ATM and SNMP
Two of the ATM standards supported by the SunATM software (the User Network Interface (UNI) and LAN Emulation (LANE) specifications) include definitions of SNMP-style Management Information Bases (MIBs) relevant to those standards. These MIBs are referred to as the ATM Forum (ATMF) and LAN Emulation (LANE) MIBs, respectively.
The ATM SNMP daemon (atmsnmpd) handles requests for information in both MIBs, as well as the system MIBs, from SNMP-based network management systems (such as the SunNet Manager program), and from ilmid, when it is required, for SNMP requests coming from the switch.
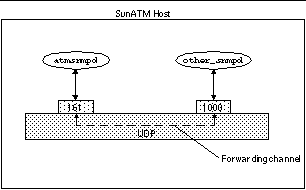
atmsnmpd can be used as a forwarding agent. If you configure it as a forwarding agent, atmsnmpd will forward SNMP requests for unknown MIBs to the port specified with the forward option, -f. This allows a system to have two SNMP agents respond to requests received over the SNMP port. Figure 6-1 illustrates the required configuration. To set up this example configuration, atmsnmpd must be started with the parameter -f 1000 and other_snmpd must be started so that it listens on port 1000.
Figure 6-1 Using atmsnmpd as a Forwarding Agent
Note -
If you do not specify a forwarding port for unknown requests, atmsnmpd will respond with a "No Such Name" error to requests for MIBs that it does not support. If you do specify a forwarding port, atmsnmpd instead forwards the request to that port. Responses received from the agent running on the forwarding port are sent to the requesting SNMP manager with no modification. If the agent does not respond, then atmsnmpd does not send a response back.
SNMP and Solaris
The ATM SNMP agent in SunATM supports a framework for SNMP agents; however, this means that its setup depends on the version of the Solaris operating environment in which it is running. This section discusses those differences, which are mostly transparent to the user.
Solaris 2.6, Solaris 7, and Solaris 8 Compatible Software
The Solaris 2.6, 7, and 8 operating environments include a bundled SNMP agent that is designed to run as a master agent, binding by default to UDP port 161. Configure other agents to listen to other UDP ports and act as subagents, then configure the master agent to forward particular requests to those subagents. This framework provides a single agent at port 161 with the combined capabilities of the master agent and all the additional subagents.
The SunATM software has been designed to take advantage of this framework if it is installed on a system running Solaris 2.6, 7, or 8. The files necessary for the ATM SNMP agent to be recognized by the master agent (atm.reg and atm.rsrc) are copied under /etc/snmp/conf by the S00sunatm startup script if it detects that the system is running Solaris 2.6, 7, or 8. SNMP requests pertaining to the ATM Forum subtree (atmForum) are forwarded to the atmsnmpd from the master agent. In addition, atmsnmpd binds, by default, to port 1000, rather than 161, under Solaris 2.6 or later. The UDP port may still be changed using atmadmin, but the default will be 1000 in Solaris 2.6, 7, or 8.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
