| C User's Guide |
Introduction to the C Compiler
This chapter provides information about the C compiler, including operating environments, standards conformance, organization of the compiler, and C-related programming tools.
Standards Conformance
The compiler conforms to the American National Standard for Programming Language - C, ANSI/ISO 9899-1990. It also conforms to ISO/IEC 9899:1990, Programming Languages - C. Finally, this compiler conforms to FIPS 160. Because the compiler also supports traditional K&R C (Kernighan and Ritchie, or pre-ANSI C), it can ease your migration to ANSI/ISO C.
Organization of the Compiler
The C compilation system consists of a compiler, an assembler, and a link editor. The
cccommand invokes each of these components automatically unless you use command-line options to specify otherwise."cc Compiler Options" on page 37 discusses all the options available with
cc.The following figure shows the organization of the C compilation system.
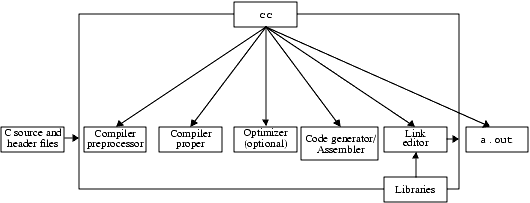
FIGURE 1-1 Organization of the C Compilation SystemThe following table summarizes the components of the compilation system.
The C compiler optimizer removes redundancies, optimally allocates registers, schedules instructions, and reorganizes code. Select from multiple levels of optimization to obtain the best balance between application speed and use of memory.
C-Related Programming Tools
There are a number of tools available to aid in developing, maintaining, and improving your C programs. The two most closely tied to C,
cscopeandlint, are described in this book. In addition, a man page exists for each of these tools. Refer to the preface of this book for a list of all the associated man pages.Sun WorkShop also provides tools for source browsing, debugging and performance analysis. See Related Documentation for more information.
|
Sun Microsystems, Inc. Copyright information. All rights reserved. Feedback |
Library | Contents | Previous | Next | Index |