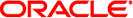Functional Architecture of Database Binding Component
The following figure shows the functional architecture of Database Binding Component.

The following table briefly describes the functional operation of each module or wizard.
Table 1 Functional Description
|
|
|---|
Installation Module |
Installs,
uninstalls, and manages the lifecycle of the Database BC. This module is used
to plug the Database BC into the JBI Framework and monitor the lifecycle
of the Binding Component such as install, uninstall, start, stop, and so on. |
Wizard Module |
Assists
in interacting with the database.
The Database Wizard create/edit interface queries the database to build WSDL from Database Table, Procedures, and Prepared SQL Statements. XSDs are created based on the Table, Procedures, and Prepared Statements in the external data source. Database Operations are added to provide the appropriate database functionality. The wizard assists in interacting with the database using JDBC API specific calls and ensures that appropriate methods are called and the data is formatted appropriately when manipulating the database. The Database Wizard can create XSDs based on any combination of Table, Procedures or Prepared Statements. The Database Wizard uses imported interfaces like the WSDL Editor and XSD Editor.
|
Wizard Launcher |
Launcher the Database Wizard. This interface basically plugged
in into the existing WSDL Editor Wizard. |
Schema Handler |
Is responsible for creating an XML Schema
for the corresponding table. The generated schema can be imported into the WSDL |
MetaData Handler |
Gets
the MetaData from the database and displays the data to the user through
the wizard. MetaData consists of the user-specific description of the table. MetaData handler
gets the MetaData of the TableColumns, Prepared Statements, and Procedures. This data is
supplied to the schema generator module to generate the schemas. |
WSDL Generator |
Generates the WSDL using
imported APIs and the Schema Handler. |
Database BC Runtime |
Provides the functionality for the Database BC
at runtime. The Database BC receives the normalized message it gets from the
NMR, denormalizes the message, and gathers the required parameters (JNDI name, Operations, and
so on) from the message. It processes the parameter, normalizes the output, and sends
it back to the NMR. |
Connection Handler |
Provides the functionality to get the connection from
different databases. This module uses the JMX API to create a connection pool
and the JNDI name to obtain the connection from the data source or
Java Naming API. This information is used to create JDBC resource and bind
it to the JDBC context of the JNDI tree. The Connection Handler uses
two methods to get connected to the database. If the user has already
created the JNDI name and wants to establish a connection to the database,
then the Connection Handler looks up the JNDI name in the JNDI context
and gets the connection. If the given JNDI Name does not exists the
Connection Handler binds as a new JDBC context to the JNDI tree
during deployment time. In the second method, the Connection Handler establishes a connection using
the connection parameters. (driver class name, URL, username, and password). |
Transaction Management |
The Database BC implements
the XAResource interface of JTA to be part of the global transaction and
enlists the resource with the Transaction Manager. The Transaction Manager is responsible for
starting and ending the XA Transaction. It implements the two-phase commit protocol to
support the global transaction. |
JMX Interface |
Provides a method to bind the Database BC context
to the JNDI tree of an application server context. |
JBI Framework |
Provides administration tools such as
install, uninstall, deploy, and undeploy and normalized message router functionality to the Database
BC. |
NetBeans Common Model |
The Database BC uses the WSDL Editor and XSD Editor imported models from
the NetBeans as part of the enterprise pack. |
|
Functional Architecture of the JDBC Binding Component — Comparative Study
The following figure depicts the functional architecture of the Database BC including various
logical components and external systems. The diagram is centered around the external and
internal interfaces provided by the binding component. The term interface is used in
a generic sense to mean any piece of information going back and forth
between components.
The architecture includes the following:
-
Public Private (External to Alaska)
-
Project Private (Internal to Alaska but External to JDBC BC)
-
Imported Interfaces
-
Exported Interfaces
-
Core JDBC BC Functional Modules