10.2 Configuration Guidelines for Sun Cluster HA for SAP
Consider these general guidelines when designing a Sun Cluster HA for SAP configuration:
-
SAP uses a large amount of memory and swap space. Consult the SAP documentation for memory and swap recommendations.
-
Be generous in estimating the total possible load on standby servers in case of failover. Allocate ample resources for CPU, swap, shared memory, and I/O bandwidth on the standby server, because in case of failover, the central instance and database instance might co-exist on the standby.
-
Limit physical and logical host names to eight characters or less, if possible.
10.2.1 Supported Configurations
See your Enterprise Services representative for the most current information about supported SAP versions. More information on each configuration type is provided in the following sections.
10.2.1.1 Two-Node Cluster With One Logical Host
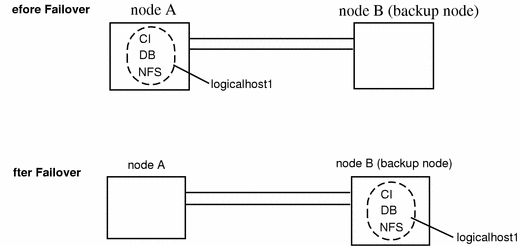
The simplest SAP cluster configuration is a two-node cluster with one logical host, as illustrated in Figure 10-1. In this asymmetric configuration, the SAP central instance and database instance (collectively called the central system), are both placed on one node. NFS is also be placed on the same node. This configuration is relatively easy to configure and administer. A drawback is that the backup node is underutilized. In case of failover, the central instance, database instance, and NFS service are switched to the backup node.
Figure 10-1 Asymmetric SAP Configuration
10.2.1.2 Two-Node Cluster With One Logical Host and Development or Test System
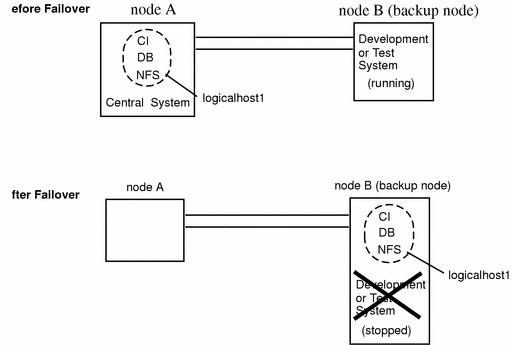
In this configuration, the central system (the central instance and database instance) is placed on one node and a development or test system is placed on a backup node. The development or test system remains running until a failover of the logical host moves the central system to the backup node. This scenario is illustrated in Figure 10-2. In this configuration, you must customize the Sun Cluster HA for SAP hasap_stop_all_instances script such that the development or test system is shut down before the SAP central instance is switched over and brought up. See the hasap_stop_all_instances(1M) man page and "10.2.4 Configuration Options for Application Servers and Test/Development Systems", for more information.
Figure 10-2 Asymmetric SAP Configuration with Development or Test System
10.2.1.3 Two-Node Cluster With One Logical Host, Application Servers, and Separate NFS Cluster
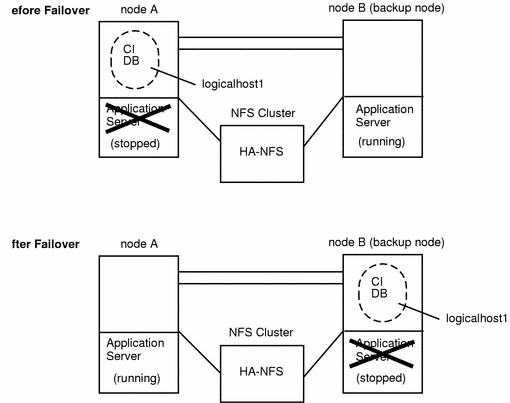
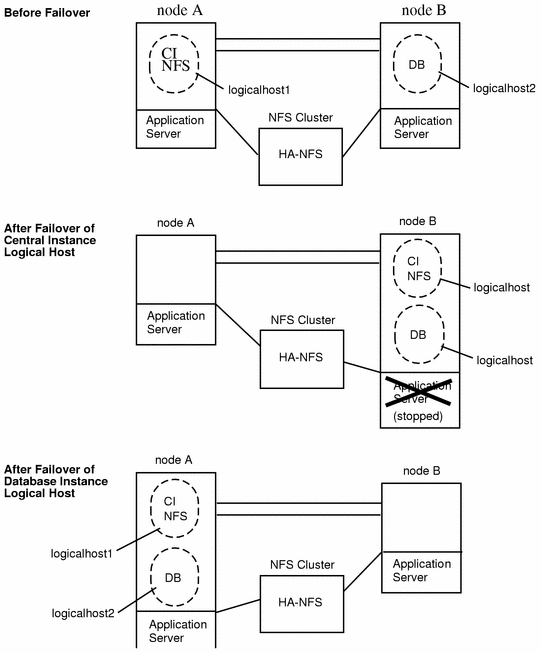
You can also place SAP application servers on one or both physical hosts. In this configuration, you must provide NFS services from a host outside the cluster. Set up the application servers to NFS-mount the file systems from the external NFS cluster, as illustrated in Figure 10-3. In case of failover, the logical host containing the central system (the central instance and database instance) switches to the backup node. The application servers do not migrate with the logical host, but are instead started or shut down depending on where the logical host is mastered. This prevents the application servers from competing for resources with the central instance and database.
NFS is protected by Sun Cluster HA for NFS. For more information, see "10.2.5 Sun Cluster HA for NFS Considerations".
Figure 10-3 Asymmetric SAP Configuration with Application Servers and External HA-NFS
10.2.1.4 Two-Node Cluster With Two Logical Hosts
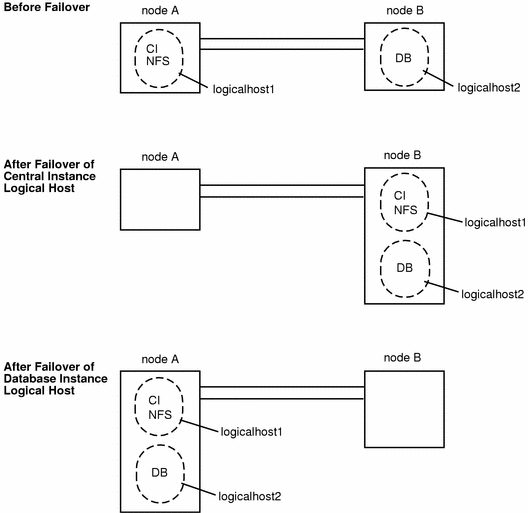
A two-node cluster with two logical hosts can be configured with the SAP central instance on one logical host and the SAP database instance on the other logical host, as illustrated in Figure 10-4. In this configuration, the nodes are load-balanced and both are utilized. In case of failover, the central instance or database instance is switched to the sibling node.
Figure 10-4 Symmetric SAP Configuration With Two Logical Hosts
10.2.1.5 Two-Node Cluster With Two Logical Hosts, Application Servers, and Separate NFS Cluster
A two-node cluster with two logical hosts can be configured with SAP application servers on one or both physical hosts. In this configuration, you must provide NFS services from a host outside the cluster. Set up the application servers to NFS-mount the file systems from the external NFS cluster, as illustrated in "10.2.2 Pre-Installation Considerations". In this case, both nodes are utilized and load-balanced.
In case of failover, the logical hosts switch over to the sibling node. The application servers do not fail over.
If the central instance logical host fails over, the application server can be shut down through the hasap_stop_all_instances script.
There are no customizable scripts to start and stop application servers in case of failover of the database logical host. If the database logical host fails over, the application servers cannot be shut down to release resources for the database logical host. Therefore, you must size your configuration to allow for the possible scenario in which the central instance, database instance, and application server are all running on the same node simultaneously.
In this configuration, NFS is protected by Sun Cluster HA for NFS. For more information, see "10.2.5 Sun Cluster HA for NFS Considerations".
Figure 10-5 Symmetric SAP Configuration With Two Logical Hosts and Application Servers
10.2.2 Pre-Installation Considerations
Before installing Sun Cluster with scinstall(1M), consider the following issues that apply to SAP configurations.
-
Use a logging file system:
-
If your volume manager is SSVM, use VxFS and Dirty Region Logging.
-
If your volume manager is Solstice DiskSuite, use either Solaris UFS logging or Solstice DiskSuite UFS logging.
-
-
Configure separate disk groups for SAP software and the database. The scinstall(1M) command cannot configure more than one disk group per logical host. Therefore, do not set up logical hosts with scinstall(1M) during initial cluster installation. Instead, set up logical hosts with scconf(1M), after the cluster is up. See the scconf(1M) man page for details.
-
Limit physical host names and logical host names to eight characters or less.
-
Do not configure any node to be an NFS client of another node within the same cluster.
-
(For SAP 4.0x with Oracle) On all potential masters of the central instance logical host, set aside space in /var/opt/oracle for the Oracle client binaries. Roughly 140 Mbytes is required. See your SAP documentation for details.
See also "10.2.5 Sun Cluster HA for NFS Considerations", and "10.4 Preparing the SAP Environment".
10.2.3 Sun Cluster Software Upgrade Considerations
Note these SAP-related issues before performing an upgrade to Sun Cluster 2.2 from HA 1.3 or Sun Cluster 2.1.
-
On each node, if you customized hasap_start_all_instances or hasap_stop_all_instances scripts in HA 1.3 or Sun Cluster 2.1, save them to a safe location before beginning the upgrade to Sun Cluster 2.2. Restore the scripts after completing the upgrade. Do this to prevent loss of your customizations when Sun Cluster 2.2 removes the old scripts.
-
The configuration parameters implemented in Sun Cluster 2.2 are different from those implemented in HA 1.3 and Sun Cluster 2.1. Therefore, after upgrading to Sun Cluster 2.2, you will have to re-configure Sun Cluster HA for SAP by running the hadsconfig(1M) command.
Before starting the upgrade, view the existing configuration and note the current configuration variables. For HA 1.3, use the hainetconfig(1M) command to view the configuration. For Sun Cluster 2.1, use the hadsconfig(1M) command to view the configuration. After upgrading to Sun Cluster 2.2, use the hadsconfig(1M) command to re-create the instance.
-
In Sun Cluster 2.2, the hareg -n command shuts down the entire Sun Cluster HA for SAP data service, including all instances and fault monitors. In previous releases, the hareg -n command, when used with Sun Cluster HA for SAP, shut down only the fault monitors.
Additionally, before turning on the Sun Cluster HA for SAP data service using hareg -y, you must stop the SAP central instance. Otherwise, the Sun Cluster HA for SAP data service will not be able to start and monitor the instance properly.
10.2.4 Configuration Options for Application Servers and Test/Development Systems
Conventionally you stop and restart the application server instances manually after the central instance is restarted. Sun Cluster HA for SAP provides hooks that are called whenever the central instance logical host switches over or fails over. These hooks are provided by calling the hasap_stop_all_instances and hasap_start_all_instances scripts. The scripts must be idempotent.
If you configure application servers and want to control them automatically when the logical host switches over or fails over, you can create start and stop scripts according to your needs. Sun Cluster provides sample scripts that can be copied and customized: /opt/SUNWcluster/ha/sap/hasap_stop_all_instances.sample and /opt/SUNWcluster/ha/sap/hasap_start_all_instances.sample. Customization examples are included in these scripts. Copy the sample scripts, rename them by removing the ".sample" suffix, and modify them as appropriate.
After failovers, Sun Cluster HA for SAP will invoke the customized scripts to restart the application servers. The scripts control the application servers from the central instance, and are invoked by the full path name.
If you include a test or development system in your configuration, modify the hasap_stop_all_instances script to stop the test or development system in case of failover of the central instance logical host.
During a central instance logical host switchover or failover, the scripts are called in the following sequence:
-
Stopping the application server instances and test or development systems by calling hasap_stop_all_instances
-
Stopping the central instance
-
Switching over the logical host(s) and disk group(s)
-
Calling hasap_stop_all_instances again to make sure all application servers and test or development systems have stopped
-
Starting the central instance
-
Starting the application server instances by calling hasap_start_all_instances
See the hasap_start_all_instances(1M) and hasap_start_all_instances(1M) man pages for more information
Additionally, you must enable root access to the SAP administrative account (<sapsid>adm) on all SAP application servers and test or development systems from all logical hosts and all physical hosts in the cluster. For test or development systems, also grant root access to the database administrative account (ora<sapsid>). Accomplish this by creating .rhosts files for these users. For example:
... phys-hahost1 root phys-hahost2 root phys-hahost3 root hahost1 root hahost2 root hahost3 root ... |
In configurations including several application servers or a test or development system, consider increasing the timeout value of the STOP_NET method for Sun Cluster HA for SAP. Increasing the STOP_NET timeout value is necessary only if the hasap_stop_all_instances script takes longer to execute than 60 seconds, because 60 seconds is the default timeout value for the STOP_NET method. If the hasap_stop_all_instances script does not finish within the 60 second timeout, then increase the STOP_NET timeout value.
Check the timeout value of the STOP_NET method by using the following command:
# hareg -q sap -T STOP_NET |
Note -
The hasap_dbms command can be used only when Sun Cluster HA for SAP is registered but is in the off state. Run the command on only one node, while that node is a member of the cluster. See the hasap_dbms(1M) man page for more information.
If the hasap_dbms(1M) command returns an error stating that it cannot add rows to or update the CCD, it might be because another cluster utility is also trying to update the CCD. If this occurs, re-run hasap_dbms(1M) until it runs successfully. After the hasap_dbms(1M) command runs successfully, verify that all necessary rows are included in the resulting CCD by running the command hareg -q sap.
If the hareg(1M) command returns an error, then first restore the original method timeouts by running the command hasap_dbms -f. Second, restore the default dependencies by running the command hasap_dbms -r. After both commands complete successfully, retry the original hasap_dbms(1M) command to configure new dependencies and method timeouts. See the hasap_dbms(1M) man page for more information.
Increase the STOP_NET timeout value by using the following command:
# /opt/SUNWcluster/ha/sap/hasap_dbms -t STOP_NET=new_timeout_value |
If you increase the STOP_NET method timeout value, you also must increase the timeouts that the Sun Cluster framework uses when remastering logical hosts during cluster reconfiguration. Use the scconf(1M) command to increase logical host timeout values. Refer to the section on configuring timeouts for cluster transition steps in the Sun Cluster 2.2 System Administration Guide for details about how to increase the timeouts for the cluster framework. Make sure that the loghost_timeout value is at least double the new STOP_NET timeout value.
10.2.5 Sun Cluster HA for NFS Considerations
If you have application servers outside the cluster, you must configure Sun Cluster HA for NFS on the central instance logical host. Application servers outside the cluster must NFS-mount the SAP profile directories and executable directories from the SAP central instance. See Chapter 11, Setting Up and Administering Sun Cluster HA for NFS, for detailed procedures on setting up Sun Cluster HA for NFS, and note the following SAP-specific guidelines:
-
Do not configure any node to be an NFS client of another node within the same cluster.
-
If you will run application servers within the cluster, you must set up an external cluster running NFS. The application servers and central instance will mount files from this NFS cluster.
-
There are start order dependencies among Sun Cluster HA for NFS, HA-DBMS, and Sun Cluster HA for SAP data services. You can use special scripts to manage these dependencies. See "10.7 Setting Data Service Dependencies for SAP", for more information.
-
Usually, you should share the following directories to all SAP instances:
-
/usr/sap/trans
-
/sapmnt/<SAPSID>/exe
-
/sapmnt/<SAPSID>/global
-
/sapmnt/<SAPSID>/profile
-
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
