9 Configuring and Using Direct Database Interrogation
This chapter contains:
About Direct Database Interrogation
Direct database interrogation enables you to interrogate a monitored database to obtain the name of the database user, operating system, and client program that originated a SQL statement, if this information is not available from the statement itself. This information then is made available in the Database Firewall reports. You can use direct database interrogation on Microsoft SQL Server and Sybase SQL Anywhere databases only.
To configure direct database interrogation, you must run a provided script to grant privileges to an existing user account in the protected database, and then enable the direct database interrogation functionality from the Database Firewall that manages the protected database.
Setting User Permissions for Direct Database Interrogation
This section contains:
-
Setting Direct Database Interrogation User Permissions in a SQL Server Database
-
Setting Direct Database Interrogation User Permissions in a Sybase SQL Anywhere Database
Setting Direct Database Interrogation User Permissions in a SQL Server Database
To set up the user account for a Microsoft SQL Server (versions 2005 or 2008) database:
-
From the Oracle Database Firewall Product CD (
Oracle Database Firewall Utilities 5.0), copy thedatabasedirectory to the server where you plan to run the script. -
Ensure that the computer where you will run the scripts has the
sqlcmd.exeutility installed. -
On this server, go to the
database/ddidirectory and uncompress thesqlservercompressed file, preferably into a directory calledsqlserver. This directory will contain the uncompressed fileddi_add_user.sql.The
ddi_add_user.sqlscript contains settings for the following information:-
$(username)refers to the user account that will be responsible for direct database interrogation. Ideally, this user account should be different from the user accounts specified for stored procedure and user role auditing (for example,ddi_auditor). -
$(password)refers to the password for this user account.
-
-
As a user who has privileges to create users and set user permissions, run the
ddi_add_user.sqlscript on the SQL Server database.The syntax is as follows:
sqlcmd -S server_name -U sa -P sa_password -i ddi_add_user.sql -v username="username" password="password"
In this specification:
-
server_name: Enter the name or the IP address of the database server where the protected database resides. Only use this argument if you are running the script from a remote server. You can omit it if you are running the script locally. -
sa_password: Enter the system administrator password. -
username: Enter the user account that you plan to create for direct database interrogation, specified by$(username)in theddi_add_user.sqlscript. Enclose this user name in double quotation marks. -
password: Enter the password for the direct database interrogation user account, specified by$(password)in theddi_add_user.sqlscript. Enclose this password in double quotation marks.
Examples:
sqlcmd -U sa -P sa_password -i ddi_add_user.sql -v username="ddi_auditor" password="abcd1234" sqlcmd -S my_server -U sa -P sa_password -i ddi_add_user.sql -v username="ddi_auditor" password="abcd1234"
-
The ddi_add_user.sql script grants the direct database interrogation user account the following privileges:
-
VIEW ANY DEFINITIONandVIEW SERVER STATEfor SQL Server 2005 and later -
SELECTon themaster.dbo.sysdatabasestable:
Setting Direct Database Interrogation User Permissions in a Sybase SQL Anywhere Database
To set user permissions for direct database interrogation in a Sybase SQL Anywhere database:
-
From the Oracle Database Firewall Product CD (
Oracle Database Firewall Utilities 5.0), copy thedatabasedirectory to the server where you plan to run the script. -
On this server, go to the
database/ddidirectory and uncompress thesqlanywherecompressed file, preferably into a directory calledsqlanywhere. This directory contains the uncompressed fileddi_add_user.sql.This script contain settings for the following information:
-
$(username)refers to the user account that will be responsible for direct database interrogation. Ideally, this user account should be different from the user accounts specified for stored procedure and user role auditing (for example,ddi_auditor). -
$(password)refers to the password for this user account.
-
-
As a user who has privileges to create users and set user permissions, run the
ddi_add_user.sqlscript on the SQL Anywhere database.The syntax is as follows:
isql -S server_name -U sa -P sa_password -i ddi_add_user.sql -v username="username" password="password" database="protected_database"
In this specification:
-
server_name: Only use this argument if the database is remote. You can enter the name of the server or its IP address. If you are running the script locally, then you can omit the-S server_nameargument. -
sa_password: Enter the system administrator password. -
username: Enter the user account that you plan to create for direct database interrogation, specified by$(username)in theddi_add_user.sqlscript. Enclose this user name in double quotation marks. -
password: Enter the password for the direct database interrogation user account, specified by$(password)in theddi_add_user.sqlscript. Enclose this password in double quotation marks. -
database="protected_database": Enter the name of the database within this server that you want to protect, specified by$(database)in theddi_add_user.sqlscript. Enclose this database name in double quotation marks.
Examples:
isql -U sa -P sa_password -i sddi_add_user.sql -v username="ddi_auditor" password="abcd1234" database="sales_db" isql -S my_server -U sa -P sa_password -i sddi_add_user.sql -v username="ddi_auditor" password="abcd1234" database="sales_db"
-
The ddi_add_user.sql script grants the direct database interrogation user account the following privileges:
-
CONNECT -
SELECTon these system tables:sys.sysuser sys.sysuserauthority sys.sysremoteuser sys.sysloginmap sys.sysgroup
Enabling Direct Database Interrogation
To enable direct database interrogation in a Database Firewall:
-
Log in to the Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Click the Monitoring tab.
By default, the Enforcement Points page appears. If it does not, click List in the Enforcement Points menu on the left side of the page.
-
Find the enforcement point that you want to use for the remote monitor, and then click the Settings button for that enforcement point.
The Monitor Settings page appears.
-
Scroll down to the Database Interrogation area and click the Activate Database Interrogation check box.
The Activate Database Interrogation area expands to enable you to complete the necessary authentication details.
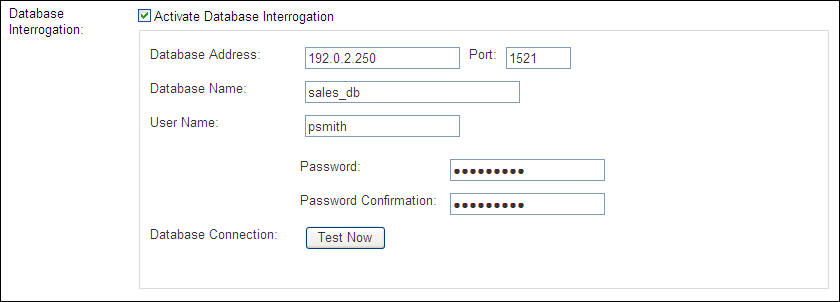
Description of the illustration image101.jpg
-
Scroll to the end of the Monitor Settings page, and then click the Save button.
Disabling Direct Database Interrogation
You can temporarily disable direct database interrogation. Oracle Database Firewall saves the configuration information that you have created for the next time that you want to enable it. If you want to remove the direct database interrogation configuration and software, see Oracle Database Firewall Installation Guide.
To disable direct database interrogation:
-
Log in to the Management Server Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
-
Select the Monitoring tab.
By default, the Enforcement Points page appears.
-
Click the Settings button for the enforcement point that you want to use for the remote monitor.
The Monitor Settings page appears.
-
Scroll down to the Direct Database Interrogation area.
-
Clear the Activate Database Interrogation check box.
-
Scroll to the end of the Monitor Settings page, and then click the Save button.