| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Using Database Operations with Oracle Java CAPS Database Adapters Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Using Database Operations with Oracle Java CAPS Database Adapters Java CAPS Documentation |
DB2 Database Operations (BPEL)
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
Collaboration Usability for a Stored Procedure ResultSet
DB2 Connect Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
DB2 Connect Adapter Database Operations (JCD)
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
JDBC Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
JDBC Adapter Database Operations (JCD)
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
Collaboration Usability for a Stored Procedure ResultSet
Oracle Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
Oracle Adapter Outbound XA Support for BPEL
Oracle Adapter Database Operations (JCD)
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
Collaboration Usability for a Stored Procedure ResultSet
Long RAW for Prepared Statements and Stored Procedure Support
Using CLOBs with the Oracle Adapter
SQL Server Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
SQL Server Adapter Database Operations (JCD)
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
Sybase Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
Sybase Adapter Database Operations (JCD)
To Perform a Query Operation on a Table
To Perform an Insert Operation on a Table
To Perform an Update Operation on a Table
To Perform a Delete Operation on a Table
Manipulating the ResultSet and Update Count Returned by Stored Procedure
Collaboration Usability for a Stored Procedure ResultSet
VSAM Adapter Database Operations (BPEL)
The database operations used in the DB2 Connect Adapter are used to access the DB2 Connect database. Database operations are either accessed through activities in BPEL, or through methods called from a JCD Collaboration.
Note - The default value of the auto-commit option for DB2 drivers varies depending on the transactional mode. For certain cases, you might want to change the value of auto-commit to true to prevent cursors from being held open until a process completes. The default modes are listed below:
DB2 Connect XA: auto-commit is set to false
DB2 Connect Non-transactional: auto-commit is set to true
DB2 Connect Local: auto-commit is set to false
The DB2 Connect Adapter uses a number operations to query the DB2 Connect database. Within a BPEL business process, the DB2 Connect Adapter uses BPEL activities to perform basic outbound database operations, including:
Insert
Update
Delete
SelectOne
SelectMultiple
SelectAll
In addition to these outbound operations, the DB2 Connect Adapter also employs the inbound activity ReceiveOne within a Prepared Statement OTD.
The Java CAPS Business Rules Designer includes Input and Output columns to map and transform data between activities displayed on the Business Process Canvas.
Figure 1-2 displays the business rules between the FileClient.write and otdDB2Connect.Db_employeeDelete activities. In this example, the whereClause attribute appears on the Input side.
Figure 1-2 Input and Output Between Activities
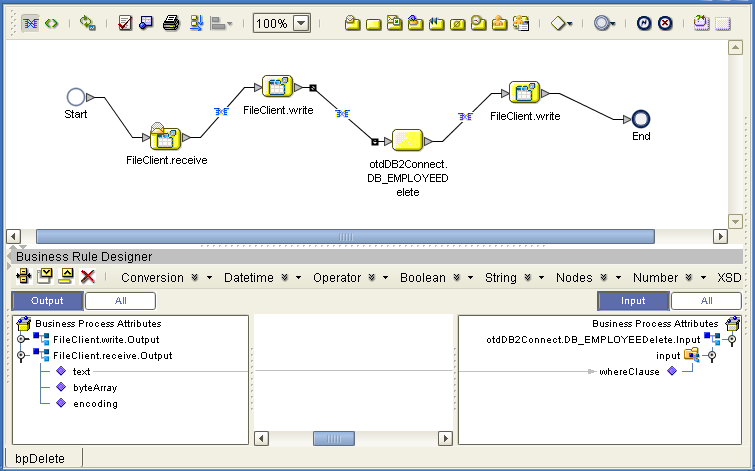
The following table lists the expected Input and Output of each database operation activity.
Table 1-2 DB2 Connect Operations
|
The same database operations are also used in the JCD, but appear as methods to call from the Collaboration.
Tables, Views, and Stored Procedures are manipulated through OTDs. Methods to call include:
update(String sWhere)
updateRow()
delete(String sWhere)
deleteRow()
select(String where)
Note - Refer to the Javadoc for a full description of methods included in the DB2 Connect Adapter.
A table OTD represents a database table. It consists of fields and methods. Fields correspond to the columns of a table while methods are the operations that you can apply to the OTD. This allows you to perform query, update, insert, and delete SQL operations in a table. The ability to update via a resultset is called “Updatable Resultset”, which is a feature supported by this adapter if the Type 4 Universal driver is used (for alternate methods for the Type 2 Legacy driver refer to Prepared Statement).
Note - The DB2 Connect Universal Driver only supports Updatable Resultsets for Update and Delete. The Insert operation is not supported. You can use a Prepared Statement to perform the Insert operation.
By default, the Table OTD has UpdatableConcurrency and ScrollTypeForwardOnly. Normally you do not have to change the default setting.
The type of result returned by the select() method can be specified using:
SetConcurrencytoUpdatable
SetConcurrencytoReadOnly
SetScrollTypetoForwardOnly
SetScrollTypetoScrollSensitive
SetScrollTypetoInsensitive
Note - The content of the input.getText() file may contain null, meaning it will not have a where clause or it can contain a where clause such as empno > 50.
For example:
package prjDB2Connect_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdTableSelect
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage
input, dtd.otdOutputDTD1325973702.DB_Employee otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1,
otdDB2Connect.OtdDB2ConnectOTD otdDB2Connect_1, com.stc.connector.
appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Selectiong records from db_employee table
via Table Select........" );
FileClient_1.write();
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().select( input.getText() );
while (otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().next()) {
otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.setEmpNo( typeConverter.shortToString(
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().getEMP_NO(), "#", false, "" ) );
otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.setLastname( otdDB2Connect_1.
getDb_employee().getLAST_NAME() );
otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.setFirstname( otdDB2Connect_1.
getDb_employee().getFIRST_NAME() );
otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.setRate( otdDB2Connect_1.
getDb_employee().getRATE().toString() );
otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.setLastDate( typeConverter.
dateToString( otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().getLAST_UPDATE(),
"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss", false, "" ) );
FileClient_1.setText( otdOutputDTD_DB_Employee_1.marshalToString() );
FileClient_1.write();
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Table Select Done." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}Note - The content of the input.getText() file may contain null, meaning it will not have a where clause or it can contain a where clause such as empno > 50.
package prjDB2Connect_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdUpdate
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage
input, otdDB2Connect.OtdDB2ConnectOTD otdDB2Connect_1, com.stc.connector.
appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Updating the Rate and Last_update fields .. " );
FileClient_1.write();
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().update( input.getText() );
while (otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().next()) {
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().setLAST_NAME( "Krishna" );
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().setFIRST_NAME( "Kishore" );
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().updateRow();
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Update Done." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}Note - The content of the input.getText() file may contain null, meaning it will not have a where clause or it can contain a where clause such as empno > 50.
In this example DELETE an employee.
package prjDB2Connect_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdDelete
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage
input, otdDB2Connect.OtdDB2ConnectOTD otdDB2Connect_1, com.stc.connector.
appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Deleting record............" );
FileClient_1.write();
otdDB2Connect_1.getDb_employee().delete( input.getText() );
FileClient_1.setText( "Delete Done." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}A Prepared Statement is a SQL statement which can also contain parameter marker as input holder. For example:
select * from table1 where col1 > ?
This statement selects all the columns from a table called table1 if column col1 is greater than a certain value. The value will be supplied during runtime.
Note - The DB2 Connect Universal Driver only supports Updatable Resultsets for Update and Delete. The Insert operation is not supported. You can use a Prepared Statement to perform the Insert operation.
To perform an insert operation using Prepared Statement, do the following:
Assign values to input fields.
Execute the executeUpdate().
This example inserts employee records. The Prepared Statement looks like this:
Insert into DB_EMPLOYEE values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
Note - If you don’t want to insert values into all columns, your insert statement should look like this:
Insert into DB_EMPLOYEE (col1, col2) values (?, ?)
public class jcdPsInsert
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
otdDB2Connect.OtdDB2ConnectOTD otdDB2Connect_1, com.stc.connector.appconn.file.
FileApplication FileClient_1, dtd.otdInputDTD_654315252.DBemployees
otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1, dtd.otdOutputDTD1750519912.DBemployee
otdOutputDTD_DBemployee_1 )
throws Throwable
{
FileClient_1.setText( "Inserting records into db_employee table using
Prepared Statement....." );
FileClient_1.write();
otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.unmarshalFromString( input.getText() );
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.countX_sequence_A(); i1 += 1) {
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().setEMP_NO( typeConverter.stringToShort(
otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getEmpNo(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().setLAST_NAME( otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.
getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getLastname() );
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().setFIRST_NAME( otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.
getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getFirstname() );
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().setRATE( new java.math.BigDecimal(
otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getRate() ) );
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().setLAST_UPDATE( typeConverter.
stringToSQLDate( otdInputDTD_DBemployees_1.getX_sequence_A( i1 ).getLastDate(),
"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss", false, "" ) );
otdDB2Connect_1.getInsert_ps().executeUpdate();
}
FileClient_1.setText( "Insert Done......" );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
To perform an update operation using Prepared Statement, do the following:
Assign value to input field.
Execute the executeUpdate() method.
This example updates employee records which matches the where clause. The Prepared Statement looks like this:
Update DB_EMPLOYEE set rate = 19 where EMP_NO = ?
Note - The content of the input.getText() file must contain the input value to substitute the parameter marker “?”.
package prjDB2Connect_JCDjcdALL;
public class jcdPsUpdate
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public com.stc.codegen.util.CollaborationContext collabContext;
public com.stc.codegen.util.TypeConverter typeConverter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage input,
otdDB2Connect.OtdDB2ConnectOTD otdDB2Connect_1,
com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1 )
throws Throwable
{ FileClient_1.setText( "Update the Rate and Last_update fields using
Prepared Statement.. " );
FileClient_1.write();
otdDB2Connect_1.getUpdate_ps().setEmp_no
( typeConverter.stringToShort( input.getText(), "#", false, 0 ) );
otdDB2Connect_1.getUpdate_ps().executeUpdate();
FileClient_1.setText( "Done Update." );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
A Stored Procedure OTD represents a database stored procedure. Fields correspond to the arguments of a stored procedure while methods are the operations that you can apply to the OTD. It allows you to execute a stored procedure. Remember that while in the Collaboration Editor you can drag and drop nodes from the OTD into the Collaboration Editor.
The OTD represents the Stored Procedure “LookUpGlobal” with two parameters, an inbound parameter (INLOCALID) and an outbound parameter (OUTGLOBALPRODUCTID). These inbound and outbound parameters are generated by the Database Wizard and are represented in the resulting OTD as nodes. Within the Transformation Designer, you can drag values from the input parameters, execute the call, collect data, and drag the values to the output parameters.
Below are the steps for executing the Stored Procedure:
Specify the input values.
Execute the Stored Procedure.
Retrieve the output parameters if any.
For example:
package Storedprocedure;
public class sp_jce
{
public com.stc.codegen.logger.Logger logger;
public com.stc.codegen.alerter.Alerter alerter;
public void receive( com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileTextMessage
input,com.stc.connector.appconn.file.FileApplication FileClient_1,
employeedb.Db_employee employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1,insert_DB.
Insert_DBOTD insert_DB_1 )
throws Throwable
{
employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.unmarshalFromString( input.getText() );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().setEmployee_no( java.lang.Integer.
parseInt( employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.getEmployee_no() ) );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().setEmployee_Lname(
employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.getEmployee_lname() );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().setEmployee_Fname(
employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.getEmployee_fname() );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().setRate(
java.lang.Float.parseFloat( employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.getRate() ) );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().setUpdate_date(
java.sql.Timestamp.valueOf( employeedb_with_top_db_employee_1.getUpdate_date() ) );
insert_DB_1.getInsert_new_employee().execute();
insert_DB_1.commit();
FileClient_1.setText( "procedure executed" );
FileClient_1.write();
}
}
For Stored Procedures that return ResultSets and Update Count, the following methods are provided to manipulate the ResultSet:
DB2 Connect stored procedures do not return records as ResultSets, instead, the records are returned through output reference cursor parameters. Reference Cursor parameters are essentially ResultSets.
The resultsAvailable() method, added to the PreparedStatementAgent class, simplifies the whole process of determining whether any results, be it Update Counts or ResultSets, are available after a stored procedure has been executed. Although JDBC provides three methods (getMoreResults(), getUpdateCount(), and getResultSet()) to access the results of a stored procedure call, the information returned from these methods can be quite confusing to the inexperienced Java JDBC programmer and they also differ between vendors. You can simply call resultsAvailable() and if Boolean true is returned, you can expect either a valid Update Count when getUpdateCount() is called and/or the next ResultSet has been retrieved and made available to one of the ResultSet nodes defined for the Stored Procedure OTD, when that node’s available() method returns true.
Frequently, Update Counts information that is returned from a Stored Procedures is insignificant. You should process returned ResultSet information and avoid looping through all of the Update Counts. The following three methods control exactly what information should be returned from a stored procedure call. The enableResultSetsOnly() method, added to the PreparedStatement Agent class allows only ResultSets to be returned and thus every resultsAvailable() called only returns Boolean true if a ResultSet is available. Likewise, the enableUpdateCountsOnly() causes resultsAvailable() to return true only if an Update Count is available. The default case of enableResultsetsAndUpdateCount() method allows both ResultSets and Update Counts to be returned.
The Column data of the ResultSets can be dragged-and-dropped from their nodes to the Business Rules. Below is a code snippet that can be generated by the Collaboration Editor:
while (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().resultsAvailable())
{
if (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getUpdateCount() > 0)
{
System.err.println("Updated "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getUpdateCount()+" rows");
}
if (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getNormRS().available())
{
while (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getNormRS().next())
{
System.err.println("Customer Id = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getNormRS().getCustomerId());
System.err.println("Customer Name = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getNormRS().getCustomerName());
System.err.println();
}
System.err.println("===");
}
else if (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getDbEmployee().available())
{
while (getSPIn().getSpS_multi().getDbEmployee().next())
{
System.err.println("EMPNO = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getEMPNO());
System.err.println("ENAME = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getENAME());
System.err.println("JOB = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getJOB());
System.err.println("MGR = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getMGR());
System.err.println("HIREDATE = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getHIREDATE());
System.err.println("SAL = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getSAL());
System.err.println("COMM = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getCOMM());
System.err.println("DEPTNO = "+getSPIn().getSpS_multi().
getDbEmployee().getDEPTNO());
System.err.println();
}
System.err.println("===");
}
}
Note - resultsAvailable() and available() cannot be indiscriminately called because each time they move ResultSet pointers to the appropriate locations.
After calling resultsAvailable(), the next result (if available) can be either a ResultSet or an UpdateCount if the default enableResultSetsAndUpdateCount()was used.
Because of limitations imposed by some DBMSs, it is recommended that for maximum portability, all of the results in a ResultSet object should be retrieved before OUT parameters are retrieved. Therefore, you should retrieve all ResultSet(s) and Update Counts first followed by retrieving the OUT type parameters and return values.
The following list includes specific ResultSet behavior that you may encounter:
The method resultsAvailable() implicitly calls getMoreResults() when it is called more than once. You should not call both methods in your Java code. Doing so may result in skipped data from one of the ResultSets when more than one ResultSet is present.
The methods available() and getResultSet() can not be used in conjunction with multiple ResultSets being open at the same time. Attempting to open more the one ResultSet at the same time closes the previous ResultSet. The recommended working pattern is:
Open one Result Set (ResultSet_1) and work with the data until you have completed your modifications and updates. Open ResultSet_2, (ResultSet_1 is now closed) and modify. When you have completed your work in ResultSet_2, open any additional ResultSets or close ResultSet_2.
If you modify the ResultSet generated by the Execute mode of the Database Wizard, you need to assure the indexes match the stored procedure. By doing this, your ResultSet indexes are preserved.
Generally, getMoreResults does not need to be called. It is needed if you do not want to use our enhanced methods and you want to follow the traditional JDBC calls on your own.
The Database Wizard Assistant expects the column names to be in English when creating a ResultSet.
A Prepared Statement OTD represents a SQL statement that has been compiled. Fields in the OTD correspond to the input values that users need to provide. Prepared statements can be used to perform insert, update, delete and query operations. A prepared statement uses a question mark (?) as a place holder for input. For example:
insert into EMP_TAB(Age, Name, Dept No) value(?, ?, ?)
To execute a prepared statement, set the input parameters and call executeUpdate() and specify the input values if any.
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(23); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(”Peter Pan’); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(6); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().executeUpdate();
To achieve better performance, consider using a bulk insert if you have to insert many records. This is the “Add Batch” capability. The only modification required is to include the addBatch() method for each SQL operation and then the executeBatch() call to submit the batch to the database server. Batch operations apply only to Prepared Statements.
getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(23); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(”Peter Pan’); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(6); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().addBatch(); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setAge(45); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setName(”Harrison Ford’); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().setDeptNo(7); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().addBatch(); getPrepStatement().getPreparedStatementTest().executeBatch();