactory method:
COTSManagedConnection.java
The managed connection represents a physical connection to the resource adapter. In the COTS adapter this physical connection is a rmi connection handle. You need to customize four methods in this class.
The following four methods need to be implemented:
- createPhysicalConnection(ConnectionrequestInfo cri)
- createPhysicalConnection(String userName, char [] password)
- doDestroy()
- do AdditionalCleanup()
createPhysicalConnection(ConnectionrequestInfo cri)
To Customize the createPhysicalConnection(ConnectionrequestInfo cri) Method
- Select the COTSManagedConnection.java class from COTS/src/spi directory.
- Add the implementation code provided below.
The following is the implementation code for the createPhysicalConnection(ConnectionrequestInfo cri) method:
createPhysicalConnection(String userName, char [] password)
To Customize the createPhysicalConnection(String userName, char [] password) Method
- Add the implementation code provided below.
The following is the implementation code for the createPhysicalConnection(String userName, char [] password) method;
doDestroy()
This method calls the close() method on COTSEISConnection object to close the physical connection.
To Customize the doDestroy Method
- Add the implementation code provided below.
The following is the implementation code for the doDestroy method:
do AdditionalCleanup()
To Customize the doAdditionalCleanup Method
- Add the implementation code provided below.
The following is the implementation code for the doAdditionalCleanup() method:
doAdditionalCleanup() method
protected void doAdditionalCleanup() throws javax.resource.ResourceException {
}
Be certain to save the changes.
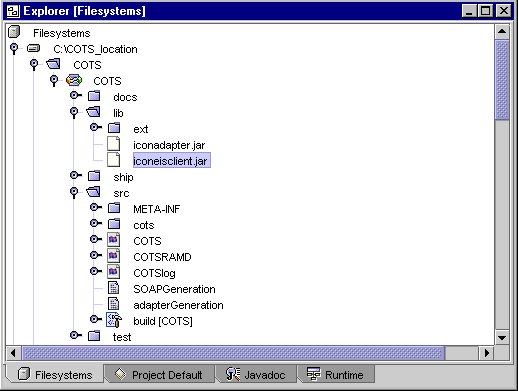
Lesson 5 - Copy the EIS Client Files
Copy the COTS client API library iconeisclient.jar file from <connector builder _install_root>/samples/cots/eissystem/lib to the adapter's lib directory..
To Copy the EIS Client File
- In Explorer, right click on COTS_location\COTS.
- Select Import Files from the contextual menu.
The following screen is displayed.
Import File Editor
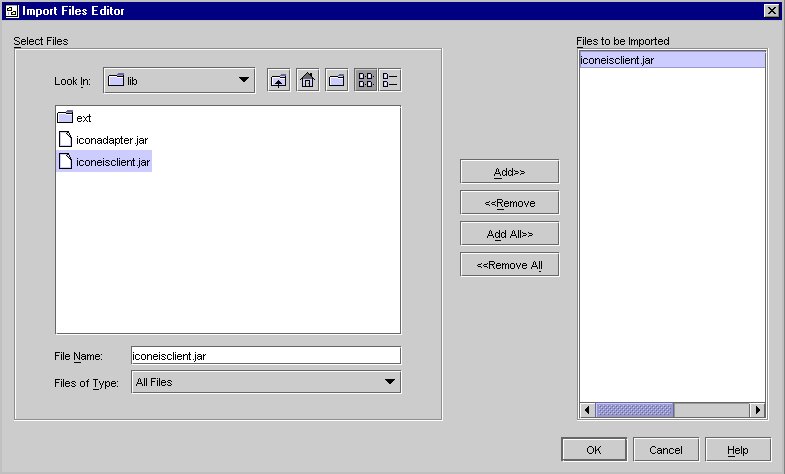
- Browse to the <connector_builder_install_root>\samples\cots\eissytem\lib.
- Select the iconeisclient.jar file and click Add.
- Click OK.
The file is copied into the COTS_location\COTS\lib directory and is packaged with the adapter.
Copied eisclient.jar file
Lesson 6 - Build and Package the Resource Adapter
Once you have defined and generated a resource adapter, the adapter must be built and packaged before it can be deployed and used. To compile the generated Java files and package the resource adapter into a resource archive (.rar) file, Connector Builder uses ANT. ANT is a Java-based, open-source build tool similar in purpose to the make utility that:
- reads an XML file that contains instructions on how to build one or more targets, or deliverable files, that make up a software system.
- executes the steps necessary to build a specified target or the entire system.
An ANT XML file is generated as part of resource adapter generation. ANT uses this generated XML file to:
- Build (compile) the generated resource adapter source classes.
- Package the generated resource adapter.
- Build and package the SOAP layer.
- Build and package user test cases.
- Generate API documentation for the generated adapter classes.
To build and package the resource adapter code.
- Right click on the adapter node to bring up the contextual menu.
- Select Build.
The following screen displays the menu selection for running the Build option.
Menu Selection for Build Option
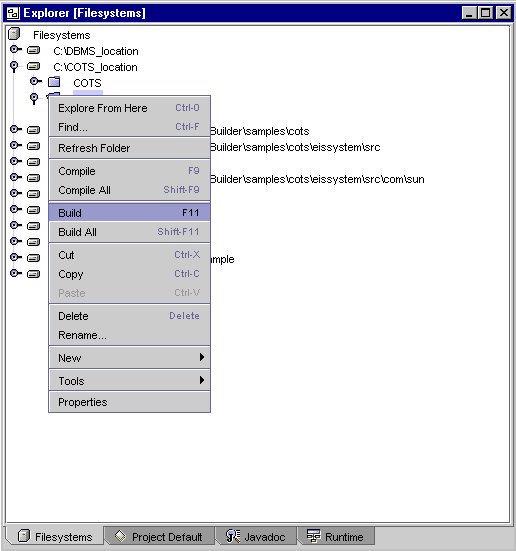
- Right click on the adapter node to bring up the contextual menu.
- Select Package.
This creates the COTS .rar file in the COTS_location\COTS\ship directory.
Lesson 7- Generate SOAP Services for the Connector Builder COTS Resource Adapter (optional)
The Connector Builder can generate the following elements of SOAP services:
- SOAP service deployment descriptor
- template serializers and deserializers - The adapter developer can customize these classes to handle datatypes that the SOAP server cannot handle itself.
- service providers (in the form of the JIOs for the resource adapter)
- utility classes useful from the client application for invoking the SOAP services.
Before the Connector Builder can generate SOAP Services the resource adapter must be defined and generated as described in the preceding lessons. Only then, can you provide the additional information that pertains to the SOAP services. Note that you can define and generate a SOAP service for each EIS API method defined in the resource adapter.
The following tasks are described in this lesson:
Adding SOAP Services Configuration
The connector builder enables your JIOs, namely, getCustomer, updateCustomer, and getAllCustomers. Refer to the Chapter 6 in the Sun ONE Conenctor Builder Developer's Guide for more information about SOAP.
To Configure SOAP Services
- Right-click on the adapter node within the Explorer area of the IDE.
The adapter's contextual menu is displayed.
- Select Configure SOAP Services.
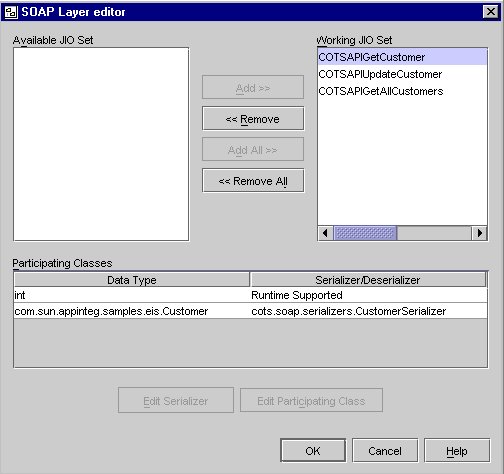
The SOAP Layer Editor opens with the names of all the JIOs that are available to be exposed as SOAP services. The service names are based on the JIO names.
- Select the JIOs in the Available JIO set to which you want to add SOAP services.
- Click Add.
The selected JIO is moved to the Working JIO set. Click OK.
SOAP Layer Editor
Edit the Serializers for Each JIO
GetCustomer JIO
The COTSAPIGetCustomerOutputRecord, refers to the Customer class. The appropriate serializer needs to be configured. Since Customer is a bean, you need to indicate to the Connector Builder to use the Apache SOAP supported bean serializer through the Customize Serializer Screen.
To Edit the Serializer for GetCustomer JIO
- In the SOAP Layer Editor select the COTSAPIGetCusotmer JIO.
- Select com.sun.appinteg.samples.eis.Customer.
- The Edit Serializer button is enabled.
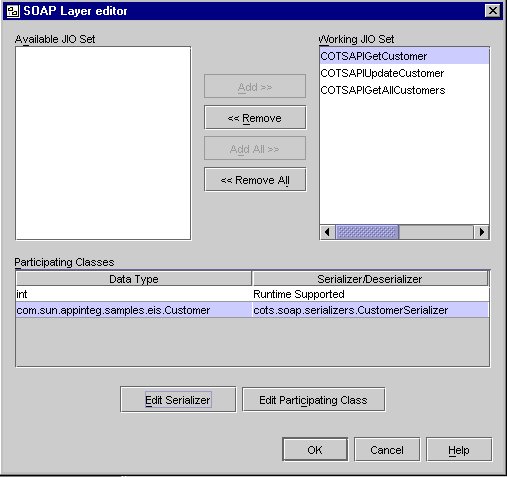
- Click Edit Serializer.
- Change the serializer from Generate Template to Use Java Bean.
Customize Serializer Screen
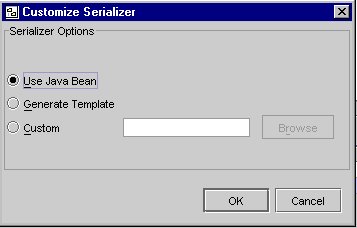
UpdateCustomer JIO
The COTSAPIUpdateCustomerInputRecord, refers to the Customer class. The appropriate serializer needs to be configured. Since Customer is a bean, you need to indicate to the Connector Builder to use the Apache SOAP supported bean serializer through the Customize Serializer Screen. If you have already configured Customer to use the bean serializer, in the 'getCustomer' context, you do not need to repeat this step.
Since Customer does not have any sub classes, you do not need to edit the participating classes.
GetAllCustomers JIO
The COTSAPIGetAllCustomersOutputRecord, refers to the vector of the Customer classes. Since Vector is supported by Apache SOAP, a serializer does not need to be configured. Since Vector refers to Customer, the Customer class needs to be added to the list of participating classes, using the Edit Participating Classes screen.
To Edit Participating Classes for GetAllCustomers JIO
- Select COTSAPIGetAllCustomers JIO in the SOAP Layer Editor.
- Select the Data Type java.util.vector from the Participating Classes. The Edit Participating Classes button is enabled.
- Click Edit Participating Classes. The Edit Participating Class Screen is displayed.
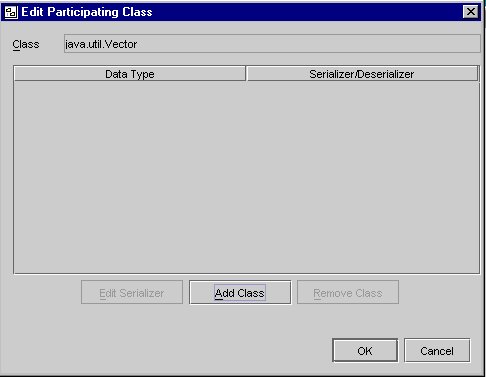
You need to add 'Customer' to the participating class list and configure its serializer.
- Click Add Class. The Add Class screen is displayed.
- Browse to the Customer class and add it to the participating class list.
The Customer class is located in the EIS API mounted, as in lesson 1
Add Class.
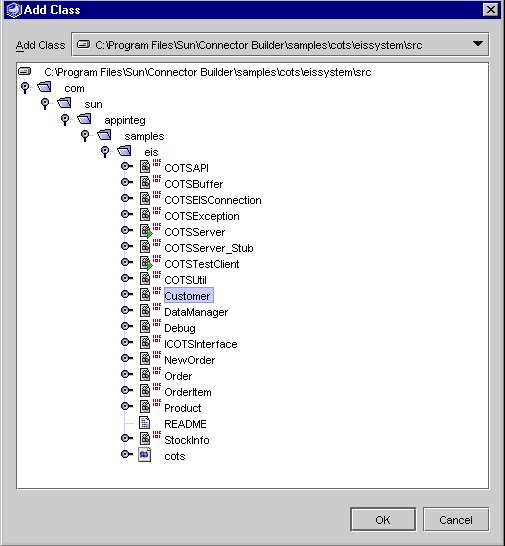
- Click OK.
Once the class is added, you need to configure the class serializer. If you have already configured the Customer serializer is earlier step, you do not need to repeat this step.
- Click OK on the Edit Participating Classes screen followed by an OK on the SOAP Layer Editor.
This completes the SOAP service definition and closes the SOAP Layer Editor.
Generating SOAP Services
Once the SOAP service configuration is added, the adapter generation automatically takes care of generating SOAP services. From the adapter node, press 'generate' to generate the SOAP services. This step would generate the SOAP related deployment descriptor, serializers and client files under the 'src' directory, as per the adapter package name.
- Right-click on the adapter node within the Explorer area of the IDE.
The adapter's contextual menu is displayed.
- Select the Generate menu option.
The Adapter and the SOAP Services generation begins. On completion, a generation report is displayed in IDE's Output window.
In the generated code directory, a SOAP directory, see SOAP Directory Structure, is created which contains the following three subdirectories:
clients
The clients directory contains one HTTP client class for each exposed SOAP service.
deployment
The deployment directory contains a deployment descriptor XML document for each SOAP service.
serializers
The serializers directory contains a serializer class for each of the participating classes for which you chose the Generate Template option.
For more information about SOAP Services see Chapter 6 in the Sun ONE Connector Builder Developer's Guide.
SOAP Directory Structure
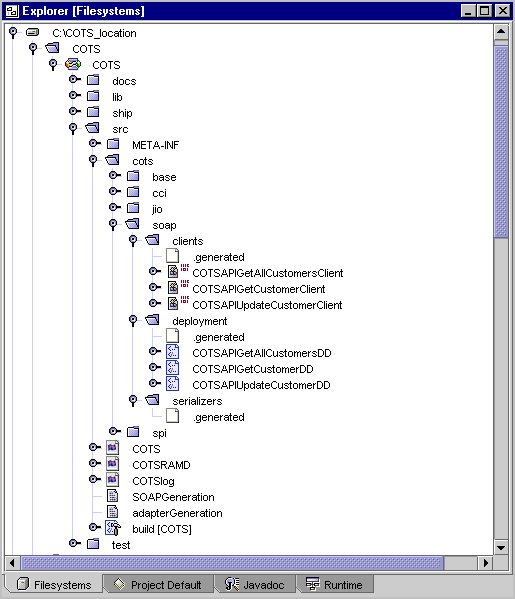
Customizing the Generated SOAP Clients
The generated SOAP clients are in the directory .../src/com/sun/appinteg/samples/cots/soap/clients
Customize the Methods for the COTS SOAP Client
The following three generated SOAP client classes need to be customized for the COTS sample resource adapter.
- COTSAPIGetCustomerClient.java
- COTSAPIGetAllCustomersClient.java
- COTSAPIUpdateCustomerClient.java
Select each of these classes from the .../src/com/sun/appinteg/samples/cots/soap/clients directory. You need to customize the initClient and populateInputData methods in all of these classes.
To Customize the InitClient Method
The initClient method is used to initialize the SOAP client with the SOAP Mapping Registry, and with the the correct URN and URL values of the service the client wants to access. The generated initClient method needs to be modified to set the correct value for the SOAP URL.
- Locate the following line in the method
// specify the URL of the apache SOAP servlet
The URL value is by default
http://localhost:8080/soap/servlet/rpcrouter.
- Set it to the correct value of your Apache SOAP servlet.
To Customize the populateInputData Method
This method is used to set the input parameter values that the SOAP service requires.
- Add the implementation code provided below in the COTSAPIGetCustomerClient.java class.
The following is the implementation code for the populateInputData method
:
Refer to the shipped COTS sample SOAP clients to learn more about customizations to other generated SOAP clients.
Summary
If you followed the above sample steps you have successfully built the COTS sample connector that is now ready for deployment to the Application Server.