|
|
| Sun ONE Application Server 7, Update 1 Administrator's Guide |
Setting Administration Server PreferencesThe Administration Server is a special instance of the Sun ONE Application Server that serves the Administration interface and provides administrative facilities for the Administration interface and the command-line interface. It manages the configuration, deployment, and monitoring facilities for the Sun ONE Application Server. This module explains how to configure the Administration Server.
This module includes the following topics:
- About the Administration Server
- Starting the Administration Server
- Shutting Down the Administration Server
- Accessing the Administration Server Settings
- Viewing Administration Server Control Settings
- Applying Changes to the Administration Server
- Editing HTTP Listener Settings for the Administration Server
- Setting SNMP, Logging, and Security Preferences
About the Administration Server
The Administration Server is a special instance of the Sun ONE Application Server that provides administrative facilities for the Administration interface and the command-line interface. It manages the configuration, deployment, and monitoring facilities for these interfaces. It serves the Administration interface pages. It must be running in order for you to use the Administration interface and to run most commands in the command-line interface.
An Administration Server is installed when you install the Sun ONE Application Server (unbundled version) or create a new domain. You can only have one Administration Server per domain, though you may create multiple Sun ONE Application Server instances that are managed by an Administration Server. You can access configuration settings, deployed applications, and other server features for each application server instance by using the Administration Server.
For more information on administrative domains, see "Configuring Administrative Domains."
If you are using the unbundled Sun ONE Application Server, when you installed the Sun ONE Application Server you chose a port number for the Administration Server, or used the default port of 4848.
If you are using the Solaris 9 bundled Sun ONE Application Server, you must create a domain and an Administration Server manually. For more information on configuring the Solaris 9 bundled version, see "Configuring the Bundled Solaris Version".
To access the Administration interface, in a web browser type:
http://hostname.domain:port/
Note that domain here is not your Sun ONE Application Server administrative domain, but your domain name.
For example:
http://austen.sun.com:4848/
If you are accessing the Administration Server from the same machine you installed Sun ONE Application Server on, you can use:
http://localhost:4848
You are prompted for a user name and password.
Starting the Administration Server
To start or restart the Administration Server, use one of the methods described in the following topics:
- Using the startserv Script
- Using the Command-Line Interface
- Using the Services Window (Windows)
- Using the Start Menu (Windows)
Using the startserv Script
To start the Administration Server using the start script, log in as root if the server runs on ports with numbers lower than 1024 (UNIX); otherwise, log in as root or with the server's user account. At the command-line prompt go to the directory:
install_dir/domains/domain_dir/admin-server/bin
where install_dir is the directory where you installed the server, and domain_dir is the administrative domain directory.
For UNIX, type:
./startserv
You can use the optional parameter -i at the end of the line. The server normally runs as a background process. The -i option prevents the server from putting itself in the background. This option is useful if you are running the server using /etc/inittab.
For Windows, run the startserv.bat file.
Using the Command-Line Interface
The command-line interface's asadmin utility has a command start-domain that you can use to start your Application Server and all associated Sun ONE Application Server instances. You can only run this command locally, that is, from the machine where your Sun ONE Application Server is installed. This command requires no arguments.
You can also use the command start-domain to start all instances within an administrative domain. It uses the syntax:
asadmin start-domain [--domain domain-name]
For more information on using the command-line interface, see the online help for the command-line interface and "Using the Command Line Interface."
Using the Services Window (Windows)
To start the server by using the Services Control Panel in Windows, follow these steps:
- In the Control Panel click Administrative Tools.
- Click Services.
- Scroll through the list of services and double-click the Application Server 7.0 Administration Server service.
Select the Administration Server for the given domain. The Name column in the Services window displays the name of an Administration Server as Sun App Server Admin Server (your_domain_name:admin-server).
- Click Start.
- Click OK.
The Application Server 7.0 Administration Server service starts automatically when you start your computer.
Using the Start Menu (Windows)
To start the server by using the Windows Start menu, follow these steps:
- From the Start menu, choose Programs.
- Choose Sun Microsystems.
- Choose Sun ONE Application Server 7
- Click Start Application Server.
Shutting Down the Administration Server
Once the Administration Server is started it runs constantly, listening for and accepting requests. You might want to stop and restart your server if, for instance, you change the Administration Server logging preferences or the port that the Administration Server's HTTP Listener listens on.
When you stop the Administration Server, it stops accepting new connections. Then it waits for all outstanding connections to complete. While the Administration Server is stopped, you cannot use the Administration interface or command-line interface.
You can stop the server using one the methods described in the following topics:
- Shutting Down Using the Administration Interface
- Shutting Down Using the stopserv Script
- Shutting Down Using the Command-Line Interface
- Shutting Down Using the Services Window (Windows)
After you shut down the server, it may take a few seconds for the server to complete its shut-down process.
Shutting Down Using the Administration Interface
To shut down the Administration Server using the Administration interface, follow these steps:
- In the left pane, click Admin Server.
- Click the Control tab.
- Click Stop.
The Administration Server shuts down immediately when you click this link. There is no additional screen.
Shutting Down Using the stopserv Script
To stop the Administration Server manually, at the command prompt go to the directory:
install_dir/domains/domain_dir/admin-server/bin
where install_dir is the directory where you installed the server and domain_dir is the domain directory.
For UNIX, type:
./stopserv
You must run this command as the user that is running the server.
If you used the */etc*/inittab file to restart the server you must remove the line starting the server from */etc*/inittab and type kill -1 before you try to stop the server. Otherwise, the server restarts automatically after it is stopped.
For Windows, run the stopserv.bat file.
Shutting Down Using the Command-Line Interface
You can stop the Administration Server using the command-line interface asadmin utility's shutdown command. This command requires no arguments and can be run either locally or remotely.
You can also stop the Administration Server and all the associated Sun ONE Application Server instances using the command-line interface asadmin utility's stop-appserv command. You can only run this command locally, that is, from the machine where your Sun ONE Application Server is installed. This command requires no arguments.
You can also shut down the Administration Server by shutting down the domain using the stop-domain command. This command shuts down all instances in the domain, including the Administration Server, by default. You can also configure it to shut down all instances in the domain except the Administration Server. This command has the following syntax:
asadmin stop-domain [--user admin_user] [--password admin_password] [--host admin_host] [--port admin_port] [--local=true/false] [--domain domain_name] [--adminserv=true/false] [--passwordfile file_name] [--secure | -s]
If you use the local option, the command runs locally. If you use the --adminserv=false option, the command will not stop the Administration Server. However, --adminserv is set to true by default, so the Administration Server is stopped by default.
For more information on using the command-line interface, see the online help for the command-line interface and "Using the Command Line Interface."
Shutting Down Using the Services Window (Windows)
To shut down the Administration Server using the Services window, follow these steps:
- In the Control Panel click Administrative Tools.
- Click Services.
- Scroll through the list of services and double-click the Sun Application Server 7 Admin Server service.
- Click Stop.
- Click OK.
Accessing the Administration Server Settings
To access the Administration Server settings, in the left pane of the Administration interface click Admin Server. The settings for the Administration Server appear in the right pane, organized by a set of tabs.
Administration Server User Interface
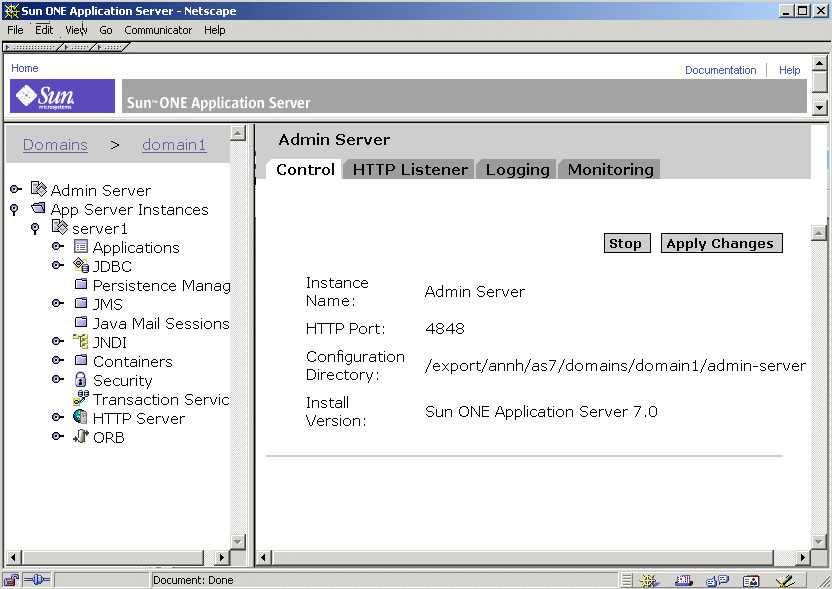
Click a tab to access the settings for a particular functional area. Sometimes clicking a tab takes you directly to a page, and sometimes clicking a tab gives you a list of pages to choose from.
This module covers the Control and HTTP Listener tabs. For information on Monitoring and SNMP settings, see "Monitoring the Sun ONE Application Server." For information on logging, see "Using Logging."
Viewing Administration Server Control Settings
The Administration Server control settings show the instance name (Admin Server), what port your Administration Server runs on, what directory contains the configuration files, and what version of the Sun ONE Application Server software you are running.
To view these settings:
- In the left pane, click Admin Server.
- Click the Control tab.
Applying Changes to the Administration Server
When you change the Administration Server's configuration information using the Administration interface or the command line interface you may need to apply your changes in order for your changes to take effect. This is also called reconfiguring the server. When you apply your changes, all changes made to the configuration since the last time you applied changes take effect.
If you've made changes to the Administration Server's configuration that require you to apply changes, a yellow icon appears next to the Admin Server in the left pane's tree view.
Warning Icon

To apply configuration changes:
- In the left pane, click Admin Server.
- Click the Control tab.
- Click Apply Changes.
When the changes are applied, the screen displays a message.
Editing HTTP Listener Settings for the Administration Server
Before the server can process a request, it must accept the request via an HTTP listener.
With the unbundled version of the Sun ONE Application Server, an HTTP listener for the Administration Server, http-listener-1, is created automatically when you install. This HTTP listener uses the IP address 0.0.0.0 and the port number you specified as your Administration Server port number during installation. The default is 4848. You cannot delete the default HTTP listener.
For an administrative server instance (in a domain), only the HTTP listener has the http-listener-1 id. Another words, if you create an administration server instance, only one HTTP listener can act in either HTTP or HTTPS protocol at any point in time. (It also means that you cannot have both HTTP and HTTPS connections to an administration server simultaneously.) For more information about configuring the Solaris 9 bundled version, see "Configuring the Bundled Solaris Version".
The HTTP listener is where you activate and configure SSL/TLS security settings for your Administration Server.
In addition, you specify the number of acceptor threads (sometimes called accept threads) in the HTTP listener. Accept threads are threads that wait for connections. The threads accept connections and put them in a queue where they are then picked up by worker threads. Ideally, you want to have enough accept threads so that there is always one available when a new request comes in, but few enough so that they do not provide too much of a burden on the system. The default is 1. A good rule is to have one accept thread per CPU on your system. You can adjust this value if you find performance suffering. For more information on performance, see the Sun ONE Application Server Performance Tuning and Sizing Guide.
To edit your Administration Server's HTTP listener settings:
- In the left pane, click Admin Server.
- Click the HTTP Listeners tab.
- Make the desired changes and click OK.
For more information on HTTP listeners, see the online help.
Setting SNMP, Logging, and Security Preferences
For information on SNMP settings, see "Monitoring the Sun ONE Application Server." For information on logging, see "Using Logging." For information on security settings, see the Sun ONE Application Server Administrator's Guide to Security.