Home | Book List | Contents | Contact Us |
Go to main content
|
|
This chapter describes procedures that you can perform to extend the functionality of the connector for addressing your specific business requirements. This section discusses the following topics:
By default, this connector provides a set of attribute mappings that are used for reconciliation and provisioning operations between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. Depending on your business requirements, you can add and map additional attributes for reconciliation and provisioning operatiocns. To do so, you can extend the connector schema by adding new attributes to the get_schema() stored procedure in the OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER.pck wrapper package.
Extending the connector schema requires you to understand the following concepts:
Attribute initialization
The following initialization statement reserves an internal array that holds attribute definitions of the connector schema:
attr.extend(NUM);
Here, NUM defines the size of the array that is to be initialized. The size of the array must always be greater than or equal to the number of attributes defined. For example, the initialization statement attr.extend(20); reserves an internal array of 20 attributes for initialization.
Attribute definition
After initialization, you define the information for each attribute by adding a statement in the following format:
attr (ORD_NO) := attributeinfo(ATTR_NAME,ATTR_TYPE,CREATE_FLAG,UPDATE_FLAG,REQUIRED_FLAG,READ_FLAG);
In this format:
ORD_NO is the order of the attribute in the array. This is mandatory.
ATTR_NAME is the name of the child or single-valued attribute.
ATTR_TYPE is the SQL datatype of the child or single-valued attribute.
CREATE_FLAG is a flag to represent whether the attribute is required during a create provisioning operation.
UPDATE_FLAG is a flag to represent whether the attribute can be updated.
REQUIRED_FLAG is a flag to represent whether the attribute is mandatory.
READ_FLAG is flag to represent whether the attribute can be read.
A value of 1 or 0 for each flag denotes True or False, respectively. For example, a value 1, 0, 1, 0 for the flags means that the attribute is a mandatory attribute and must be considered during create provisioning operations.
Attribute array extension
You can increase the array size post initialization by including the following statement:
attr.extend;
Each inclusion of this statement increments the array size by 1.
By default, the fields listed in Table 4-4 are mapped for reconciliation between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. If required, you can map additional fields for trusted source reconciliation. The following sections describe the procedures to be performed for adding new attributes:
The following a summary of high-level steps to be performed to add a new attribute for trusted source reconciliation:
You must extend the connector schema by updating the DB wrapper package to include the new attribute for trusted source reconciliation as follows:
Open any SQL client. For example, SQL Developer.
Open the body of the OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER.pck wrapper package.
Select the get_schema() stored procedure. The list of attributes defined in the stored procedure is displayed.
If the number of attributes defined exceeds the number of attributes initialized, then:
Add the following attribute initialization statement:
attr.extend;
Enter the definition for the new attribute that you want to add in the following format:
attr (ORD_NO) := attributeinfo(ATTR_NAME,ATTR_TYPE,CREATE_FLAG,UPDATE_FLAG,REQUIRED_FLAG,READ_FLAG);
For example, if you are adding a new attribute to hold the blood type for a user account, then include the following statements:
attr.extend;
attr (28) := attributeinfo('BLOOD_TYPE','varchar2',1,1,0,1);
In this example, a value of 1,1,0,1 for the flags means that the BLOOD_TYPE attribute is required during create provisioning operations, it can be updated and read.
See Also:
Understanding Connector Schema Extension for more information about format in which you must add the new attribute definition
If the number of attributes defined does not exceed the number of attributes initialized then add only the definition for the new attribute. For example, attr (28) := attributeinfo('BLOOD_TYPE','varchar2',1,1,0,1);
Re-compile the wrapper package.
You must update the connector artifacts to include the new attribute added in Extending the Connector Schema for Trusted Source Reconciliation. Updating connector artifacts involves performing the following procedures:
To create a user-defined field (UDF) in Oracle Identity Manager, see Creating a Custom Attribute in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for detailed instructions.
Update the resource object to add a reconciliation field corresponding to the new attribute created in Updating the Oracle EBS HRMS Trusted User Resource Object as follows:
Blood Type.Create a reconciliation field mapping for the UDF (created in Creating a User-Defined Field) in the process definition as follows:
Add an entry for the attribute in the lookup definition for reconciliation attribute mapping as follows:
Blood Type.BLOOD_TYPE.Create a reconciliation profile to copy all the changes made to the resource object (in the earlier section) into MDS:
By default, the attributes listed in Table 3-4 are mapped for reconciliation between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. Similarly, the attributes listed in Table 3-3 are mapped for provisioning between Oracle Identity Manager and target system. If required, you can map additional fields for target resource reconciliation and provisioning. The following sections describe the procedures to be performed for adding new attributes:
The following is a summary of high-level steps to be performed to add a new attribute for trusted source reconciliation:
You must extend the connector schema by updating the DB wrapper package to include the new attribute for target resource reconciliation and provisioning as follows:
Open any SQL client. For example, SQL Developer.
Open the body of the OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER.pck wrapper package.
Select the get_schema() stored procedure. The list of attributes defined in the stored procedure is displayed.
If the number of attributes defined exceeds the number of attributes initialized, then:
Add the following attribute initialization statement:
attr.extend;
Enter the definition for the new attribute that you want to add in the following format:
attr (ORD_NO) := attributeinfo(ATTR_NAME,ATTR_TYPE,CREATE_FLAG,UPDATE_FLAG,REQUIRED_FLAG,READ_FLAG);
For example, if you are adding a new attribute to hold the blood type for a user account, then include the following statements:
attr.extend;
attr (28) := attributeinfo('BLOOD_TYPE','varchar2',1,1,0,1);
In the example, a value of 1,1,0,1 for the flags means that the BLOOD_TYPE attribute is required during create provisioning operations, it can be updated and read.
See Also:
Understanding Connector Schema Extension for more information about format in which you must add the new attribute definition
If the number of attributes defined does not exceed the number of attributes initialized then add only the definition for the new attribute. For example, attr (28) := attributeinfo('BLOOD_TYPE','varchar2',1,1,0,1);
Re-compile the wrapper package.
You must update the connector artifacts to include the new attribute added in Extending the Connector Schema for Target Resource Reconciliation and Provisioning. Updating connector artifacts involves performing the following procedures:
Update the resource object to add a reconciliation field corresponding to the new attribute created in Creating a User-Defined Field. as follows:
Blood Type.Create a reconciliation field mapping for the custom attribute in the process definition as follows:
Add an entry for the attribute in the lookup definition for reconciliation attribute mapping as follows:
Add an entry for the attribute in the lookup definition for provisioning attribute mapping as follows:
Blood Type.BLOOD_TYPE.Create a reconciliation profile to copy all the changes made to the resource object (in the earlier section) into MDS:
Update the search.properties file to include the new attribute as follows:
In order to support the Blood Type attribute during create and update provisioning operations, you must update the stored procedure that is invoked in the Procedures.properties file. To do so:
In a text editor, open the Procedures.properties file for editing.
Search for and determine the names of wrapper packages and stored procedures used for invoking the create person and update person provisioning operations. For example, OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER.CREATE_PERSON_API and OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER.UPDATE_PERSON_API are the wrapper packages and stored procedures used for the create person and update person provisioning operations.
Update the stored procedures determined in the earlier step as follows:
Open any SQL client. For example, SQL Developer.
Open the wrapper package and add the newly added attribute (for example, Blood Type) to the create person and update person stored procedures. For example, open the OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER package and add the newly added attribute to the CREATE_PERSON_API and UPDATE_PERSON_API stored procedures.
Figure 5-4 highlights the stored procedures that must be updated in the OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER package to include the newly added attribute.
Figure 5-4 Stored Procedures To Be Updated in OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER Package
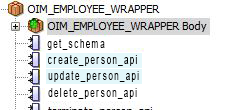
Select the CREATE_PERSON_API stored procedure and update the input parameters to include the newly added attribute.
Figure 5-5 highlights the newly added attribute in both the CREATE_PERSON_API and UPDATE_PERSON_API stored procedures.
Figure 5-5 Stored Procedures with the Newly Added Attribute

Open OIM_EMPLOYEE_WRAPPER Body and select the CREATE_PERSON_API stored procedure.
Update the HR_EMPLOYEE_API.create_employee API call in the procedure with the newly added attribute.
Figure 5-6 shows the updated HR_EMPLOYEE_API.create_employee API.
Figure 5-6 HR_EMPLOYEE_API.create_employee API with the Newly Added Attribute

Update the HR_CONTINGENT_WORKER_API.create_cwk API call in the procedure with the newly added attribute.
Figure 5-7 shows the updated HR_CONTINGENT_WORKER_API.create_cwk API.
Figure 5-7 HR_CONTINGENT_WORKER_API.create_cwk API with the Newly Added Attribute

Repeat Steps 3.c through 3.f to update the UPDATE_PERSON_API stored procedure to include the newly added attribute.
Re-compile the wrapper package.
By default, the attributes listed in Table 3-4 are mapped for reconciliation between Oracle Identity Manager and the target system. Similarly, the attributes listed in Table 3-3 are mapped for provisioning between Oracle Identity Manager and target system. If required, you can map additional multivalued attributes for target resource reconciliation and provisioning. See Adding New Multivalued Attributes for Reconciliation and Provisioning in Oracle Identity Manager Connector Guide for Oracle E-Business Suite User Management for detailed information about the procedure to add a new multivalued attribute.
Note:
This section describes an optional procedure. Perform this procedure only if you want to configure transformation of data during reconciliation.
To configure transformation of data:
Write code that implements the required transformation logic in a Java class.
The following sample transformation class creates a value for the Email attribute by using values fetched from the EMAIL_ADDRESS column of the target system:
package oracle.iam.connectors.common.transform;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class TransformAttribute {
/*
Description:Abstract method for transforming the attributes
param hmUserDetails<String,Object>
HashMap containing parent data details
param hmEntitlementDetails <String,Object>
HashMap containing child data details
*/
public Object transform(HashMap hmUserDetails, HashMap hmEntitlementDetails,String sField) {
/*
* You must write code to transform the attributes.
Parent data attribute values can be fetched by
using hmUserDetails.get("Field Name").
*To fetch child data values, loop through the
* ArrayList/Vector fetched by hmEntitlementDetails.get("Child Table")
* Return the transformed attribute.
*/
String sEmail= "trans" + (String)hmUserDetails.get(sField);
return sEmail;
}
}
Create a JAR file to hold the Java class.
Run the Oracle Identity Manager Upload JARs utility to post the JAR file to the Oracle Identity Manager database. This utility is copied into the following location when you install Oracle Identity Manager:
Note:
Before you use this utility, verify that the WL_HOME environment variable is set to the directory in which Oracle WebLogic Server is installed.
For Microsoft Windows:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.bat
For UNIX:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.sh
When you run the utility, you are prompted to enter the login credentials of the Oracle Identity Manager administrator, URL of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer, context factory value, type of JAR file being uploaded, and the location from which the JAR file is to be uploaded. Specify 1 as the value of the JAR type.
Create a lookup definition for transformation and add an entry to it as follows:
Log in to the Design Console.
Expand Administration, and then double-click Lookup Definition.
In the Code field, if you are using the HRMS Trusted connector, enter Lookup.Oracle EBSHRMS.Person.ReconTransformation as the name of the lookup definition.
In the Code field, if you are using the HRMS Target connector, enter Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ReconTransformation as the name of the lookup definition.
Select the Lookup Type option.
On the Lookup Code Information tab, click Add.
A new row is added.
In the Code Key column, enter the name of the resource object field into which you want to store the transformed value. For example: Email.
In the Decode column, enter the name of the class that implements the transformation logic. For example, oracle.iam.connectors.common.transform.TransformAttribute.
Save the changes to the lookup definition.
Add an entry in the Configuration lookup definition to enable transformation as follows:
Expand Administration, and then double-click Lookup Definition.
For the HRMS Trusted connector, search for and open Lookup.EBSHRMS.Person.Configuration.Trusted lookup definition.
For the HRMS Target connector, search for and open Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.Configuration lookup definition.
Create an entry that holds the name of the lookup definition used for transformation as follows:
Code Key: Recon Transformation Lookup
Decode: Depending on the connector that you are using, enter one of the value:
For HRMS Trusted connector:
Lookup.EBSHRMS.Person.ReconTransformation.Trusted
For HRMS Target connector:
Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ReconTransformation
Save the changes to the lookup definition.
You can configure validation of reconciled and provisioned single-valued data according to your requirements. For example, you can validate data fetched from the Email attribute to ensure that it does not contain the number sign (#). In addition, you can validate data entered in the First Name field on the process form so that the number sign (#) is not sent to the target system during provisioning operations.
For data that fails the validation check, the following message is displayed or recorded in the log file:
oracle.iam.connectors.icfcommon.recon.SearchReconTask : handle : Recon event skipped, validation failed [Validation failed for attribute: [FIELD_NAME]]
To configure validation of data:
Write code that implements the required validation logic in a Java class.
The following sample validation class checks if the value in the Email attribute contains the number sign (#):
package com.validate;
import java.util.*;
public class MyValidation {
public boolean validate(HashMap hmUserDetails,
HashMap hmEntitlementDetails, String field) {
/*
* You must write code to validate attributes. Parent
* data values can be fetched by using hmUserDetails.get(field)
* For child data values, loop through the
* ArrayList/Vector fetched by hmEntitlementDetails.get("Child Table")
* Depending on the outcome of the validation operation,
* the code must return true or false.
*/
/*
* In this sample code, the value "false" is returned if the field
* contains the number sign (#). Otherwise, the value "true" is
* returned.
*/
boolean valid=true;
String sEmail=(String) hmUserDetails.get(field);
for(int i=0;i<sEmail.length();i++){
if (sEmail.charAt(i) == '#'){
valid=false;
break;
}
}
return valid;
}
}
Create a JAR file to hold the Java class.
Run the Oracle Identity Manager Upload JARs utility to post the JAR file to the Oracle Identity Manager database. This utility is copied into the following location when you install Oracle Identity Manager:
Note:
Before you use this utility, verify that the WL_HOME environment variable is set to the directory in which Oracle WebLogic Server is installed.
For Microsoft Windows:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.bat
For UNIX:
OIM_HOME/server/bin/UploadJars.sh
When you run the utility, you are prompted to enter the login credentials of the Oracle Identity Manager administrator, URL of the Oracle Identity Manager host computer, context factory value, type of JAR file being uploaded, and the location from which the JAR file is to be uploaded. Specify 1 as the value of the JAR type.
If you created the Java class for validating a process form field for reconciliation, then:
Log in to the Design Console.
Expand Administration, and then double-click Lookup Definition.
In the Code field, enter Lookup.Oracle EBSHRMS.UM.ReconValidation as the name of the lookup definition.
In the Code field, if you are using the HRMS Trusted connector, enter Lookup.Oracle EBSHRMS.Person.ReconValidation as the name of the lookup definition.
In the Code field, if you are using the HRMS Target connector, enter Lookup.Oracle Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ReconValidation as the name of the lookup definition
Select the Lookup Type option.
On the Lookup Code Information tab, click Add.
A new row is added.
In the Code Key column, enter the resource object field name. For example, Email.
In the Decode column, enter the class name. For example, com.validate.MyValidation.
Save the changes to the lookup definition.
Depending on the connector that you are using, search for and open one of the following lookup definitions:
For HRMS Trusted connector:
Lookup.EBSHRMS.Person.Configuration.Trusted
For HRMS Target connector
Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.Configuration
Create an entry with the following values:
Code Key: Recon Validation Lookup
Decode: Depending on the connector that you are using, enter one of the value:
For HRMS Trusted connector:
Lookup.EBSHRMS.Person.ReconValidation.Trusted
For HRMS Target connector
Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ReconValidation
Save the changes to the lookup definition.
If you created the Java class for validating a process form field for provisioning, then:
Note:
Perform the procedure described in this step only of you are using the HRMS Target connector.
Log in to the Design Console.
Expand Administration, and then double-click Lookup Definition.
In the Code field, enter Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ProvValidation as the name of the lookup definition.
Select the Lookup Type option.
On the Lookup Code Information tab, click Add.
A new row is added.
In the Code Key column, enter the process form field name. In the Decode column, enter the class name.
Save the changes to the lookup definition.
Search for and open the Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.Configuration lookup definition.
Create an entry with the following values:
Code Key: Provisioning Validation Lookup
Decode: Lookup.EBSHRMS.UM.ProvValidation
Save the changes to the lookup definition.