| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS JMS Reference Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS JMS Reference Java CAPS Documentation |
Implementing JMS in Java CAPS Projects
To Implement JMS Following the Java CAPS Model
Creating and Configuring Message Destinations
Creating OTDs and Collaborations
Using the JMS OTD in Collaboration Definitions
Using JMS Messages in Collaboration Definitions
Database Configuration and Operation
Message Redelivery and Redirection
Specifying Redelivery Options in the JMS IQ Manager
Specifying Redelivery Options in a JMS Client
Example of Producer Throttling and Unthrottling
Additional JMS Message Properties
requestReply(timeout, message)
requestReplyTo(message, destName)
requestReplyTo(timeout, message, destName)
send(message, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
sendBytes(payload, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
sendBytesTo(payload, destination)
sendBytesTo(payload, destination, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
sendText(payload, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
sendTextTo(payload, destination)
sendTextTo(payload, destination, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
sendTo(message, destination, deliveryMode, priority, timeToLive)
retrieveBytesFromMessage(arg0)
retrieveStringFromMessage(arg0)
JMS IQ Manager Runtime Configuration
Accessing the Configuration Properties
Configuration Properties Interface
Journaling and Expiration Properties
Per-Destination Throttling Threshold
Overview of MS Control Utility Features
To Create a Backup Archive File
To Set the MS Control Utility Timeout Period
Message Destination (Queue) Examples
You have several options for controlling the message processing order in Java CAPS Projects:
You can specify first-in, first out (FIFO) ordering modes, or a set of message destinations with a specific processing order, when you configure the JMS IQ Manager. See JMS IQ Manager Delivery Modes.
You can specify message processing, either connection consumer or serial mode, at the JMS client level. See JMS Client Delivery Modes.
For a single consumer with a single process, processing for queues is fully serialized, by default. The process of processing a message is as follows:
The receiver requests, or is ready to receive, a message
The receiver receives the message
The receiver processes the message
When multiple receivers or multiple processes within a single receiver subscribe to the same message destination (queues only), you have a choice of three first-in, first-out (FIFO) delivery modes, as listed below. These ordering modes apply globally to all queues in the Java CAPS Project
Fully concurrent
Receivers can retrieve messages when all older messages have been received, or are being received, and can commit messages in any order (without using time sequence).
Protected concurrent
Receivers can retrieve messages when all older messages have been received or are being received, but must commit using time sequence.
Fully serialized
Receivers read a messages only after all messages have been received and commit messages using a time sequence.
In fully concurrent mode, receivers can retrieve messages from a destination only when all older messages have been received or are in the process of being received. Receivers can then commit messages without restrictions. By default, JMS IQ Managers use fully concurrent processing for queues.
Figure 5 Fully Concurrent Processing
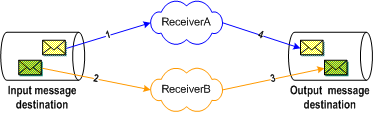
The figure above shows a sample delivery sequence for fully concurrent processing. In steps 1 and 2, the receivers retrieve their messages from the input queue. Both receivers must wait until each consumer has retrieved its messages, or is in the process of retrieving them, before they are able to commit messages to the output destination.
As steps 3 and 4 infer, receivers can commit messages in any order; therefore, messages can be committed out of sequence, which might not be acceptable. For example, a patient release record may be committed before the patient admittance record is committed. The following table indicates the benefits and drawbacks of fully concurrent processing.
Table 1 Tradeoffs for Fully Concurrent Processing
|
In protected concurrent mode, receivers retrieve messages just as in fully concurrent mode, after all messages have been received or are being received. Messages can only be committed, however, if all older messages have previously been committed.
Figure 6 Protected Concurrent Processing
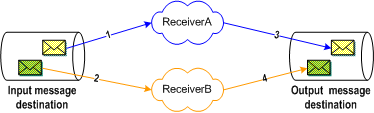
The figure above shows a sample delivery sequence for protected concurrent processing. In steps 1 and 2, the receivers retrieve their messages from the input queue. Both receivers must wait until each consumer has retrieved, or is in the process of retrieving, its messages before being able to commit messages to the output destination. ReceiverB might be ready to commit its message before ReceiverA, but must wait until ReceiverA commits its message (step 3). Only when ReceiverA’s message has been committed, can ReceiverB commit its message (step 4).
Protected concurrent processing thus is a more workable solution in a scenario where a Project deals with messages such as patient records, where the admittance record must be committed before the release record.
The following table shows the benefits and drawbacks of protected concurrent processing.
Table 2 Tradeoffs for Protected Concurrent Processing
|
You specify protected concurrent processing for JMS IQ Managers with the Protected Concurrent Queues property as described in Special FIFO Mode Properties.
Note - By design, protected concurrent FIFO works only within one transaction, either in the form of one session or in the form of one XA transaction on the same server. You should always use XA when using the protected concurrent FIFO mode with a message-driven bean (MDB), since Java CAPS does not support single sessions with MDBs.
In fully serialized mode, receivers can only retrieve messages after all older messages have been received and committed.
Figure 7 Fully Serialized Processing
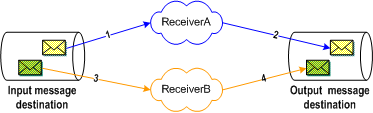
The figure above shows a sample delivery sequence for serialized processing. In step 1, ReceiverA retrieves its message. ReceiverB might at this point be ready to receive its message, but must wait until ReceiverA has committed its message. After ReceiverA commits the message in step 2, ReceiverB can then retrieve and commit its message (steps 3 and 4).
The following table shows the benefits and drawbacks of protected concurrent processing.
Table 3 Tradeoffs for Fully Serialized Processing
|
You specify fully serialized processing for JMS IQ Managers with the Fully Serialized Queues property as described in Special FIFO Mode Properties.
You can also specify delivery order specifically for a set of topics and queues (time order groups). For these groups, consumers can only receive messages when all other messages in the time order group have been received or are in the process of being received. For information on specifying a time order group, refer to Time Dependency Properties.
The delivery order options above are configured for the JMS IQ Manager. The Oracle Java CAPS Enterprise Service Bus JMS implementation enables you to configure topic subscribers as connection consumers to improve message throughput through concurrent processing. You can set the JMS client configuration with the Concurrency property as described in Concurrency.
The use of connection consumers increases message processing performance by enabling concurrent processing using multiple threads. You can specify the number of message driven beans (MDBs) or the server session pool to assign to a JMS Collaboration to process messages concurrently. When you use connection consumer with fully concurrent or protected concurrent FIFO processing, this default setting allows the integration server to assign multiple threads to execute the Collaboration on a particular message destination.
For queues, you can also process messages concurrently using multiple integration servers; these integration servers may run on different systems.
Using a JMS client connection consumer affects the message processing order. For example, consider the scenario shown in the following figure. The JMS IQ Manager is set to fully concurrent FIFO processing. However, each Collaboration on each integration server retrieves messages as they come in, and is able to commit them unrestricted to the queue. Therefore, although the JMS IQ Manager is configured for fully concurrent FIFO processing, message order cannot be guaranteed.
Figure 8 Multiple Application Server Configuration
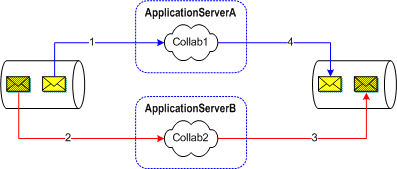
The concurrency mode affects FIFO processing in several ways. The following table lists how the JMS client concurrency mode settings affect the JMS IQ Manager FIFO mode selections for topics. For topics, only one integration server per subscriber can be used.
Table 4 Concurrency/FIFO Mode Interaction: Topics
|
The following table lists how the JMS client concurrency mode settings affect the JMS IQ Manager FIFO mode selections for queues.
Table 5 Concurrency/FIFO Mode Interaction: Queues
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||