| C H A P T E R 4 |
|
Practical Examples of DR |
This chapter provides examples of DR operations, such as the addition, deletion, move, and replacement of system boards.
Each example shows an operation procedure using the command line interface of the XSCF shell. Similar procedures can also be applied to DR operations using the browser-based interface of the XSCF Web.
Note that the sections below explain only procedures such as those for checking the status of parts and devices for DR operations and not hardware operations (e.g., installing, removing, and replacing system boards). See the Service Manual for your server, as needed.
| Note - If your server is configured with SPARC64 VII processors, some restrictions regarding DR might apply. Please see SPARC64 VII+, SPARC64 VII, and SPARC64 VI Processors and CPU Operational Modes. |
This chapter includes these sections:
Example: Adding a System Board
Example: Deleting a System Board
Example: Moving a System Board
Examples: Replacing a System Board
Examples: Reserving Domain Configuration Changes
This section provides the flows of basic DR operations to add, delete, move, and replace system boards, along with flow diagrams.
FIGURE 4-1 Flow: Adding a System Board
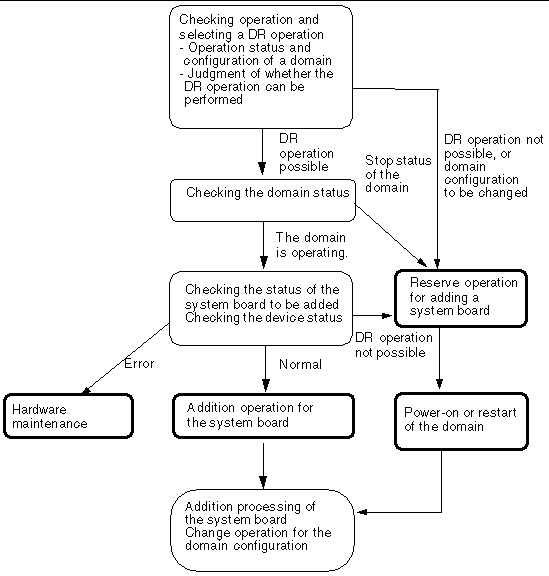
FIGURE 4-2 Flow: Deleting a System Board
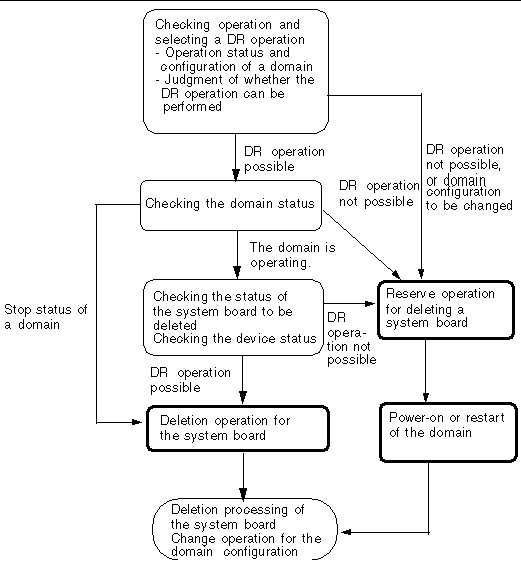
FIGURE 4-3 Flow: Moving a System Board
FIGURE 4-4 Flow: Replacing a System Board
This section provides an example of the DR operation to add a system board to a domain. In the example, a procedure conforming to section Flow: Adding a System Board, is used, and the system board shown in the figure is added by using the XSCF shell.
FIGURE 4-5 Example: Adding a System Board
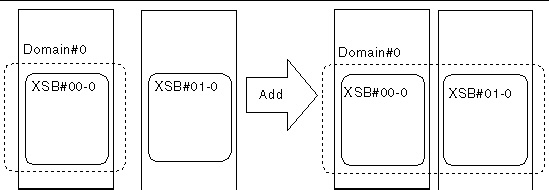
2. Check the status of the domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the domain. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or change the domain configuration.
3. Check the status of the system board to be added.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be added and confirm its registration in the DCL.
If you need to change the PSB configuration, use the setupfru(8) command. If the system board to be added is not registered in the DCL, register the system board in the DCL of the target domain by using the setdcl(8) command.
Execute the addboard(8) command to add the system board to the move-destination domain.
5. Check the status of the domain and added system board.
When the addboard(8) command ends normally, execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the added system board.
If the addboard(8) command completes abnormally or leaves the board in an unwanted status, refer output messages to identify the problem, then correct it.
This section provides an example of operation to delete a system board from a domain. In the example, a procedure conforming to Flow: Deleting a System Board, is used, and the system board shown in the figure is deleted using the XSCF shell.
FIGURE 4-6 Example: Deleting a System Board
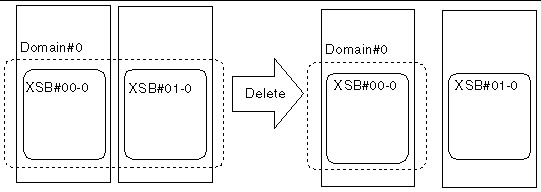
2. Check the status of the domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the domain. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or change the domain configuration.
3. Check the status of the system board to be deleted.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be deleted.
Execute the deleteboard(8) command to delete the system board and pool it in the system board pool.
5. Check the status of the domain and deleted system board.
When the deleteboard(8) command ends normally, execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the deleted system board.
If the deleteboard(8) command completes abnormally or leaves the board in an unwanted status, refer output messages to identify the problem, then correct it.
This section provides an example of an operation to move a system board between domains. In the example, a procedure conforming to Flow: Moving a System Board, is used, and the system board shown in the figure is moved using the XSCF shell.
FIGURE 4-7 Example: Moving a System Board
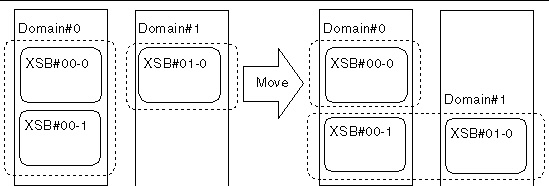
2. Check the status of the move-source domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the move-source domain.
3. Check the status of the move-destination domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the move-destination domain. Based on the operation status of the move-source and move-destination domains, determine whether to perform the DR operation or change the domain configuration.
4. Check the status of the system board to be moved.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be moved.
XSCF> showboards 00-1 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ---- -------- ----------- ---- ---- ---- ------- --------------- 00-1 00(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
Execute the moveboard(8) command to delete the system board from the move-source domain and add it to the move-destination domain.
6. Check the status of the move-source domain.
When the moveboard(8) command ends normally, execute the showdcl(8) command to display and check the operation status of the move-source domain.
If the moveboard(8) command completes abnormally or leaves the board in an unwanted status, refer output messages to identify the problem, then correct it.
7. Check the status of the move-destination domain and moved system board.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the move-destination domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the moved system board.
XSCF> showboards 00-1 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------- 00-1 01(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
This section provides examples of operations to replace a system board in a domain. The examples illustrate replacement of a system board in a Uni-XSB environment and a system board in a Quad-XSB environment. In each sample operation, a procedure conforming to Flow: Replacing a System Board, is used, and the system board shown in each figure is replaced using the XSCF shell.
FIGURE 4-8 Example: Replacing a Uni-XSB System Board
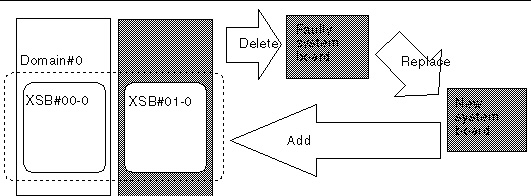
2. Check the status of the domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the domain. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or replace the system board after stopping the domain.
3. Check the status of the system board to be replaced.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be deleted. The DR operation for replacement may not be possible if the board to be replaced does not support the DR delete operation.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ----------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 00(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
Execute the deleteboard(8) command to delete the system board.
5. Check the status of the system board.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ----------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 00(01) Assigned y n n Passed Normal |
6. Physically replace the system board.
Execute the replacefru(8) command, then follow the displayed instructions to replace the system board per the Active Replacement procedure. For information about Active Replacement, see the Service Manual for your server.
7. Check the status of the replaced system board.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of all related system boards and confirm their registration in the DCL.
If necessary to change the system board configuration (e.g., number of divisions), do so by using the setupfru(8) command. If the system board is not registered in the DCL, register it in the DCL for the target domain by using the setdcl(8) command.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ----------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 00(01) Assigned y n n Passed Normal |
8. Check the status of the domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the domain. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or reboot the domains.
9. Add the new system board to the domain.
Execute the addboard(8) command to add the system board to the move-destination domain.
10. Check the status of the domain and added system board.
When the addboard(8) command ends normally, execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the added system board.
If the addboard(8) command completes abnormally or leaves the board in an unwanted status, see the output messages to identify the problem, then correct it.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ----------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 00(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
FIGURE 4-9 Example: Replacing a Quad-XSB System Board
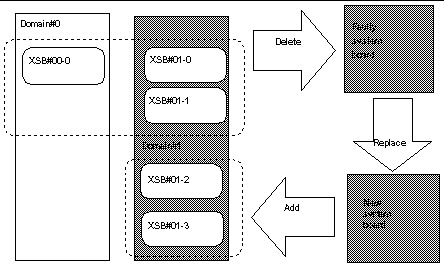
2. Check the configurations and status of all domains to which the relevant system boards belong.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the configurations and operation status of all domains to which the relevant XSBs belong.
Based on the configurations and operation status of the domains, determine whether to perform the DR operation or replace the replacement-target system board after stopping the domains. If a domain is configured by only the XSBs in the PSB to be replaced, the DR operation for replacement is disabled, and the domain must be stopped for replacement.
In this example, domain #1 has a configuration that requires it to be stopped for system board replacement.
XSCF> showdcl -a DID LSB XSB Status 00 Running 00 00-0 01 01-0 02 01-1 ------- 01 Running 00 01-2 01 01-3 |
3. Check the status of all related system boards.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of all system boards related to the PSB to be replaced. The DR operation for replacement may not be possible if the board to be replaced does not support the DR delete operation.
4. Delete all system boards related to the CMU to be replaced.
Execute the deleteboard(8) command to delete the system boards, and then assign the boards to a domain that permits the DR operation.
5. Power off Domain #1 so the CMU can be replaced.
Execute the poweroff(8) command so that the CMU being replaced will not be in use by domain #1.
6. Check the status of all related system boards.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of all related system boards.
7. Physically replace the system board.
Execute the replacefru(8) command, then follow the displayed instructions to replace the system board per the Active Replacement procedure. For information about Active Replacement, see the Service Manual for your server.
8. Check the status of the replaced system board.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be added and confirm its registration in the DCL.
If you need to change the PSB configuration, use the setupfru(8) command. If the system board is not registered in the DCL, register it in the DCL for the target domain by using the setdcl(8) command.
9. Check the status of all related domains.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of all related domains. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or reboot the domains.
XSCF> showdcl -a DID LSB XSB Status 00 Running 00 00-0 01 01-0 02 01-1 ------- 01 Powered Off 00 01-2 01 01-3 |
10. Add the new system board to the domain.
Execute the addboard(8) command in the domain to add the new system board.
11. Check the status of the related domains and system boards.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of related domains, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of related system boards.
In this example, domain #1 is booted by power-on in this stage.
XSCF> showdcl -a DID LSB XSB Status 00 Running 00 00-0 01 01-0 02 01-1 ------- 01 Running 00 01-2 01 01-3 |
This section provides examples of operations to reserve a change in domain configuration by DR. In the examples, the XSCF shell is used to reserve the addition, deletion, and movement of a system board as shown in the given configuration diagram.
FIGURE 4-10 Example: Reserve a System Board Add
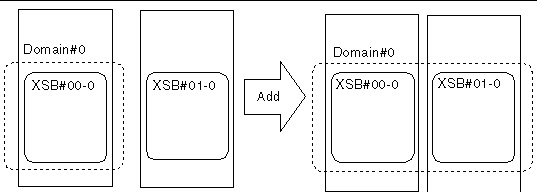
2. Check the status of the system board to be added.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be added and confirm its registration in the DCL.
If you need to change the PSB configuration, use the setupfru(8) command. If the system board is not registered in the DCL, register the system board in the DCL for the target domain by using the setdcl(8) command.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------ 01-0 SP Available y n n Passed Normal |
3. Reserve the addition of the system board.
Execute the addboard(8) command to reserve the addition of the system board.
4. Check the status of the system board.
When the addboard(8) command ends normally, execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the target system board and confirm that the addition of the target system board has been reserved.
If the addboard(8) command ends abnormally, identify the cause of the abnormality based on the messages output, and then take appropriate corrective action.
XSCF> showboards -v 01-0 XSB R DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault COD -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 * SP Available y n n Passed Normal n |
Stop or reboot the domain. This operation executes the reserved deletion of the system board as a change in domain configuration.
FIGURE 4-11 Example: Reserving a System Board Delete
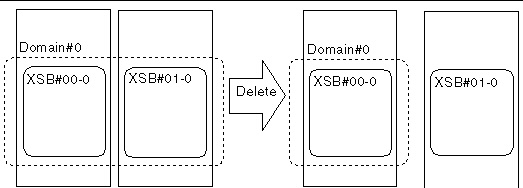
2. Check the status of the domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the domain. Based on the operation status of the domain, determine whether to perform the DR operation or change the domain configuration.
3. Check the status of the system board to be deleted.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be deleted.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------ 01-0 00(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
4. Reserve the deletion of the system board.
Execute the deleteboard(8) command to reserve deletion of the system board.
5. Check the reserved status of the system board.
Execute the showboards(8) command with the -v option specified to display system board information, and then confirm that deletion of the system board has been reserved.
XSCF> showboards -v 01-0 XSB R DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault COD -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 * 00(01) Assigned y y y Passed Normal n |
This operation changes the domain’s configuration, reserving deletion of the system board.
FIGURE 4-12 Example: Reserving a System Board Move
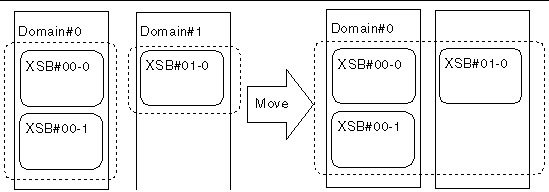
2. Check the status of the move-source domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the move-source domain.
3. Check the status of the move-destination domain.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to display domain information, and then check the operation status of the move-destination domain. Based on the operation status of the move-source and move-destination domains, determine whether to perform the DR operation or change the domain configuration.
4. Check the status of the system board to be moved.
Execute the showboards(8) command to display system board information, and then check the status of the system board to be moved.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------ 01-0 01(00) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
5. Reserve the move of the system board.
Execute the moveboard(8) command to reserve deletion of the system board from the move-source domain and addition of the system board to the move-destination domain.
6. Check the reserved status of the system board.
Execute the showboards(8) command with the -v option specified to display system board information, and confirm that moving the system board to the move-destination domain has been reserved.
XSCF> showboards -v 01-0 XSB R DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault COD -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 01-0 * 01(00) Assigned y y y Passed Normal n |
7. Stop the move-source domain.
Stop the move-source domain. This operation executes the reserved deletion of the system board from the move-source domain as a change in domain configuration, and the reservation of the addition of the system board to the move-destination domain.
8. Check the status of the move-destination domain and moved system board.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the move-destination domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the system board and confirm that addition of the system board has been reserved in the move-destination domain.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------ 01-0 00(02) Assigned y n n Passed Normal |
9. Add the system board to the move-destination domain.
Execute the addboard(8) command to add the system board to the move-destination domain. If the move-destination domain is in stopped status, the system board will be added the next time the domain is booted.
10. Check the status of the move-destination domain and moved system board.
Execute the showdcl(8) command to check the operation status of the move-destination domain, and then execute the showboards(8) command to check the status of the moved system board.
XSCF> showboards 01-0 XSB DID(LSB) Assignment Pwr Conn Conf Test Fault ------------------------------------------------------------------ 01-0 00(02) Assigned y y y Passed Normal |
Copyright © 2010, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.