2 Configuring an Oracle Database Firewall
This chapter contains:
-
Step 3: Specify the Standalone Database Firewall System Settings
-
Step 4: Enable Secure Log Access in the Standalone Database Firewall
-
Step 5: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Syslog Destinations
-
Step 6: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Enforcement Points
-
Step 7: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Bridge IP Address
-
Step 8: Test the Standalone Database Firewall System Operation
About Configuring an Oracle Database Firewall
This chapter explains how to configure a standalone Oracle Database Firewall. Where indicated, a procedure also applies to a managed Oracle Database Firewall. For more information on which tasks can be done on which type of Database Firewall, see these topics:
"Tasks Performed in a Standalone Database Firewall Administration Console"
"Tasks Performed in a Managed Database Firewall Administration Console"
If you want to configure a standalone Database Firewall to be managed by a Management Server, see Chapter 3, "Configuring a Database Firewall Management Server."
Before you start, ensure that the Database Firewall has been installed, as described in the Oracle Database Firewall Installation Guide.
Note:
Your Web browser should have JavaScript enabled to allow any error messages to be displayed. In Internet Explorer, select Tools, Internet Options, click Custom Level in the Security tab, and choose Enable for Active scripting. In Mozilla Firefox, select Tools, Options, and select Enable JavaScript in the Content tab.Step 1: Set the Standalone Database Firewall Date and Time
It is important to ensure that the Database Firewall uses the correct date and time, because events are logged with the date and time they occur, and archiving take place at specified intervals.
To set the standalone Database Firewall date and time:
-
Log in to the standalone Database Firewall Administration Console.
See "Logging in to the Administration Console" for more information.
The Administration Console appears. The following screen shows how a standalone Database Firewall Administration Console appears.
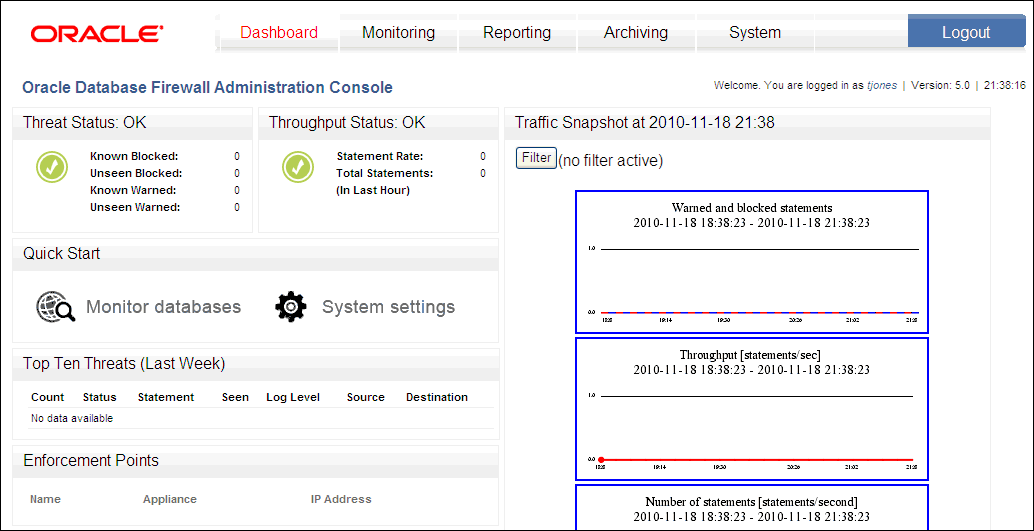
Description of the illustration standalone_fw.gif
-
In the System menu, select Settings.
The System Settings page appears.
-
Click Change in the Time Settings area.
-
Enter the correct date and time, then click Apply.
-
Restart the Database Firewall.
In System menu, select Management, and then under Reboot and power off, click the Reboot button.
Step 2: Specify the Management Server NTP Time Server
You can use a Network Time Protocol (NTP) time server to update the time for either a standalone or managed Oracle Database Firewall automatically.
To specify the NTP time server settings:
-
In the Administration Console for the Database Firewall (either standalone or managed), under System, click Time Synchronization, and then click the Change button.
The following page is displayed.
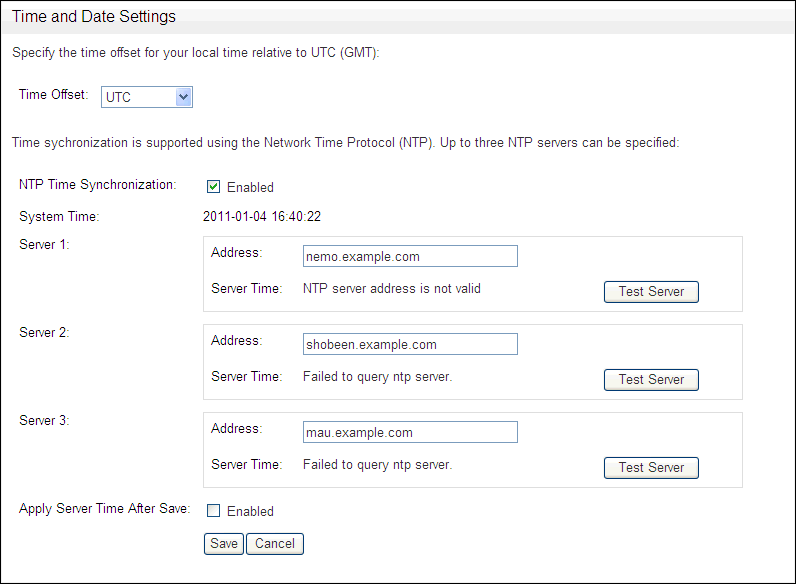
Description of the illustration image013.gif
-
Use the Time Offset menu to select your local time with respect to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC).
For example, UTC-5 is five hours behind UTC. It is essential to select the correct setting to ensure that the time is set accurately during synchronization.
If you do not select the correct setting, the time will be set incorrectly when time synchronization occurs.
-
Select NTP time synchronization.
Selecting NTP Time Synchronization keeps the time at the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server or Oracle Database Firewall synchronized with the average of the time recovered from the time servers specified in the Server 1/2/3 fields, which can contain an IP address or name. If a name is specified, the DNS server specified in the System Settings page is used for name resolution.
-
Use the default server addresses, or enter the addresses of your preferred time servers.
Test Server displays the time from the server, but does not update the time at the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server or Oracle Database Firewall.
Selecting Apply Server Time After Save causes the time to be synchronized when you click Save.
-
Click Save.
To enable time synchronization, you also must specify the IP address of the default gateway and a DNS server, as described in the next section.
Step 3: Specify the Standalone Database Firewall System Settings
To configure the standalone Database Firewall system settings:
-
In the Database Firewall Administration Console, click the System tab, and under the System menu, select Settings.
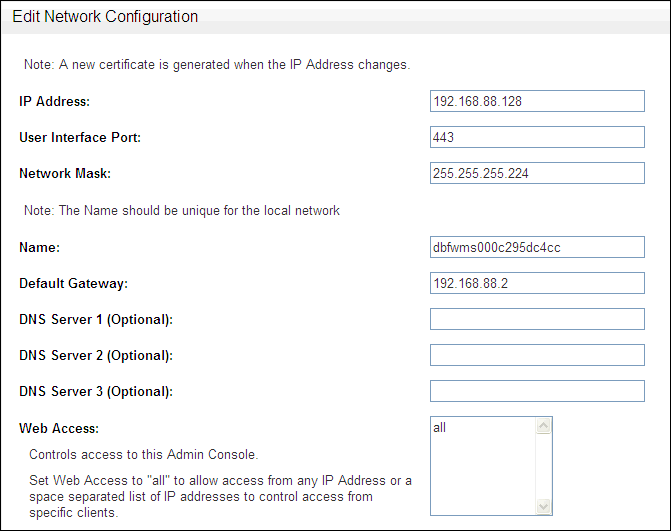
Description of the illustration image028.gif
-
In the System Settings page, click Change.
-
Complete the fields as necessary.
-
IP Address: The IP address of the currently accessed Database Firewall. This IP address connects to the Administration Console, or accesses the unit from Oracle Database Firewall applications such as the Analyzer. An IP address was set during installation. If you want to use a different address, then you can change it now. The IP address is static and must be obtained from the network administrator.
-
User Interface Port: The port number used to connect to the Administration Console. The default port numbers are listed in Oracle Database Firewall Installation Guide. If you change this port number, then you must specify the new one in the URL when you log in to the Database Firewall Administration Console. Use the following syntax:
https://ip_address:port/user/login
-
Network Mask: The subnet mask of Oracle Database Firewall.
-
Name: Enter a descriptive name for this Database Firewall, such as
Database Firewall to monitor Oracle Database. -
Default Gateway: (optional) The IP address of the default gateway (for example, for internet access). The default gateway must be on the same subnet as the host.
-
DNS Servers: (optional) The IP addresses of up to three DNS servers on the network. These are used to resolve any network names that may be used by Oracle Database Firewall. Keep the fields blank if there is no DNS server, otherwise system performance may be impaired.
-
Web Access: If you want to allow only selected computers to access the Administration Console, enter their IP addresses in the box. Using the default of all allows access from any computer in your site.
-
Terminal Access: You can specify a list of IP addresses that are allowed to access Oracle Database Firewall from a remote console. Entering all allows access from any computer in your site. The default of disabled prevents console access from any computer.
-
SNMP Access: Specifies a list of IP addresses that are allowed to access the network configuration of Oracle Database Firewall through SNMP (settings as per Terminal Access). The SNMP community string is
gT8@fq+E. -
Secure Log Access (Reporting): Specifies a list of IP addresses that are allowed to access the log data held on the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server, for example, to report using external reporting systems (settings as per Terminal Access). If you complete this setting, then ensure that you complete "Step 4: Enable Secure Log Access in the Standalone Database Firewall".
-
Traffic Log Access (Analyzer): Specifies a list of IP addresses of computers running the Analyzer software that are allowed to access the traffic log on the Oracle Database Firewall Management Server (settings as per Terminal Access).
-
Link properties: Leave the setting at the default, unless your network has been configured not to use autonegotiation.
-
-
Click Apply.
Step 4: Enable Secure Log Access in the Standalone Database Firewall
If you completed the settings in the Secure Log Access (Reporting) field in "Step 3: Specify the Standalone Database Firewall System Settings", then you must enable the access in the Database Firewall server.
-
Log in to the Database Firewall server as user
root. -
Change to the oracle user.
su - oracle
-
Set the following environment variables:
export ORACLE_HOME=/var/lib/oracle/dbfw export ORACLE_SID=dbfwdb export PATH=$PATH:$ORACLE_HOME/bin/
-
The following message is displayed:
The Oracle base has been set to /var/lib/oracle
-
Log in to the database on this server using SQL*Plus.
sqlplus / as sysdba
-
Enable the
dbfw_reportaccount and grant this user a password.ALTER USER dbfw_report ACCOUNT UNLOCK IDENTIFIED BY password; -
Exit SQL*Plus.
Step 5: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Syslog Destinations
Use the following procedure to configure the types of syslog messages to send from this Database Firewall (for example, to signal blocked statements).
-
In the standalone Database Firewall Administration Console, click the System tab.
-
Click Syslog in the Connectors menu.
The following page appears.
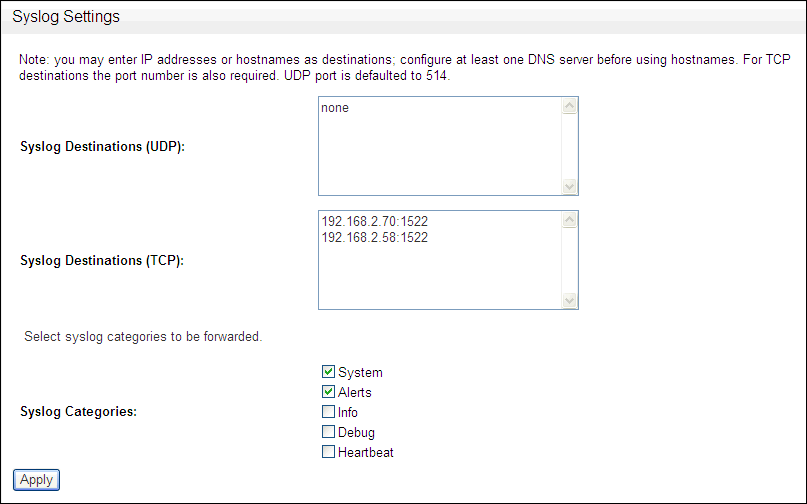
Description of the illustration image017.gif
-
Complete the fields, as necessary:
-
Syslog Destinations (UDP): Use this box if you are using a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to communicate syslog messages. Enter the IP address of each computer that is permitted to receive the syslog messages.
-
Syslog Destinations (TCP): Use this box if you are using Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) to communicate syslog messages. TCP guarantees that the packets are sent and received correctly. Enter the IP address and port number of each machine that is permitted to receive the syslog messages.
-
Syslog Categories: You can select the types of syslog messages to generate. The syslog messages are in the following categories:
-
System: System messages generated by Oracle Database Firewall or other software, which have a syslog priority level of at least "INFO".
-
Alerts: Oracle Database Firewall and F5 alerts (Oracle Database Firewall syslog message IDs 9, 10, 11 and 12).
-
Info: General Oracle Database Firewall messages and property changes (Oracle Database Firewall syslog message IDs 1, 4 and 8).
-
Debug: Engineering debug messages (for Oracle Database Firewall use only).
-
Heartbeat: Oracle Database Firewall heartbeat message and current statistics (Oracle Database Firewall syslog message ID 3). Oracle Database Firewall sends a heartbeat every second for each Enforcement Point that you have configured for this system. (If you select this check box, be aware of the potential volume issues when you enable the Heartbeat feature.)
-
-
-
Click Apply.
Step 6: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Enforcement Points
You must configure each enforcement point that the standalone Database Firewall will use. (For a managed Database Firewall, you use the Management Server.)
To configure the enforcement points:
-
In the standalone Database Firewall Administration Console, select the Monitoring tab.
-
In the Enforcement Points menu, select Create.
The Enforcement Point Wizard: Step 1 page appears.
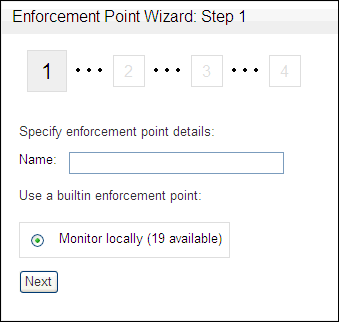
Description of the illustration image019.gif
-
Enter the following information:
-
Name: Enter a name for the enforcement point.
-
Use a builtin enforcement point (Monitor locally): The number of currently available enforcement points you can create is displayed.
-
-
Click Next.
The Enforcement Point Wizard: Step 2 page appears.
-
Enter the following information:
-
Protected Database: Select from the list of available databases.
-
Name: Enter a name for the database to be monitored (this and the remaining options are not used if you have not selected an existing database).
-
Database Type: Select the database type.
-
Address and Port: Specify the IP address and port number of the database management system (i.e. the IP settings used by database clients to send traffic to the database), then click Add. If the protected database has more than one interface and/or port, enter the additional Address and Port details, then click Add again. If you are using a Domain Name Server (DNS), you can enter a hostname instead of an IP address.
-
-
Click Next.
The Enforcement Point Wizard: Step 3 page appears.
-
Enter the following settings:
-
Monitoring Mode: Select Database Activity Monitoring (DAM) if the enforcement point is to be used only to log statements and provide warnings of potential attacks. Select Database Policy Enforcement (DPE) if the enforcement point is also required to block potential attacks. Database Policy Enforcement is available only if you upload a policy (as described next).
-
Policy: Select a baseline policy. You can select a custom policy developed using the Analyzer software by clicking Browse to select the file, then Upload. You can use the text box to add a description, which will be displayed in the Description column. If this is the first time you are creating a baseline policy, then Oracle recommends that you select the unique.dna policy.
-
-
Click Next.
The Enforcement Point Wizard: Step 4 page appears.
-
Check your settings, and if you are satisfied, then click the Finish button.
Step 7: Configure the Standalone Database Firewall Bridge IP Address
If you want Oracle Database Firewall to block potential attacks, or if you are using the Oracle Database Firewall local monitoring software, then you must allocate an additional IP address that is unique to the database network. This is used as a bridge IP address to redirect traffic within the unit.
Note:
The IP address of the bridge must be on the same subnet as all protected databases deployed in DPE mode on that bridge. This restriction does not apply to protected databases deployed in DAM mode.To configure the standalone Database Firewall bridge IP address:
-
In the standalone Database Firewall Administration Console, click the Monitoring tab.
-
Click List in the Traffic Sources menu. An area similar to the following is displayed.
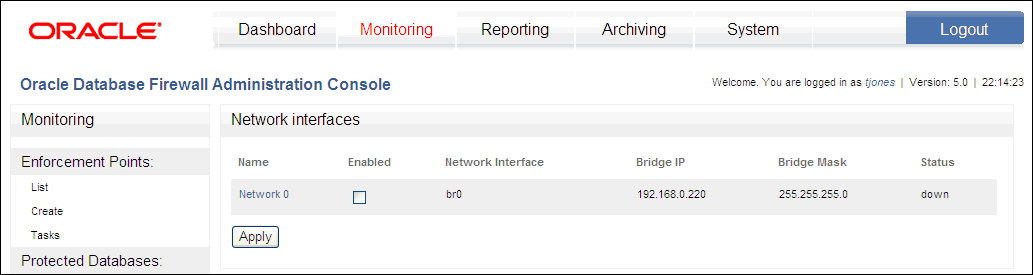
Description of the illustration image021.gif
-
From the list, find the network that you want to configure.
Select Enabled against the appropriate network interface and click the name of the interface.
Specify an IP address and subnet mask if either of the following is true (the address must be unique to the network, and is used as a bridge IP address to redirect traffic within the unit):
-
The pair of ports connect the Oracle Database Firewall in-line between the database and clients (whether Database Policy Enforcement or Database Activity Monitoring mode is used).
-
The ports are used to monitor traffic with the Oracle Database Firewall Local Monitoring software.
Enabled is automatically selected if the ports are currently used to monitor traffic for enforcement points that have the Local Monitoring or DPE (Database Policy Enforcement) mode selected.
-
-
Click Save Settings
Step 8: Test the Standalone Database Firewall System Operation
You should verify that the standalone Database Firewall configuration is fully operational before you begin monitoring your protected database SQL traffic.
To test the system operation:
-
In the standalone Database Firewall Administration Console, click the Monitoring tab, and then from the Enforcement Points menu, select List to display the list of configured enforcement points. Check the status as follows:
-
Click the Status button for the appropriate enforcement point.
-
In the Appliances area, ensure that you see a green check-mark indicator in the Status column against the device that is performing the monitoring.
-
-
Click the Dashboard tab, and check that Number of statements increases every minute. This setting indicates that statements are being recognized.
-
Click the Reporting tab, then View in Traffic Log menu.
Click Start to see the statements that are being saved to the traffic log. You may need to wait for 5 to 10 minutes.
-
Verify that data can be obtained from the traffic log.
See Oracle Database Firewall Security Management Guide for information about accessing and viewing the traffic log.
What's Next?
The tasks in chapter complete the initial configuration of a Database Firewall. You next step is to configure to configure the Management Server, described in Chapter 3, "Configuring a Database Firewall Management Server." Depending on site requirements, you may need to configure other features, such as stored procedure auditing, user role auditing and local monitoring. These features are explained in later chapters of this guide.
After you have configured the standalone Database Firewall, users will be able to begin analyzing data. Once a policy has been developed, you must upload it. Oracle Database Firewall Security Management Guide covers these tasks in detail.
Chapter 13, "System Administration," explains system administration tasks, including how to set up new users, monitor the system and produce reports.