Chapter 9 Examples of End-to-End Solution Deployment
This chapter provides examples of installing Sun OTP using GUI installation and command-line installation.
The following topics are discussed:
Prerequisites for Sun OTP Installation
The following table describes the prerequisites that you must meet before installing Sun OTP.
Table 9–1 Prerequisites for Sun OTP Installation|
Tasks |
Documentation |
|---|---|
|
Determine the system requirements of Sun OTP hosts. Upgrade firmware and install patches on Sun OTP host if required. All Sun OTP hosts and storage devices must meet the minimum patch and firmware requirements. | |
|
Set up a naming service such as DNS, NIS, NIS+, or /etc/hosts and all host names and IP addresses must be set up on that naming service. |
System Administration Guide: Naming and Directory Services (DNS, NIS, and LDAP) |
|
Install Solaris 10 Update 3 OS on the Sun OTP provisioning server and on each Sun OTP host. | |
|
Prepare the Sun OTP hosts for Sun OTP installation. | |
|
Set up the self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server. | |
|
Prepare the Sun OTP host plan worksheet. Plan information includes items such as logical host names, IP addresses for each Sun OTP host, the clustered Sun OTP system name, IPMP options, zone information, and more. Using the worksheets will assist you during installation and configuration, and reduce the chance for errors. |
Prerequisite Tasks for Sun OTP Installation
The following prerequisite tasks must be met before you install Sun OTP.
 To Install Solaris OS from the Bootable DVD
To Install Solaris OS from the Bootable DVD
-
Install Solaris OS from the bootable OTP DVD.
Refer to Solaris 10 11/06 Installation Guide: Basic Installations or Solaris 10 11/06 Installation Guide: Solaris Flash Archives (Creation and Installation) for more information.
-
On SPARC systems
-
Insert the bootable Sun OTP DVD.
Note –The bootable DVD for SPARC contains the hybrid flash image that can be used for deploying the sun4v and sun4u hardware architecture platforms.
-
Start the installation from the bootable DVD by typing the following command:
boot cdrom
This will prompt you for an interactive Solaris installation.
-
Respond to the system identification and configuration screens.
-
From the Solaris Interactive Installation screen, select F4_Flash install.
-
From the Flash Archive Retrieval Method screen, place the X symbol on Local File and press F2_Continue.
-
From the Flash Archive Addition screen, provide the /cdrom/Solaris_10/otp_sparc.flarc path and then press F2_Continue.
Continue to respond to the remaining screens until the installation starts and completes.
-
When the system reboots, insert the installation DVD.
-
-
On x64 systems
 Caution –
Caution – Installation does not ask for the partitioning or image name. The first disk is chosen automatically and OTP default disk formatting is applied. The existing data, if any, is overwritten.
-
 To Prepare the Sun OTP Hosts
To Prepare the Sun OTP Hosts
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the Sun OTP host.
-
Install the remote agent on the Sun OTP host.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/setupRemoteAgent -c RAW|SSH mediadir
mediadir is the fully qualified path name to the Open Telecommunications Platform installation source directory. The media directory is the path where the installation DVD is mounted.
Repeat this step on each Sun OTP host. All the remote agents on the cluster must use the same connection type (SSH or RAW).
-
(Applicable for SSH connection type) Configure SSH for the remote agent.
-
(Applicable for SSH connection type) Initialize the SSH keys.
-
Log in as spsotp user (su - spsotp) to the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Append the ssh public key of spsotp user from the Sun OTP provisioning server to authorized ssh keys located in the home directory of n1spsotp user on each Sun OTP host.
cat /var/otp/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh n1spsotp@hostname "tee >> /export/home/n1spsotp/.ssh/authorized_keys2"
hostname is the host name of Sun OTP host.
-
 To Set up the Self-Contained Sun OTP Provisioning Server
To Set up the Self-Contained Sun OTP Provisioning Server
Self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server is installed on the first host of the cluster.
Self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server uses a specific logical host name and IP address defined at the beginning of the Sun OTP installation. However, to make Sun OTP application provisioning service highly available, the server is moved to a different logical host name (logical host name for management and provisioning services) at the end of “Configure Components as Highly Available Services” plan. After “Configure Components as Highly Available Services” plan is finished, this new logical host name has to be used to access the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the first host of the cluster.
-
Add the logical host name and the logical IP address to the /etc/hosts file.
This logical host name and the logical IP address is used in the next step to set up the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Set up the Sun OTP provisioning server in the first host of the cluster.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/setupExternalInstallServer -M mediadir -N nodetype -R RAW|SSH -P passwordfile -L logicalhost -I logicalip
mediadir is the fully qualified path name to the Open Telecommunications Platform installation source directory. The media directory is the path where the installation DVD is mounted.
nodetype can either be single (for stand-alone deployments) or first (for clustered deployments).
-R is the connection type between Sun OTP application provisioning service master server and the remote agent. RAW and SSH are the possible connection types between Sun OTP application provisioning service master server and the remote agent.
logicalhost and logicalip are unused logical host names and logical IP addresses.
passwordfile is the absolute path of the password file. You can create this file in your home directory. The password file must contain a line with a valid password for the Sun OTP provisioning server. The password can be 8 to 12 alphanumeric characters.
Note –Once you set up the Sun OTP provisioning server with this password, the user name to access the Sun OTP provisioning server is otpadmin and the password is the password in the password file.
The password specified in this step and the password that will be specified during the Setup Configuration plan must be the same.
Installing Sun OTP Using GUI Installation
This section describes Sun OTP installation on a clustered system using the GUI installation method.
Note –
Sun OTP can also be installed on a stand-alone system with logical domains. In this configuration, all the Sun OTP components are deployed inside a logical domain. This logical domain must be created before installing Sun OTP.
The following topics are discussed:
 To Install Sun OTP on a Clustered System
To Install Sun OTP on a Clustered System
-
It is recommended that the shared storage is configured to provide redundancy of shared disks using hardware RAID (RAID1 or RAID5).
-
If the above feature is not available in the storage, it is recommended to use software RAID (RAID1 or RAID5) for shared storage provided by Solaris Volume Manager. See Solaris Volume Manager Administration Guide for more information. In this case, the shared storage needs to be set up manually.
-
In this procedure, the cluster host set refers to all the Sun OTP hosts in the cluster and the additional cluster host set refers to all the additional Sun OTP hosts in the cluster except the first Sun OTP host.
Before You Begin
Make sure that you complete the tasks described in Prerequisite Tasks for Sun OTP Installation.
-
Open a browser and log in to the Sun OTP application provisioning service on the Sun OTP provisioning server.
Go to the URL https://install server:9090 where install server is the IP address or the fully-qualified name of the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Type the user name and password.
The user name is otpadmin. The password is the password provided in the password file while setting up the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Add Sun OTP hosts to the Sun OTP provisioning server. Repeat this step on each Sun OTP host.
-
Click Host Setup in the left menu to display the Host Setup page.
-
Click hosts in the central menu to display the hosts page.
-
In the host field, type the name of the new Sun OTP host.
-
(Optional) In the description field, type a description of the new Sun OTP host.
-
Click create.
The host details edit page is displayed.
-
To include the remote agent, select the include remote agent on this physical host check box.
-
Choose SSH (encrypted) or RAW from the connection type drop-down list.
SSH (encrypted) is the recommended value.
-
Type the host name in the ip address or name field.
-
Type the appropriate entry according to the connection type.
Figure 9–1 Add OTP Hosts to the Provisioning Server Screen
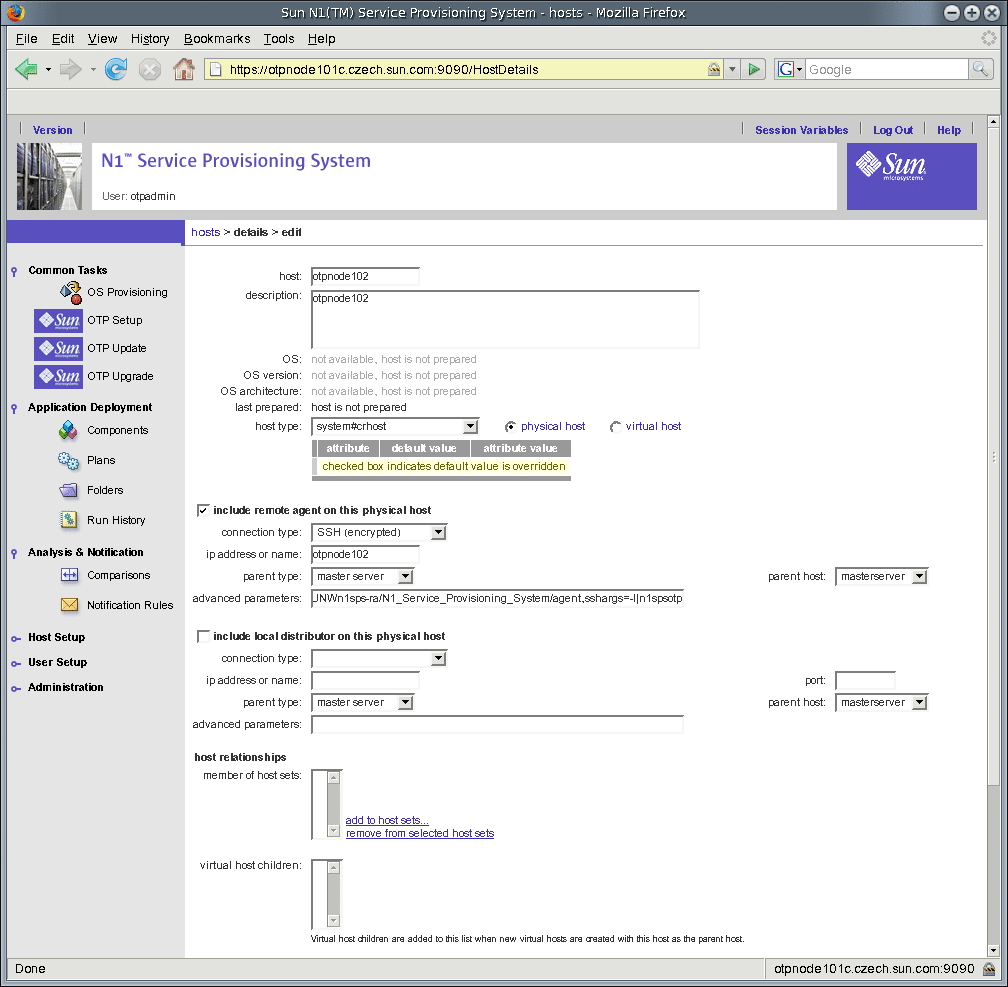
-
Click add to host sets.
-
Select com.sun.solaris#SolarisHostSet from the add host sets drop-down list.
-
Click add host to selected host sets.
-
Scroll to the bottom of the page and click save.
The host preparation is in progress and Sun OTP host is added to the hosts list on the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
In the hosts page, click the name of the host that is added.
-
Click update remote agent.
-
After successful update, click prepare remote agent.
The host is prepared for provisioning.
-
-
(Optional but recommended) Create host sets.
It is recommended to create two host sets. One host set will contain all the Sun OTP additional hosts in the cluster and the other host set will contain the previously created host set and the first cluster host.
-
Click Host Setup.
-
Click host sets to display the host sets page.
-
Click create.
-
Type the name of the host set in the host set field.
-
Click select from list.
-
Select the hosts that you want to add to the host set.
Note –Select only the Sun OTP host names and not the zone host names.
-
Click add hosts to main window.
-
Click add host.
-
Click save.
-
-
Click OTP Setup to display the Sun Open Telecommunications Platform installation steps page.
-
Configure Sun OTP installation plan variables. Repeat this step on each Sun OTP host.
-
Click Setup Configuration and click run.
The SetupConfig screen appears.
-
Type the host name on which you want to install Sun OTP in the target host field.
-
Enter the password for the otpadmin user in the Enter otpadmin password field.
-
Confirm the password in the Confirm otpadmin password field.
-
Click select from list under variable settings.
The select variable setting from list... screen appears.
-
At the bottom of the select variable setting from list... screen, click create set to create a new variable set.
-
Type a new variable set name in the Set Name field.
-
Click the check boxes for the appropriate plan variables for which you want to enter the values.
Figure 9–2 Configure OTP Plan Variables Screen
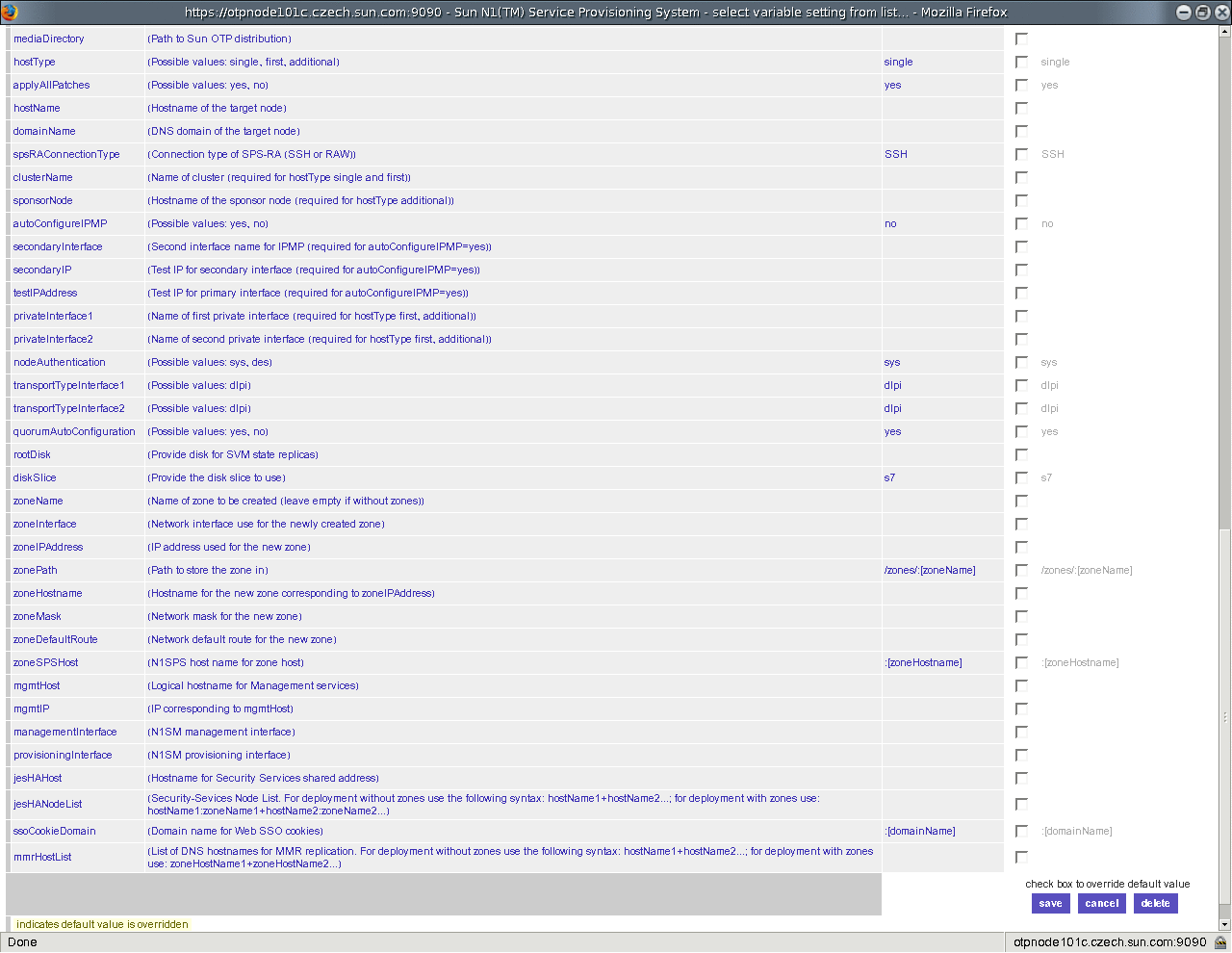
-
Type the values for the appropriate plan variables in the text fields. Refer to Appendix A, Sun OTP Plan Worksheet to determine the values for these variables.
-
Click save to save the variable set.
-
Close the select variable setting from list... screen.
-
In the SetupConfig screen, click the drop-down list under variable settings, and choose the new variable set.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
-
-
Install the OS patches on the additional Sun OTP hosts.
-
Install the OS patches on the first Sun OTP host.
-
Click Patch and click run.
The Patch screen appears.
-
Type the first Sun OTP host name in the target host field.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
When the plan completes, wait for the first Sun OTP host to boot into multi-user mode.
-
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP high availability service on the first Sun OTP host.
-
Click Install Availability Service and click run.
The InstallAvailability1 screen appears.
-
Type the first Sun OTP host name in the target host field.
Figure 9–3 Install Availability Service Screen
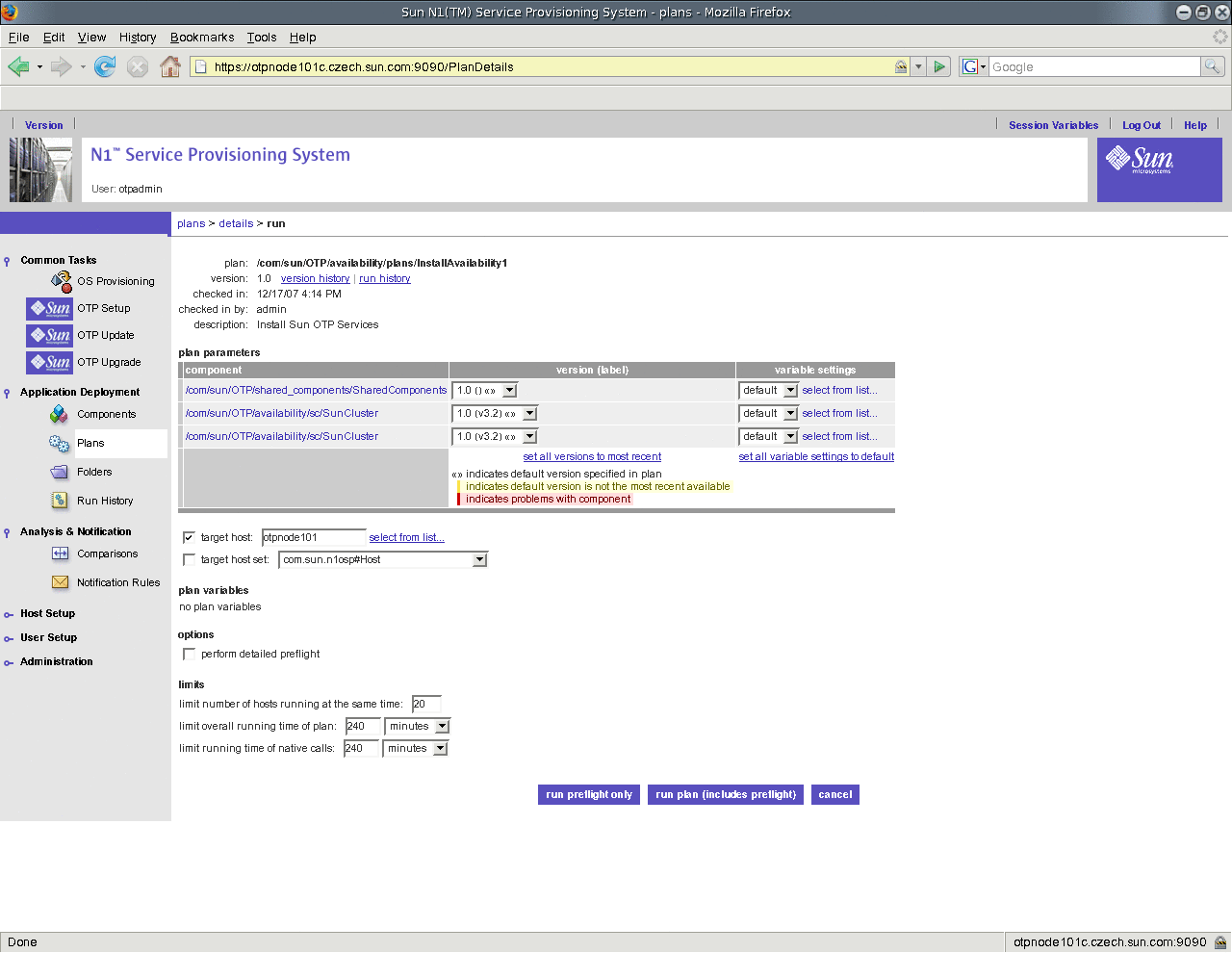
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
When the plan completes, wait for the first Sun OTP host to reboot.
-
Click Configure Availability Service and click run.
The InstallAvailability2 screen appears.
-
Type the first Sun OTP host name in the target host field.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
-
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP high availability service on the additional Sun OTP hosts.
-
Click Install Availability Service and click run.
The InstallAvailability1 screen appears.
-
Choose the additional cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
When the plan completes, wait for the Sun OTP host to reboot.
-
Click Configure Availability Service and click run.
The InstallAvailability2 screen appears.
-
Choose the additional cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
-
-
(Applicable for zones) Create and configure a non-global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Click Configure Solaris Containers and click run.
The InstallZones screen appears.
This step also installs the remote agent in the non-global zone.
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
-
-
(Applicable for zones) Configure SSH for the remote agent in the newly created non-global zone on the Sun OTP host.
Note –Perform this step only when you have chosen SSH (encrypted) connection type between Sun OTP application provisioning service master server and the remote agent.
-
Log in to the non-global zone on the Sun OTP host.
zlogin zonename
Where zonename is the name of the non-global zone.
-
Set a password for n1spsotp user.
-
Log in as spsotp user (su - spsotp) on the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Append the ssh public key of the spsotp user from the Sun OTP provisioning server to the authorized ssh keys located in the home directory of the n1spsotp user on each non-global zone on Sun OTP host.
cat /var/otp/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh n1spsotp@zonehostname "tee >> /export/home/n1spsotp/.ssh/authorized_keys2"
where zonehostname is the zone host name of Sun OTP host.
-
-
Create shared storage on the clustered Sun OTP system.
The shared storage is used for high availability of Sun OTP system management service and Sun OTP application provisioning service. These services are installed on the shared storage. If one host fails, the shared storage is mounted onto the other host and services will be restarted.
The shared storage will contain the otp-system-rg resource group.
-
Click Setup Shared Storage and click run.
The CreateSharedStorage screen appears.
Ensure that the shared storage has at least 4 GB space.
-
Click select from list... under variable settings.
The select variable setting from list... screen appears.
-
At the bottom of the select variable setting from list... screen, click create set to create a new variable set.
-
Type the variable set name in the Set Name field.
-
Provide values for the following parameters:
-
rootDisk - Name of the root disk.
-
diskSlice - Name of the disk slice where Solaris Volume Manager (SVM) database is created.
-
mntPoint - Name of the mount point. The value must be /var/js.
-
diskGroup - Name of the disk group. For example, sm-dg.
-
hostList - List of all the Sun OTP hosts. Separate the host names by a colon. For example, hostname1:hostname2.
-
metasetDID - Name of the valid shared did. For example, d5.
Type the command cldevice list -v to determine the shared did.
-
-
Close the select variable setting from list... screen.
-
In the CreateSharedStorage screen, click the drop-down list under variable settings, and choose the new variable set.
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
-
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP system management service in the global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Click Install System Management Service and click run.
The InstallManagement screen appears.
Figure 9–4 Install System Management Service Screen
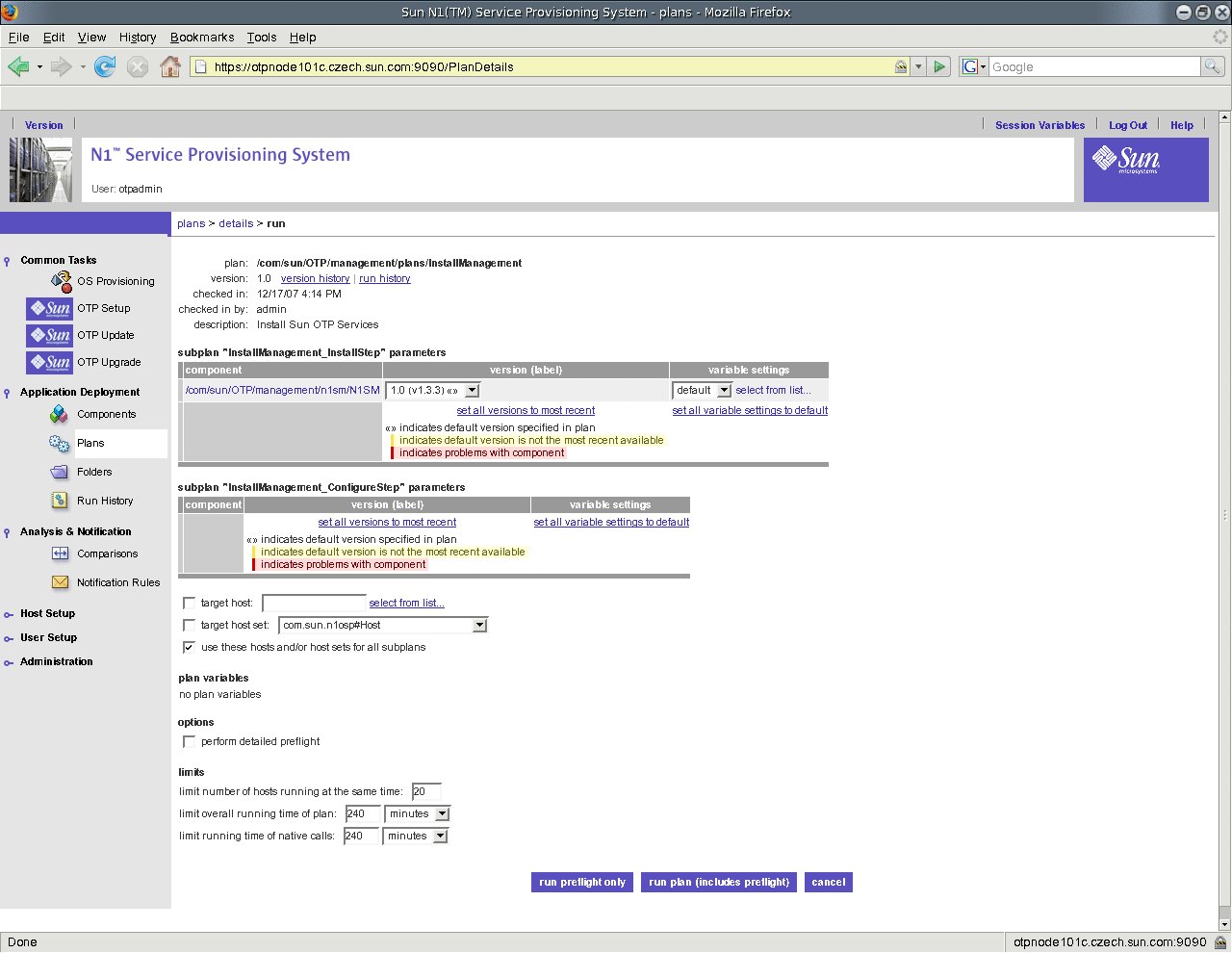
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
-
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP application provisioning service in the global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
(Applicable for zones) Update and prepare the new zone host with the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
(Applicable for zones) Configure Sun OTP installation plan variables for the new zone host.
-
Click OTP Setup to display the Sun Open Telecommunications Platform installation steps page.
-
Click Setup Configuration and click run.
-
Choose the same variable set that you chose in Step 6.
-
Type the zone host name in the target host field.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
-
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP security service on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Click Install Security Service and click run.
The InstallSecurity screen appears.
Figure 9–5 Install Security Service Screen
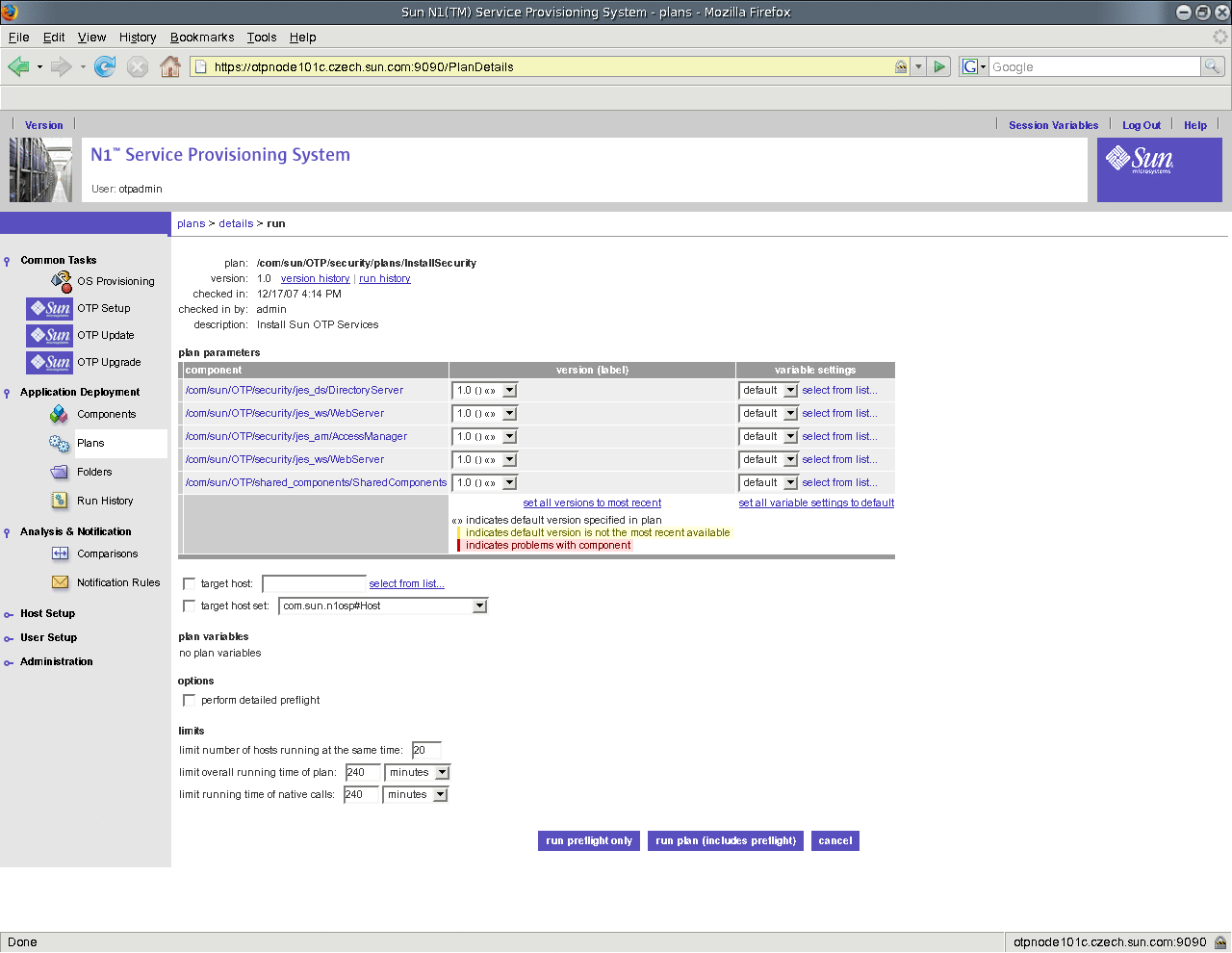
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
-
-
Configure and enable high availability for Sun OTP services on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Click Configure Components and click run.
The Configure screen appears.
This step creates and starts resource groups for Sun OTP system management service, Sun OTP application provisioning service, and Sun OTP security service. This step also configures and starts master-to-master replication (MMR).
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
The page is reloaded and a progress bar is displayed during the process.
Note –Self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server uses a specific logical host name and IP address defined at the beginning of the Sun OTP installation. However, to make Sun OTP application provisioning service highly available, the server is moved to a different logical host name (logical host name for management and provisioning services) at the end of this plan. After this plan is finished, this new logical host name has to be used to access the Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
-
Install Web SSO.
Note –When you install Sun OTP through GUI installation from a self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server, you need to verify the completion status of the previous plan (Configure and Enable HA plan) through the /var/OTP/SUNWotp.log file before running the Install Web SSO plan. The file must have the line that reads “enableHA - COMPLETED”.
-
Click Install Web SSO and click run.
The InstallWebSSO screen appears.
-
Choose the cluster host set from the target host set drop-down list.
-
Click run plan (includes preflight).
Note –Monitor the /var/OTP/SUNWotp-debug.log file to check whether the resource group otp-system-rg has been restarted. If the resource group has not been restarted, restart the resource group manually by typing the following command on any host of the cluster.
/usr/cluster/bin/clrg online otp-system-rg
The installation log files, input files generated for the plans, installation registry information, and the debug log files are stored in the /var/OTP directory.
-
See Also
On a two-host cluster, if you chose no for quorumAutoConfiguration during variable set creation, you must manually select and configure the quorum disk as described in To Configure the Quorum Disk on a Two-Host Cluster.
 To Configure the Quorum Disk on a Two-Host Cluster
To Configure the Quorum Disk on a Two-Host Cluster
On a two-host cluster, if you chose no for Quorum Auto Configuration in the input_otp.dat file, you must manually select and configure the quorum disk as described in this procedure.
Note –
The following substeps apply only to a two-host cluster. If you are setting up a three-host or more clustered Sun OTP system, this procedure is optional.
-
Open a separate terminal window and log in as root to the first Sun OTP host.
-
Type the following command to display the cluster disk information.
/usr/cluster/bin/cldev list -v
DID Device Full Device Path d1 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c0t8d0 d1 pcl44-otp2:/dev/rdsk/c1t8d0 d2 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c0t9d0 d2 pcl44-otp2:/dev/rdsk/c1t9d0 d3 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c1t10d0 d4 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c1t11d0 d4 pcl44-otp2:/dev/rdsk/c0t11d0 d5 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c2t1d0 d6 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c2t3d0 d7 pcl44-otp1:/dev/rdsk/c3t0d0 d9 pcl44-otp2:/dev/rdsk/c2t3d0 d10 pcl44-otp2:/dev/rdsk/c3t0d0
In the above example, disks d1 and d2 are shared by both hosts of the two-host cluster. The quorum disk must be a shared disk.
-
Configure a quorum disk.
/usr/cluster/bin/clq add shared disk ID
Where shared disk ID is a shared disk ID.
For example, to configure d4 as a quorum disk, type the following command.
/usr/cluster/bin/clq add d4
-
Reset the two-host cluster to normal mode.
/usr/cluster/bin/clq reset
Installing Sun OTP Using Command-Line Installation
This section describes Sun OTP installation on a clustered system using the command-line installation method.
Note –
The procedures for command-line installation are examples and are provided only for demonstration purposes.
 To Install Sun OTP on a Clustered System
To Install Sun OTP on a Clustered System
-
It is recommended that the shared storage is configured to provide redundancy of shared disks using hardware RAID (RAID1 or RAID5).
-
If the above feature is not available in the storage, it is recommended to use software RAID (RAID1 or RAID5) for shared storage provided by Solaris Volume Manager. See Solaris Volume Manager Administration Guide for more information. In this case, the shared storage needs to be set up manually.
Before You Begin
Make sure that you complete the tasks described in Prerequisite Tasks for Sun OTP Installation.
-
Log in as root (su - root) to the self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Copy the input_otp.dat file to a local non-temporary directory.
cp /opt/SUNWotp/cli/templates/input_otp.dat /export/
-
Edit the /export/input_otp.dat file.
Type the values for the appropriate plan variables in the text fields. Refer to Appendix A, Sun OTP Plan Worksheet to determine the values for these variables.
-
Set up the Sun OTP configuration on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i S -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-P passwordfile"
This command specifies the Sun OTP deployment parameters and validates these parameters provided in the input_otp.dat file.
-
Install the OS patches on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i P -f /export/input_otp.dat
When the command completes, wait for the Sun OTP hosts to boot into multi-user mode.
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP high availability service in the global zone on the first Sun OTP host.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i a -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-N first"
When the command completes, wait for the Sun OTP host to reboot completely and then type the following command:
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -c a -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-N first"
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP high availability service in the global zone on the additional Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i a -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-N additional"
When the command completes, wait for the Sun OTP host to reboot completely and then type the following command:
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -c a -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-N additional"
-
(Applicable for zones) Create and configure a non-global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i z -f /export/input_otp.dat
This command takes the zone-related parameters in the input_otp.dat file and creates a non-global zone. This command also installs the remote agent in the non-global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
(Applicable for zones) Configure SSH for the remote agent in the newly created non-global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Log in to the non-global zone on the Sun OTP host.
zlogin zonename
Where zonename is the name of the non-global zone.
-
Set a password for n1spsotp user in the global zone on the Sun OTP host.
-
Log in as the spsotp user (su - spsotp) on Sun OTP provisioning server.
-
Append the ssh public key of the spsotp user from the provisioning server to the authorized ssh keys located in the home directory of the n1spsotp user on each Sun OTP host.
cat /var/otp/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | ssh n1spsotp@zonehostname "tee >> /export/home/n1spsotp/.ssh/authorized_keys2"
where zonehostname is the zone host name of Sun OTP host.
-
-
Create shared storage on the clustered Sun OTP system.
The shared storage is used for high availability of Sun OTP system management service and Sun OTP application provisioning service. These services are installed on the shared storage. If one host fails, the shared storage is mounted onto the other host and services will be restarted.
The shared storage will contain the otp-system-rg resource group.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i d -f /export/input_otp.dat -o "-D did -L hostlist -G diskgroup -M mountpoint"
Where did is the valid shared did. For example, d5.
hostlist is the list of all Sun OTP hosts connected to shared storage. Separate the host names by a colon. For example, hostname1:hostname2.
diskgroup is the disk group. For example, sm-dg.
mountpoint is the mount point.
To determine the shared did, type the following command:
/usr/cluster/bin/cldev list -v
Choose the did that is shared among the Sun OTP hosts.
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP system management service in the global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i m -f /export/input_otp.dat
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP application provisioning service in the global zone on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i p -f /export/input_otp.dat
-
Install and configure the Sun OTP security service on all the Sun OTP hosts.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i s -f /export/input_otp.dat
-
Configure and enable high availability for Sun OTP services on the first Sun OTP host.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -c h -f /export/input_otp.dat
This command creates and starts resource groups for Sun OTP system management service, Sun OTP application provisioning service, and Sun OTP security service. This command also configures and starts master-to-master replication (MMR).
Note –Self-contained Sun OTP provisioning server uses a specific logical host name and IP address defined at the beginning of the Sun OTP installation. However, to make Sun OTP application provisioning service highly available, the logical hostname that was previously used will be released upon successful completion of the Configure and Enable HA service plan, and the Sun OTP application provisioning service will be accessible through the Management and Provisioning logical hostname and IP address.
-
Install Web SSO.
/opt/SUNWotp/cli/deploy_otp -i o -f /export/input_otp.dat
Note –Monitor the /var/OTP/SUNWotp-debug.log file to check whether the resource group otp-system-rg has been restarted. If the resource group has not been restarted, restart the resource group manually by typing the following command on any host of the cluster.
/usr/cluster/bin/clrg online otp-system-rg
The installation log files, input files generated for the plans, installation registry information, and the debug log files are stored in the /var/OTP directory.
See Also
On a two-host cluster, if you chose no for quorumAutoConfiguration during variable set creation, you must manually select and configure the quorum disk as described in To Configure the Quorum Disk on a Two-Host Cluster.
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates
