Distinguished Name and Relative Distinguished Name
Directory information is hierarchical, with entries organized in a tree structure. Each entry has a parent entry and can have child entries. The top of the hierarchy is known as the root entry.
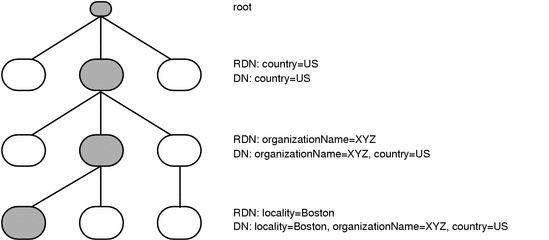
An entry is identified by its distinguished name (DN). A distinguished name is a sequence of attributes and values. The first attribute and its value provide the entry's relative distinguished name (RDN). The rest of the sequence is the distinguished name of the parent entry. A distinguished name is unique throughout the whole directory service.
Figure 1-1 shows an example of how directory information is structured, with the DNs and RDNs of the shaded entries.
Figure 1-1 Directory Information Structure
The attributes that can be part of a DN are called naming attributes. In the default schema provided with Sun Directory Services, the naming attributes are:
-
countryName, or c
-
localityName, or l
-
organizationName, or o
-
organizationalUnitName, or ou
-
commonName, or cn
-
channelName, or ch
-
domainComponent, or dc
-
stateOrProvinceName, or st
-
streetAddress, or street
-
uid
-
ref
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
