| C H A P T E R 9 |
|
Expert3D and Expert3D-Lite Graphics Accelerator |
This chapter describes how to change the Sun Expert3D and Expert3D-Lite graphics accelerators screen resolutions to work properly with different monitors. It also describes the internal and external connectors and their use.
The Expert3D graphics accelerator is a high-resolution, high-performance graphics frame buffer that provides hardware texture mapping. The Expert3D system only, supports screen resolutions up to 1920 x 1200, double-buffered,
z-buffered, and 1280 x 1024 stereo.
|
Note - ifb is the UNIX device name for the Expert3D and Expert3D-Lite graphics accelerators. |
Two configuration utilities are available for the Expert3D and Expert3D-Lite graphics accelerators: fbconfig and SUNWifb_config. References to Expert3D also applies to Expert3D-Lite.
The fbconfig utility is a generic command line interface to query and configure frame buffer attributes. fbconfig works with the Creator3D and Elite3D graphics accelerators, in addition to the Expert3D.
The fbconfig utility can be used to do the following:
For more information on fbconfig, see the fbconfig man page.
The SUNWifb_config utility is specific to Expert3D; it cannot be used with any other frame buffers. You can use the SUNWifb_config utility to:
For more information, see the SUNWifb_config man page.
For most installations, the Expert3D automatically configures itself to the proper screen resolution and refresh rate for the attached monitor. However, if a non-Sun monitor is attached to the Expert3D, the monitor may not have the proper screen resolution.
TABLE 9-1 lists the default screen resolutions by monitor sense code.
If the Expert3D system is unable to determine the monitor type, such as for non-Sun monitors, it defaults to a resolution of 1152 x 900 at 66 Hz.
TABLE 9-2 lists the Expert3D-supported screen resolutions. The fbconfig or SUNWifb_config utilities can be used to set the Expert3D system to any one of these resolutions.
|
|
 Use the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
Use the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
SUNWifb_config -res \? |
You can change the screen resolution temporarily as a test to determine if the monitor supports the specified resolution.
|
Caution - Do not change screen resolution while the window system is running. Changing screen resolution while the window system is running may put the screen display in an unusable state. |
 Use the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
Use the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
SUNWifb_config -res video-mode try |
See TABLE 9-2 for the list of video-mode options (see the "Video Mode Format" and "Symbolic Name" columns in the table). You will have five seconds to confirm the video mode by typing y.
SUNWifb_config -res stereo |
This changes the resolution to 960 x 680 at 112 Hz stereo the next time Xsun is run.
The X server screen visuals list can be altered through SUNWifb_config. The SUNWifb_config options in TABLE 9-3 can be used to configure the list of the exported visuals for the specified device.
By default, the nonlinear visual comes before the linear visual on the screen visual list. You can modify the order of the visual list by using the SUNWifb_config command.
Most 3D applications require a linear visual. Some 3D applications do not search for a linear visual using XSolarisGetVisualGamma(3). Instead, these applications search the screen visual list for the first 24-bit TrueColor visual they find. To enable these applications to run with the correct visual, use the -linearorder option to change the visual list order so that the linear 24-bit TrueColor visual is the first one the application finds.
The desired visual ordering in the screen visuals list will be available whenever the window system is restarted.
 To change the setting, enter the SUNWifb_config command with one of the
To change the setting, enter the SUNWifb_config command with one of the
-linearorder options.
SUNWifb_config -linearorder first |
By default, the 8-bit PseudoColor visual comes before the 8-bit PseudoColor Overlay visual on the screen visual list. You can modify the order of the visual list by using the SUNWifb_config command.
Some applications that use the 8-bit PseudoColor Overlay visual, search the visual list for the first 8-bit PseudoColor visual they find. To enable these applications to run with the correct visual, use the -overlayorder option to change the visual list order so that the 8-bit PseudoColor Overlay visual is the first 8-bit PseudoColor visual the application finds.
The desired visual ordering in the screen visuals list will be available whenever the window system is restarted.
 To change the setting, enter the SUNWifb_config command with one of the
To change the setting, enter the SUNWifb_config command with one of the
-overlayorder options.
SUNWifb_config -overlayorder first |
By default, the 8-bit PseudoColor underlay visual is the default visual of the screen. The default visual can be changed to either a linear underlay visual or an overlay visual through SUNWifb_config.
 To set the default visual to be a linear visual, enter the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
To set the default visual to be a linear visual, enter the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
SUNWifb_config -deflinear true |
 To set the default visual to be an overlay visual, enter the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
To set the default visual to be an overlay visual, enter the SUNWifb_config command as follows:
SUNWifb_config -defoverlay true |
|
Caution - Since there is no linear overlay visual, the user should not specify both "-deflinear true" and "-defoverlay true" simultaneously, or the result will be undefined. |
Solaris supports the OpenGL visual expansion. With visual expansion, five visual groups: the 8-bit PseudoColor, 24-bit TrueColor (Linear and Non-Linear), 24-bit DirectColor, and 8-bit PseudoColor Overlay, are expanded from a single visual to multiple visual instances of the same visual type. Different instances of the same visual groups represent different GLX capabilities (e.g. single-buffer or double-buffer capable, monoscopic or stereoscopic capable, or a combination of both). The number of visual instances depends on whether the X server is started in monoscopic or stereoscopic mode.
SUNWifb_config -expvis enable |
SERVER_OVERLAY_VISUALS is one of the root window's properties that contains the visual ID, transparent type, transparent value, and layer of the server overlay visuals (SOV) of the screen. You can toggle the advertisement of this property and the export of the transparent server overlay visuals using SUNWifb_config.
SUNWifb_config -sov enable |
Gamma correction may be set by specifying a gamma correction value or by specifying a file that contains a gamma table.
The -g option will set the gamma table entries based on the gamma value specified. A gamma value of 2.22 represents linear gamma correction and matches the fixed value on the Expert3D system. This value is a per-screen value and therefore all gamma corrected or linear visuals will use this value.
SUNWifb_config -g 2.22 |
The -gfile option will set the gamma table entries explicitly from a file containing three columns of 256 integers ranging from 0 to 255. The format is three integers separated by a newline character. Each line contains the RGB value to be put in the table for that entry. This value is a per-screen value and therefore all gamma-corrected or linear visuals will use this value.
SUNWifb_config -gfile filename |
Enabling the extended overlay option will switch the Expert3D system to the extended overlay functionality. The extended overlay mode enables full 256-color overlays and hardware-accelerated Server Overlay Visuals. The maximum number of underlay Window IDs (WIDs) is increased from 32 to 64 and three new overlay WIDs are provided.
SUNWifb_config -extovl enable |
To run more than one frame buffer, you need to modify your /etc/config/Xservers file. The Expert3D device is identified as ifbx (for example, ifb0 and ifb1 for two Expert3D devices. To do this:
1. Become superuser and open the /etc/dt/config/Xservers file.
# cd /etc/dt/config # vi Xservers |
2. Modify the file by adding the device locations for the applicable frame buffers being used.
The following example shows the Xservers configuration file modified for one Creator card and two Expert3D cards:
:0 Local local_uid@console root /usr/openwin/bin/Xsun :0 -dev /dev/fbs/ffb0 -dev /dev/fbs/ifb1 -dev /dev/fbs/ifb0 -nobanner |
See Multiview Ports for information on configuring multiple Expert3D cards in a single system.
On a multiple-monitor system, you may wish to define which of the monitors is your default console. To make your Expert3D card be the default console displa
1. At the OpenBoot prompt, type the following:
ok show_displays |
The Expert3D system will output a list of the available frame buffers, similar to the following:
a) /PCI@@l1, 2000/SUNW,Expert3D@1 b) /PCI@@l5, 2000/SUNW,afb@1 q) NO SELECTION |
The Expert3D-Lite system will output a list of the available frame buffers, similar to the following:
2. Select the option for the device you want to use as the console.
In the above example, you would select option a if you want to make the Expert3D device be the console.
3. Set this device to be the console device.
At the OpenBoot prompt, enter the following:
ok setenv output-device <Control-Y> <ENTER> ok reset |
You can also create an alias for the Expert3D system to simplify future OpenBoot commands. After running the show-displays command and choosing the Expert3D device from the menu, type the following:
ok nvalias screen1 <Control-Y> ok nvstore |
To verify that this alias is correctly set, type the following:
ok devaliases |
You can then refer to screen1 for the Expert3D device. For example:
ok setenv output-device screen1 |
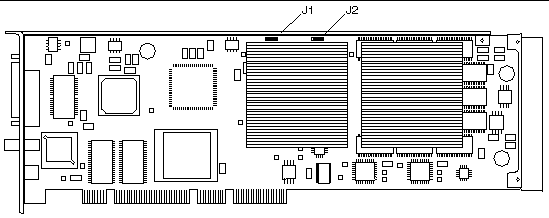
The internal Multiview In and Multiview Out ports on the Expert3D card, shown as J1 and J2 in FIGURE 9-1, are used for cable connections from one Expert3D card to another. These ports are accessible only inside the system chassis.
You can frame lock only two Expert3D cards for multiviewing. When two Expert3D cards are used in a multiviewing configuration, one of the cards is designated as the master and the other as the slave.
To configure two Expert3D cards for multiviewing through frame locking:
1. Select an Expert3D card to designate as the master for the system.
One solution for designating an Expert3D to be the master is to use the Expert3D card that serves as the boot/console head for the system.
2. Make sure that each Expert3D card installed has the same screen resolution as the Expert3D in the master mode.
If the resolution on each Expert3D card is not the same, you must change it to match the Expert3D in master mode.
To check the resolution of an Expert3D card, use the SUNWifb_config utility. For example:
% SUNWifb_config -dev /dev/fbs/ifb0 -prconf |
You must repeat this command for each Expert3D card in the system.
The SUNWifb_config utility displays the current screen resolution setting. It also displays additional information, such as whether the Expert3D card is a master or a slave.
If you need to change the resolution of an Expert3D card, use the SUNWifb_config utility. For example:
% SUNWifb_config -dev /dev/fbs/ifb1 -res 1280x1024x76 now nocheck |
3. Connect the frame lock multiview cable to each Expert3D card.
See FIGURE 9-1.
a. Connect the top of the multiview frame lock cable assembly to the Multiview-out J2 connector of the master Expert3D card.
b. Connect the other end of the multiview frame lock cable to the Multiview-in J1 connector of the slave Expert3D card.
4. From the master Expert3D card display window, configure the other Expert3D card in slave mode.
To do this, use the SUNWifb_config utility.
% SUNWifb_config -dev /dev/fbs/ifb1 -slave on |
You must configure each card separately.
Your system is now ready for frame lock and buffer swap synchronization software applications.
To reconfigure your Expert3D card from slave mode back to master mode, do one of the following:
Copyright © 2002, Sun Microsystems, Inc. All rights reserved.