
This chapter describes how to diagnose a problem with a SPARCstation 10 system and run diagnostic tests. You should be familiar with troubleshooting hardware, running diagnostic tests, and replacing or upgrading hardware.
---------------------------------------
Default Boot Mode page 2-1 Diagnostic Tools page 2-5 OpenBoot PROM Diagnostics page 2-6 SunDiag System Exerciser page 2-10 ---------------------------------------
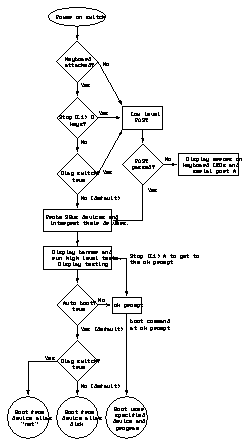
Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2 outline the roles played by various diagnostics during the default boot mode. A description of the flowchart follows Figure 2-1 and Figure 2-2.
Figure 2-2 Default Boot Mode (Systems With Open Boot PROM Version 2.14 and Later)
This section describes how the various diagnostic tools work together in the different power-on modes.
Note - POST will run at power on if the Stop (L1)-d keys are pressed and held down, the diag-switch? parameter is set to true, or the keyboard is disconnected.
While the low-level POST code executes, the Caps Lock LED on the keyboard flashes to indicate that testing is in progress. If a failure occurs in POST, the failing replaceable unit is encoded on three LEDs located on the Type-5 keyboard. See Chapter 3, "Power-On Self-Test (POST)."
If the POST passes, the system probes for SBus devices and interprets their
drivers. Next, high-level tests are performed. You will see the word Testing
while the high-level tests are running. After Testing is displayed, if you
want to use the OpenBoot PROM commands (ok prompt), press the
Stop (L1)-a keys simultaneously.
If the autoboot switch parameter is set to false (not the default), you will get the ok prompt. To change to the monitor prompt () see the manual OpenBoot Command Reference.
If the autoboot switch parameter is set to true (default), and the diagnostic switch parameter is set to false (default), the operating system is booted using the device alias disk. If the autoboot switch parameter is set to true (default), and the diagnostic switch parameter is set to true (not the default), the operating system is booted using the device alias net. See Table 2-1.
To run user-specified programs, you must be at the ok prompt.
Table 2-1 describes the autoboot and diagnostic switch parameters.
----------------------------------------------------------------
Autoboot Diagnostic Results will be: Switch set to: Switch set to: ----------------------------------------------------------------
False Don't care ok prompt (Open Boot PROM
commands)
True False Boot operating system (vmunix)
from disk automatically
True True Boot operating system (vmunix)
from network automatically
----------------------------------------------------------------
The main categories of diagnostic tests are:
You should use each type of diagnostic tool in the appropriate circumstances. Table 2-2 provides a summary of the available diagnostic tools and lists when to use each diagnostic tool.
Table 2-2 Diagnostic Tools
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Diagnostic Description ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Power-On Self-Test POST tells you if the following fails: system board,
DSIMM in slot 0, MBus modules.
POST code, residing in the OpenBoot PROM, executes
at power-on when you press and hold the Stop
(L1)-d keys, if the diag-switch? parameter is set
to true, or the keyboard is disconnected.
On-Board Diagnostics Includes tests such as: Ethernet and the diskette drive
controller tests. To run on-board diagnostics, you
must be at the ok prompt.
Forth Toolkit Allows input to the system at the OpenBoot PROM
level. Supports functions such as changing NVRAM
parameters, resetting the system, running diagnostic
tests, displaying system information, and redirecting
input and output. See the manual OpenBoot Command
Reference.
SunDiag System Exerciser Runs under the operating system and displays real-
time use of the system resources and peripherals. See
the SunDiag User's Guide for more information. If
SunDiag fails, run the Power-On Self-Test.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The diagnostics stored in the OpenBoot PROM include:
See Table 2-2 and Chapter 3, "Power-On Self-Test (POST)" for information on POST. If there is system trouble, you can run on-board diagnostics for thorough tests, including but not limited to:
You can run on-board diagnostics from the ok prompt. If there is a problem with your operating system, the operating system brings the system to the ok prompt. You can also get to the ok prompt by shutting down the operating system.
Table 2-3 describes selected on-board diagnostic tests, what you must do before you run each test, and when to run it. Some of the tests verify the proper operation of the network controller, the diskette drive system, memory, and the system clock. See Appendix E, "Selected On-Board Diagnostics" for a detailed description of each test.
Table 2-3 Selected On-Board Diagnostic Tests
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Type of Test Description Preparation When to Use ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
test screen Tests the system video graphics The diag-switch? NVRAM Monitor or graphics card
hardware and monitor. parameter must be set true. does not function.
test floppy Tests the floppy drive ability to Insert a formatted diskette into Diskette drive does not
respond to commands. the drive. respond to commands.
test scsi Tests the SCSI interface logic on The diag-switch? NVRAM SCSI interface is not
the system board. parameter must be set to true. communicating.
test net-aui Performs an internal and external A cable must be connected to Ethernet interface or cable
loopback test on the AUI (Thick) the system AUI Ethernet port may be defective.
Ethernet interface. and to an Ethernet Tap or the
test will fail the external
loopback phase.
test net-tpe Performs an internal and external A cable must be connected to Ethernet interface or cable
loopback test on the TPE interface. the system TPE port and to a may be defective.
TPE hub or the test will fail the
external loopback phase. If the
tpe-link-test? parameter is
false (disabled), the external
loopback test will appear to pass
even if a cable is not connected.
test net Performs an internal and external A cable must be attached to the Ethernet interface or cable
loopback test on the auto-selected system and to an Ethernet tap or may be defective.
system Ethernet interface. hub or the external loopback test
will fail.
test disk Tests internal or external SCSI The drive must be spinning Disk drive does not
test disk0 disks which have a self-diagnostic before this test is executed or the function properly.
test disk1 program contained in the drive test will fail. Enter a boot disk
test disk2 controller. alias command to cause the
test disk3 drive to spin up.
test cdrom Performs a self-test diagnostic on The CD-ROM must be set to CD-ROM does not respond
the CD-ROM drive. SCSI target 6 and have a CD to commands.
inserted in the caddy or the test
will fail.
test tape Tests the SCSI tape drive by Tape drive does not
test tape0 executing the drive self-test respond to commands.
test tape1 program. tape and tape 0 are
the first tape drive. tape 1 is the
second tape drive.
test ttya Outputs an alphanumeric test Attach a terminal to the serial Tests serial ports.
test ttyb pattern on the system serial ports port to observe the output.
(ttya = serial port A, ttyb = serial
port B).
test This test executes the keyboard Keyboard must be connected. See description.
keyboard self- test. The four LEDs on the
keyboard should flash on once,
and the message Keyboard
Present is displayed.
test-memory Tests all of the system main None. Memory (DSIMM) may
memory if the diag-switch? is have failed.
true. If diag-switch? is set to
false, it test the memory according
to the number specified in
selftest-#megs.
test-all Tests all devices in the system None. When a device driven by an
(such as SBus cards) which have a SBus card is not functioning
built-in test program. Hard disks, properly.
tapes, and
CD-ROMs are not tested.
watch-clock Displays seconds from the
system's Time of Day chip.
watch-net Monitors broadcast Ethernet Connect system to active Ethernet cable or
packets on the Ethernet cable(s) Ethernet. connections may have
connected to the system. failed.
watch-aui Monitors broadcast Ethernet Connect system to active Ethernet cable or
packets (10Base5 - Thicknet) on Ethernet. connections may have
the Ethernet cable(s) connected to failed.
the system.
watch-tpe Monitors broadcast Ethernet Connect system to active Ethernet cable or
packets (10BaseT - Twisted Pair Ethernet. connections may have
Ethernet) on the Ethernet cable(s) failed.
connected to the system.
watch-net- Monitors broadcast Ethernet Connect system and Ethernet When an SBus network
all packets on all Ethernet interfaces cards to active Ethernet. controller card is installed.
installed in the system, one at a
time.
probe-scsi Returns the SCSI devices (internal Connect SCSI devices to SCSI To determine if a SCSI
and external) and their SCSI port of the system. peripheral is talking to the
targets connected to the built-in system.
SCSI port.
To determine the SCSI
targets (addresses) of a SCSI
device.
To determine if more than
one SCSI peripheral is
assigned the same SCSI
address.
To determine if the built-in
SCSI controller is defective.
probe-scsi- Returns the SCSI devices and their Connect SCSI devices to SCSI See probe-scsi.
all SCSI targets connected to all SCSI port of the system.
port (both the built-in SCSI port To determine if a SCSI host
and any additional SCSI host adapter controller is
adapter cards). defective.
power-off Powers off the system. You must have a Type-5 To power off the system
keyboard in order to use this with a type 5 keyboard.
command.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Use the SunDiag system exerciser, which runs under the operating system, to determine real-time use of system resources and peripheral equipment.
SunDiag is shipped with the operating system. If SunDiag has been selected during the operating system loading procedure, it can be run at any time. SunDiag is located in the directory /usr/diag/sundiag (SunOS 4.1.3) or /opt/SUNWdiag/bin (SunOS 5.1 and later). If the SunDiag System Exerciser is not on the system hard disk or server, you can load it from CD-ROM. For more information, see the SunDiag User's Guide.
If SunDiag passes, the system is operating properly. If SunDiag fails, the error messages indicate the part of the system which has failed. If the error messages are not descriptive enough, you can run POST. See Chapter 3, "Power-On Self-Test (POST)."
The following restrictions apply if you run cg14test or sxtest, the S10BSX service code model VSIMM frame buffer tests. These restrictions are due to a conflict between the S10BSX service code model VSIMM frame buffer, which has its off-screen memory used by OpenWindows, and SunDiag frame buffer tests, which use a frame buffer locking scheme unknown to non-SunDiag application programs.
