1 About the Office 365 Connector
The Office 365 connector integrates Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) with the Office 365 service.
The following topics provide a high-level overview of the Office 365 connector:
1.1 Introduction to Office 365 Connector
The Office 365 connector enables you to manage all your user and group identities in Office 365. This connector also provides management of entitlements such as roles, licenses, and groups for your user identities.
Note:
At some places in this guide, Office 365 has been referred to as the target system.
In the account management (target resource) mode of the connector, information about users created or modified directly on the target system can be reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager. This data is used to add or modify resources (that is, accounts) allocated to OIM Users. In addition, you can use Oracle Identity Manager to provision or update Office 365 resources (accounts) assigned to OIM Users. These provisioning operations performed on Oracle Identity Manager translate into the creation or updates to target system accounts.
In the identity reconciliation (trusted source) mode of the connector, users are created or modified only on the target system and information about these users is reconciled into Oracle Identity Manager.
1.2 Certified Components for the Office 365 Connector
These are the software components and their versions required for installing and using Office 365 connector.
Table 1-1 lists the required components for the Office 365 Connector.
Table 1-1 Certified Components
| Component | Requirement |
|---|---|
|
Oracle Identity Governance or Oracle Identity Manager |
You can use one of the following releases of Oracle Identity Governance or Oracle Identity Manager:
|
|
Target systems |
Microsoft Office 365 Enterprise Editions |
|
Connector Server |
11.1.2.1.0 |
|
Connector Server JDK |
JDK 1.6 or Later |
1.3 Certified Languages for Office 365 Connector
These are the languages that the connector supports.
-
Arabic
-
Chinese (Simplified)
-
Chinese (Traditional)
-
Czech
-
Danish
-
Dutch
-
English (US)
-
Finnish
-
French
-
French (Canadian)
-
German
-
Greek
-
Hebrew
-
Hungarian
-
Italian
-
Japanese
-
Korean
-
Norwegian
-
Polish
-
Portuguese
-
Portuguese (Brazilian)
-
Romanian
-
Russian
-
Slovak
-
Spanish
-
Swedish
-
Thai
-
Turkish
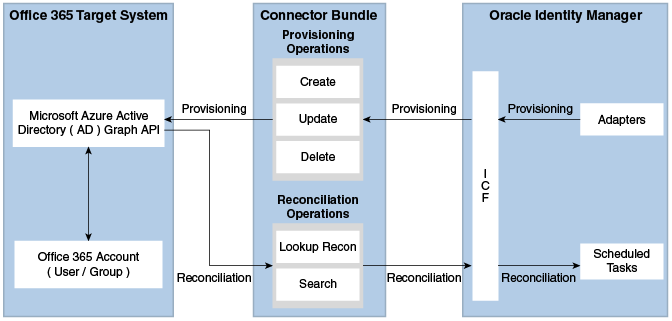
1.4 Connector Architecture of the Office 365 Connector
The Office 365 connector is implemented by using the Identity Connector Framework (ICF).
The ICF is a component that is required in order to use Identity Connector. ICF provides basic reconciliation and provisioning operations that are common to all Oracle Identity Manager connectors. In addition, ICF provides common features that developers would otherwise need to implement on their own, such as, buffering, time outs, and filtering. ICF is distributed together with Oracle Identity Manager. Therefore, you do not need to configure or modify ICF.
Figure 1-1 shows the architecture of the Office 365 connector.
-
Identity reconciliation
Identity reconciliation is also known as authoritative or trusted source reconciliation. In this mode, the target system is used as the trusted source and users are directly created and modified on it. During reconciliation, a scheduled task invokes an ICF operation. ICF inturn invokes a search operation on the Office 365 Identity Connector Bundle and then the bundle calls Office 365 API for Reconciliation operation. The API extracts user records that match the reconciliation criteria and hands them over through the bundle and ICF back to the scheduled task, which brings the records to Oracle Identity Manager.
Each user record fetched from the target system is compared with existing OIM Users. If a match is found between the target system record and the OIM User, then the OIM User attributes are updated with changes made to the target system record. If no match is found, then the target system record is used to create an OIM User.
-
Account management
Account management is also known as target resource management. In this mode, the target system is used as a target resource and the connector enables the following operations:
-
Provisioning
Provisioning involves creating, updating, or deleting users on the target system through Oracle Identity Manager. During provisioning, the Adapters invoke ICF operation, ICF inturn invokes create operation on the Office 365 Identity Connector Bundle and then the bundle calls the target system API (Microsoft Azure Active Directory (AD) Graph API) for provisioning operations. The API on the target system accepts provisioning data from the bundle, carries out the required operation on the target system, and returns the response from the target system back to the bundle, which passes it to the adapters.
-
Target resource reconciliation
During reconciliation, a scheduled task invokes an ICF operation. ICF inturn invokes a search operation on the Office 365 Identity Connector Bundle and then the bundle calls Office 365 API for Reconciliation operation. The API extracts user records that match the reconciliation criteria and hands them over through the bundle and ICF back to the scheduled task, which brings the records to Oracle Identity Manager.
Each record fetched from the target system is compared with Office 365 resources that are already provisioned to OIM Users. If a match is found, then the update made to the Office 365 record from the target system is copied to the Office 365 resource in Oracle Identity Manager. If no match is found, then the user ID of the record is compared with the user ID of each OIM User. If a match is found, then data in the target system record is used to provision an Office 365 resource to the OIM User.
-
The Office 365 Identity Connector Bundle communicates with the Microsoft Azure Active Directory Graph API using the HTTPS protocol. The Microsoft Azure Active Directory Graph API provides programmatic access to Azure Active Directory through REST API endpoints. Apps can use the Microsoft Azure Active Directory Graph API to perform create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations on directory data and directory objects, such as users, groups.
See Also:
Understanding the Identity Connector Framework in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about ICF
1.5 Use Cases Supported by the Office 365 Connector
The Office 365 connector is used to integrate OIM with Office 365 to ensure that all Office 365 accounts are created, updated, and deactivated on an integrated cycle with the rest of the identity-aware applications in your enterprise. The Office 365 connector supports management of identities for Cloud Identity, Synchronized Identity, and Federated Identity models of Office 365. In a typical IT scenario, an organization using OIM wants to manage accounts, groups, roles and licenses across Office 365 Cloud Service.
-
Office 365 User Management
An organization using Office 365 wants to integrate with OIM to manage identities. The organization wants to manage its user identities by creating them in the target system using OIM. The organization also wants to synchronize user identity changes performed directly in the target system with OIM. In such a scenario, a quick and an easy way is to install the Office 365 connector and configure it with your target system by providing connection information in the IT resource.
To create a new user in the target system, fill in and submit the OIM process form to trigger the provisioning operation. The connector executes the CreateOp operation against your target system and the user is created on successful execution of the operation. Similarly, operations like delete and update can be performed.
To search or retrieve the user identities, you must run a scheduled task from OIM. The connector will run the corresponding SearchOp against the user identities in the target system and fetch all the changes to OIM.
-
Office 365 Group Management
An organization has a number of Office 365 Security Groups allowing its users to set up new groups, manage memberships, and delete groups. The organization now wants to know the list of groups that have not been recently accessed or who have inactive members. In such a scenario, you can use the Office 365 connector to highlight the usage trend for groups. By using the Office 365 connector, you can leverage the reporting capabilities of Oracle Identity Manager to track any operations (such as create, update, delete) performed on groups and changes made in their memberships .
-
Office 365 Admin Role Management
In large organizations, it may be necessary for an administrator to designate other employees to act as administrators to serve different functions. For example, you can set admin roles for your IT staff that can act as support agents to other employees, partners, customers and vendors. With the Office 365 connector, you can assign or revoke an Office 365 admin role to users as an entitlement, thus facilitating you to leverage the delegated administration capability of Office 365.
-
Office 365 User License Management
Another scenario is one in which an organization is using Office 365 for business and manages user licenses as per the changing needs of the organization by assigning or unassigning licenses for users. What is needed is an effective way to keep track of all the licenses and user rights both in cloud and on-premise servers. In such a scenario, you can use the Office 365 connector to effectively track all user licenses. You can keep track of these license assignment changes by leveraging OIM capability of auditing and reporting.
1.6 Features of the Office 365 Connector
The features of the connector include support for connector server, full reconciliation, limited reconciliation, and reconciliation of deleted account data.
1.6.1 Full Reconciliation
In full reconciliation, all records are fetched from the target system to Oracle Identity Manager.
Note:
The connector supports incremental reconciliation if the target system contains an attribute that holds the timestamp at which an object is created or modified.1.6.2 Support for the Connector Server
Connector Server is one of the features provided by ICF. By using one or more connector servers, the connector architecture permits your application to communicate with externally deployed bundles.
A Java connector server is useful when you do not want to execute a Java connector bundle in the same VM as your application. It can be beneficial to run a Java connector on a different host for performance improvements if the bundle works faster when deployed on the same host as the native managed resource.
See Installation.
See Also:
Using an Identity Connector Server in Oracle Fusion Middleware Developing and Customizing Applications for Oracle Identity Manager for more information about installing and configuring connector server and running the connector server
1.6.3 Limited (Filtered) Reconciliation
You can reconcile records from the target system based on a specified filter criterion.
You can set a reconciliation filter as the value of the Filter Suffix attribute of the user reconciliation scheduled job. This filter specifies the subset of newly added and modified target system records that must be reconciled. The Filter Suffix attribute helps you to assign filters to the API based on which you will get a filtered response from target.
1.6.4 Transformation and Validation of Account Data
You can configure validation of account data that is brought into or sent from Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation and provisioning.
In addition, you can configure transformation of account data that is brought into Oracle Identity Manager during reconciliation. The following sections provide more information
1.7 Lookup Definitions Used During Reconciliation and Provisioning
Lookup definitions used during reconciliation and provisioning are either preconfigured or can be synchronized with the target system.
This section discusses the following categories of lookup definitions:
1.7.1 Lookup Definitions Synchronized with the Target System
After you deploy the connector, the following lookup definitions, which are used as an input source for lookup fields, are automatically created in Oracle Identity Manager:
-
Lookup.Office365.Groups
-
Lookup.Office365.Roles
-
Lookup.Office365.Licenses
-
Lookup.Office365.Manager
These lookup definitions are empty by default. They are populated with values fetched from the target system when you run the scheduled jobs for lookup field synchronization. For example, when you run the scheduled job for role lookup field synchronization, all Roles on the target system are fetched to Oracle Identity Manager and populated in the Lookup.Office365.Roles lookup definition.
After lookup field synchronization, data in each of the lookup definitions for lookup field synchronization is stored in the following format:
-
Code Key: <IT_RESOURCE_NAME>~<FIELD_VALUE>
In this format:-
IT_RESOURCE_NAME is the name of the IT resource in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
FIELD_VALUE is the value of the field in the target system.
Office365~System Administrator.In this example,Office365is the name of the IT resource andSystem Administratoris the value of the Role field in the target system. -
-
Decode: <IT_RESOURCE_KEY>~<FIELD_VALUE_ID>
In this format:-
IT_RESOURCE_KEY is the numeric code assigned to an IT resource in Oracle Identity Manager.
-
FIELD_VALUE_ID is the ID of the target system field value.
89~1b5d6697-f4a6-4f03-8df7-4fae1512fd16In this example,89is the numeric code assigned to the IT resource associated with the target system and1b5d6697-f4a6-4f03-8df7-4fae1512fd16is the ID of the Role in the target system. -
Table 1-2 shows sample entries in the Lookup.Office365.Groups lookup definition.
Table 1-2 Sample Entries in the Lookup.Office365.Groups Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode |
|---|---|
|
Office365~Finance |
89~9b3b3faf-e7fb-427e-8038-b8021cfbab30 |
|
Office365~HR |
89~eb1b204e-2de0-41ec-98e9-1c33684d698a |
|
Office365~ISP |
89~4457f158-d1ec-47f2-aeb4-79d5a2be0e38 |
1.7.2 Preconfigured Lookup Definitions
Preconfigured lookup definitions are the other lookup definitions that are created in Oracle Identity Manager when you deploy the connector. These lookup definitions are either prepopulated with values or values must be manually entered in them after the connector is deployed.
The other lookup definitions are as follows:
1.7.2.1 Lookup.Office365.Configuration
The Lookup.Office365.Configuration lookup definition holds connector configuration entries that are used during target resource reconciliation and provisioning operations.
Note:
Do not modify the entries in this lookup definition.Table 1-3 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.Configuration Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Bundle Name |
org.identityconnectors.genericrest |
This entry holds the name of the connector bundle. |
|
Bundle Version |
1.0.1115 |
This entry holds the version of the connector bundle. |
|
Connector Name |
org.identityconnectors.genericrest.GenericRESTConnector |
This entry holds the name of the connector class. |
|
Group Configuration Lookup |
Lookup.Office365.GM.Configuration |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that contains group-specific configuration properties. This lookup definition is used as the configuration lookup definition when you perform reconciliation of groups. |
|
relURI’s |
"__ACCOUNT__.CREATEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.UPDATEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users?$(api_version)$/$(Filter Suffix)$","__ACCOUNT__=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.manager.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/manager?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.manager=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/$links/manager?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/memberOf?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.DELETEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/groups/$(__GROUP__.objectId)$/$links/members/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__=/$(tenant_id)$/groups/$(__GROUP__.objectId)$/$links/members?$(api_version)$","__GROUP__.CREATEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/groups?$(api_version)$","__GROUP__.UPDATEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/groups/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__GROUP__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/groups?$(api_version)$/$(Filter Suffix)$","__GROUP__=/$(tenant_id)$/groups/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__GROUP__.member=/$(tenant_id)$/groups/$(__UID__)$/$links/members?$(api_version)$","__ROLE__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/directoryRoles?$(api_version)$/$(Filter Suffix)$","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__=/$(tenant_id)$/directoryRoles/$(__ROLE__.objectId)$/$links/members?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.DELETEOP=/$(tenant_id)$/directoryRoles/$(__ROLE__.objectId)$/$links/members/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__ROLE__.member=/$(tenant_id)$/directoryRoles/$(__UID__)$/$links/members?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/memberOf?$(api_version)$","__LICENSE__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/subscribedSkus?$(api_version)$/$(Filter Suffix)$","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.ADDATTRIBUTE=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/assignLicense?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.REMOVEATTRIBUTE=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/assignLicense?$(api_version)$" |
This entry holds the relative URL of every object class supported by this connector and the connector operations that can be performed on these object classes. For example, the |
|
User Configuration |
Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that stores configuration information used during user management operations. |
|
nameAttributes |
"__ACCOUNT__.userPrincipalName","__GROUP__.displayName","__ROLE__.displayName","__LICENSE__.skuPartNumber" |
This entry holds the name attribute for all the objects that are handled by this connector. For example, for the __ACCOUNT__ object class that it used for User accounts, the name attribute is userPrincipalName. |
|
uidAttributes |
"__ACCOUNT__.objectId","__GROUP__.objectId","__ROLE__.objectId","__LICENSE__.skuId” |
This entry holds the uid attribute for all the objects that are handled by this connector. For example, for User accounts, the uid attribute is objectId. In other words, the value “__ACCOUNT__.objectId” in decode implies that the __UID__ attribute (that is, GUID) of the connector for __ACCOUNT__ object class is mapped to objectId which is the corresponding uid attribute for user accounts in the target system. |
|
statusAttribute |
“__ACCOUNT__.accountEnabled” |
This entry lists the name of the target system attribute that holds the status of an account. For example, for the __ACCOUNT__ object class that it used for User accounts, the status attribute is accountEnabled. |
|
Any Incremental Recon Attribute Type |
True |
By default, during incremental reconciliation, OIM accepts timestamp information sent from the target system only in Long datatype format. A decode value of True for the Incremental Recon Attribute Type entry indicates that OIM will accept timestamp information in any datatype format. |
|
customPayload |
\"}","__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.CREATEOP={\"url \":\<tenant_id>/directoryObjects/ <__UID__> \"}","__ACCOUNT__.manager.CREATEOP={\"url\": \<tenant_id>/directoryObjects/ <manager> \"}","__ACCOUNT__.manager.UPDATEOP={\"url\": \<tenant_id>/directoryObjects/ <manager> \"}","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.UPDATEOP={\"url\": \<tenant_id>/directoryObjects/ <__UID__> \"}","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.CREATEOP={\"url\": \<tenant_id>/directoryObjects/ <__UID__> \"}","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.ADDATTRIBUTE ={\"addLicenses\": [{\"skuId\": \"<skuId>\"}], \"removeLicenses\": []}","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.REMOVEATTRIBUTE={\"addLicenses\": [],\"removeLicenses\": [\"<skuId>\"]}" |
This entry lists the payloads for all operations that are not in the standard format. |
|
httpHeaderAccept |
application/json |
This entry holds the accept type expected from the target system in the header. |
|
httpHeaderContentType |
application/json |
This entry holds the content type expected by the target system in the header. |
|
jsonResourcesTag |
"__ACCOUNT__=value","__GROUP__=value","__ROLE__=value","__LICENSE__=value" |
This entry holds the json tag value that is used during reconciliation for parsing multiple entries in a single payload. |
|
opTypes |
“__ACCOUNT__.CREATEOP=POST","__ACCOUNT__.UPDATEOP=PATCH","__ACCOUNT__.SEARCHOP=GET", "__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.UPDATEOP=POST","__ACCOUNT__.manager.CREATEOP=PUT","__ACCOUNT__.manager.UPDATEOP=PUT", "__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.UPDATEOP=POST","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.ADDATTRIBUTE=POST","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.REMOVEATTRIBUTE=POST" |
This entry specifies the HTTP operation type for each object class supported by the connector. Values are comma separated and are in the following format: OBJ_CLASS.OP=HTTP_OP In this format, OBJ_CLASS is the connector object class, OP is the connector operation (for example, CreateOp, UpdateOp, SearchOp), and HTTP_OP is the HTTP operation (GET, PUT, or POST). |
|
passwordAttribute |
passwordProfile.password |
This entry holds the name of the target system attribute that is mapped to the __PASSWORD__ attribute of the connector in OIM. |
|
specialAttributeHandling |
"__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.CREATEOP=SINGLE","__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__.UPDATEOP=SINGLE","__ACCOUNT__.manager.CREATEOP=SINGLE" ,"__ACCOUNT__.manager.UPDATEOP=SINGLE","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.CREATEOP=SINGLE","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__.UPDATEOP=SINGLE", "__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.ADDATTRIBUTE=SINGLE","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__.REMOVEATTRIBUTE=SINGLE" |
This entry lists the special attributes whose values should be send to target one by one ("SINGLE"). Values are comma separated and are in the following format: OBJ_CLASS.ATTR_NAME.PROV_OP=SINGLE For example, the |
|
specialAttributeTargetFormat |
"__ACCOUNT__.manager=objectId","__GROUP__.member=url","__ROLE__.member=url", "__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__=value","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__=value","__ROLE__.member=value", "__GROUP__.member=value","__ACCOUNT__.__LICENSE__=value.skuId" |
This entry lists the format in which an attribute is present in the target system endpoint. For example, the alias attribute will be present as aliases.alias in the target system endpoint. Values are comma separated and are presented in the following format: OBJ_CLASS.ATTR_NAME= TARGET_FORMAT |
|
targetObjectIdentifier |
"__ACCOUNT__.__GROUP__=objectType;Group","__ACCOUNT__.__ROLE__=objectType;Role" |
This entry specifies the key-value pair for replacing place holders in the relURIs. Values are comma separated and in the KEY;VALUE format. |
1.7.2.2 Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration
The Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration lookup definition holds configuration entries that are specific to the user object type. This lookup definition is used during user management operations.
Table 1-4 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Provisioning Attribute Map |
Lookup.Office365 UM.ProvAttrMap |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps process form fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is used during user provisioning operations. |
|
Recon Attribute Map |
Lookup.Office365 UM.ReconAttrMap |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps resource object fields and target system attributes.. This lookup definition is used during reconciliation. |
1.7.2.3 Lookup.Office365.UM.ProvAttrMap
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ProvAttrMap lookup definitions hold mappings between process form fields and target system attributes.
This lookup definition is preconfigured and used during provisioning. Table 1-5 lists the default entries.
You can add entries in this lookup definitions if you want to map new target system attributes for provisioning. See Adding New User or Group Attributes for Provisioning.
1.7.2.4 Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and target system attributes.
This lookup definition is preconfigured and used during target resource reconciliation. Table 1-12 lists the default entries.
You can add entries in this lookup definitions if you want to map new target system attributes for target resource reconciliation. See Adding New User or Group Attributes for Reconciliation.
1.7.2.5 Lookup.Office365.GM.Configuration
The Lookup.Office365.GM.Configuration lookup definition holds configuration entries that are specific to the group object type. This lookup definition is used during group management operations when your target system is configured as a target resource.
Do not modify the entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-5 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.GM.Configuration Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Provisioning Attribute Map |
Lookup.Office365 GM.ProvAttrMap |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps process form fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is discussed later in the guide. |
|
Recon Attribute Map |
Lookup.Office365 GM.ReconAttrMap |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps resource object fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is discussed later in the guide. |
1.7.2.6 Lookup.Office365.GM.ProvAttrMap
The Lookup.Office365.GM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition holds mappings between process form fields and target system attributes.
This lookup definition is preconfigured and used during group provisioning operations.Table 1-17 lists the default entries.
You can add entries in this lookup definitions if you want to map new target system attributes for provisioning. See Adding New User or Group Attributes for Provisioning.
1.7.2.7 Lookup.Office365.GM.ReconAttrMap
The Lookup.Office365.GM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and target system attributes.
This lookup definition is preconfigured and used during target resource reconciliation of groups. Table 1-13 lists the default entries.
You can add entries in this lookup definitions if you want to map new target system attributes for reconciliation. See Adding Attributes to the Resource Object for more information.
1.7.2.8 Lookup.Office365.BooleanValues
The Lookup.Office365.BooleanValues lookup definition maps boolean values that are used for some of the fields in the target system with the corresponding boolean values to be displayed in the fields of the OIM User form.
Table 1-6 lists the default entries in the Lookup.Office365.BooleanValues lookup definition.
Table 1-6 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.BooleanValues Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
true |
True |
|
false |
False |
1.7.2.9 Lookup.Office365.Countries
The Lookup.Office365.Countries lookup definition holds information about country names that you can select for a target system account that you create through Oracle Identity Manager. This is a static lookup definition.
You must populate the entries of this lookup definition manually. The following is the format of the Code Key and Decode values in this lookup definition:
-
Code Key: 2–letter ISO code for a country
-
Decode: Country name
Table 1-7 lists the default entries in the Lookup.Office365.Countries lookup definition:
Table 1-7 Default Entries in the Lookup.Office365.Countries Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
US |
United States |
|
UK |
United Kingdom |
1.7.2.10 Lookup.Office365.UsageLocation
The Lookup.Office365.UsageLocation lookup definition holds information about license usage locations that you can select for a target system account that you create through Oracle Identity Manager. This is a static lookup definition.
You must populate the entries of this lookup definition manually. The following is the format of the Code Key and Decode values in this lookup definition:
-
Code Key: 2–letter ISO code for a country
-
Decode: Country name
Table 1-8 lists the default entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-8 Default Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UsageLocation Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
US |
United State |
|
UK |
United Kingdom |
|
JP |
Japan |
1.7.2.11 Lookup.Office365.Configuration.Trusted
The Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration.Trusted lookup definition holds configuration entries that are used during trusted source reconciliation.
Note:
Do not modify the entries in this lookup definitionTable 1-9 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.Configuration.Trusted
| Code Key | Decode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Bundle Name |
org.identityconnectors.genericrest |
This entry holds the name of the connector bundle. |
|
Bundle Version |
1.0.1115 |
This entry holds the version of the connector bundle. |
|
Connector Name |
org.identityconnectors.genericrest.GenericRESTConnector |
This entry holds the name of the connector class. |
|
relURI’s |
"__ACCOUNT__.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users?$(api_version)$/$(Filter Suffix)$","__ACCOUNT__=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.manager.SEARCHOP=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/manager?$(api_version)$","__ACCOUNT__.manager=/$(tenant_id)$/users/$(__UID__)$/$links/manager?$(api_version)$"" |
The entry holds the relative URL of every object class supported by this connector and the connector operations that can be performed on these object classes. For example, the |
|
User Configuration Lookup |
Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration.Trusted |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that contains user-specific configuration properties. Do not modify this entry. |
|
nameAttributes |
"__ACCOUNT__.userPrincipalName " |
This entry holds the name attribute for all the objects that are handled by this connector. For example, for the __ACCOUNT__ object class that it used for User accounts, the name attribute is userPrincipalName. |
|
uidAttributes |
"__ACCOUNT__.objectId” |
This entry holds the uid attribute for all the objects that are handled by this connector. For example, for User accounts, the uid attribute is objectId. In other words, the value “__ACCOUNT__.objectId” in decode implies that the __UID__ attribute (that is, GUID) of the connector for __ACCOUNT__ object class is mapped to objectId which corresponds to the uid attribute of user accounts in the target system. |
|
statusAttribute |
“__ACCOUNT__.accountEnabled” |
This entry lists the name of the target system attribute that holds the status of an account. For example, for the __ACCOUNT__ object class that it used for User accounts, the status attribute is accountEnabled. |
|
Any Incremental Recon Attribute Type |
True |
By default, during incremental reconciliation, OIM accepts timestamp information sent from the target system only in Long datatype format. A decode value of True for the Incremental Recon Attribute Type entry indicates that OIM will accept timestamp information in any datatype format. |
|
httpHeaderAccept |
application/json |
This entry holds the accept type expected from the target system in the header. |
|
httpHeaderContentType |
application/json |
This entry holds the content type expected by the target system in the header. |
|
jsonResourcesTag |
"__ACCOUNT__=value" |
This entry holds the json tag value that is used during reconciliation for parsing multiple entries in a single payload. |
|
opTypes |
“__ACCOUNT__.SEARCHOP=GET" |
This entry specifies the HTTP operation type for each object class supported by the connector. Values must be comma separated and must be in the following format: OBJ_CLASS.OP=HTTP_OP In this format, replaceOBJ_CLASS with the connector object class, OP with the connector operation (for example, CreateOp, UpdateOp, SearchOp), and HTTP_OP with the HTTP operation (GET or POST) |
|
specialAttributeTargetFormat |
“__ACCOUNT__.manager=userPrincipalName” |
This entry lists the format in which an attribute is present in the target system endpoint. For example, the alias attribute will be present as aliases.alias in the target system endpoint. Values are comma separated and are presented in the following format: OBJ_CLASS.ATTR_NAME= TARGET_FORMAT |
1.7.2.12 Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration.Trusted
The Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration.Trusted lookup definition holds configuration entries that are specific to the user object type. This lookup definition is used during trusted source user reconciliation runs.
Table 1-10 lists the default entries in this lookup definition:
Table 1-10 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.Configuration.Trusted Lookup Definition
| Code Key | Decode | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Recon Attribute defaults |
Lookup.Office365. UM.ReconAttrMap.TrustedDefaults |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps reconciliation fields to their default values. This lookup definition is discussed later in this guide. |
|
Recon Attribute Map |
Lookup.Office365. UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted |
This entry holds the name of the lookup definition that maps resource object fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is discussed later in this guide. |
1.7.2.13 Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted lookup definition holds mappings between resource object fields and target system attributes.
This lookup definition is preconfigured and used during trusted source user reconciliation runs. Trusted Source Reconciliation Action Rules for Users lists the default entries.
You can add entries in this lookup definition if you want to map new target system attributes for trusted source reconciliation.
1.7.2.14 Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.TrustedDefaults
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted.Defaults lookup definition holds mappings between reconciliation fields and their default values.
This lookup definition is used when there is a mandatory field on the OIM User form, but no corresponding field in the target system from which values can be fetched during trusted source reconciliation. This is explained in the following example:
For example, Employee Type is a mandatory field on the OIM User form. The target system contains no field that stores information about the employee type for a user account. During reconciliation, no value for the Employee Type field is fetched from the target system. However, as the Employee Type field cannot be left empty, the connector uses the decode value of the Employee Type entry of this lookup definition. This implies that the value of the Employee Type field on the OIM User form displays Full-Time for all user accounts reconciled from the target system.
Table 1-11 lists the default entries in this lookup definition. Do not add or modify entries to this lookup definition
Table 1-11 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.TrustedDefaults Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
Employee Type |
Full-Time |
|
Organization |
Xellerate Users |
|
User Type |
End-User |
1.8 Connector Objects Used During Target Resource Reconciliation
Target resource reconciliation involves fetching data about newly created or modified accounts on the target system and using this data to add or modify resources assigned to OIM Users.
The Office 365 Target Resource User Reconciliation scheduled job is used to initiate a reconciliation run. This scheduled job is discussed in Reconciliation Scheduled Jobs for Office 365 Connector.
See Also:
Managing Reconciliation in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for generic information about connector reconciliation
1.8.1 User Fields for Target Resource Reconciliation
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition maps resource object fields with target system attributes. This lookup definition is used for performing target resource user reconciliation runs.
In this lookup definition, entries are in the following format:
-
Code Key: Reconciliation field of the resource object
-
Decode: Name of the target system user attribute at the Graph API level
Table 1-12 lists the entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-12 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
User Principal Name |
__NAME__ |
|
Preferred Language |
preferredLanguage |
|
Account Enabled |
accountEnabled=”$(accountEnabled)” |
|
Roles~Role Name[Lookup] |
__ROLE__~__ROLE__~objectId |
|
Country |
country |
|
Display Name |
displayName |
|
Licenses~Licesnse Name[Lookup] |
assignedLicenses~assignedLicenses~skuId |
|
Last Name |
surname |
|
Mail NickName |
mailNickname |
|
Manager[LOOKUP] |
manager |
|
Status |
__ENABLE__ |
|
Object Id |
__UID__ |
|
City |
city |
|
Group Names~Group Name[Lookup] |
__GROUP__~__GROUP__~objectId |
|
Usage Location |
usageLocation |
|
FirstName |
givenName |
Roles, Groups, and Licenses are embedded objects that are listed in this table using the naming convention followed to name embedded object lookup definitions.
1.8.2 Group Fields for Reconciliation
The Lookup.Office365.GM.ReconAttrMap lookup definition maps user resource object fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is used for performing target resource group reconciliation runs.
In this lookup definition, entries are in the following format:
-
Code Key: Reconciliation field of the resource object
-
Decode: Name of the target system group attribute at the Graph API level
Table 1-13 lists the group fields of the target system from which values are fetched during reconciliation. The Office365 Group Recon scheduled job is used to reconcile group data:
Table 1-13 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.GM.ReconAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Group Field on Oracle Identity Manager | Office 365 Field |
|---|---|
|
ObjectId |
__UID__ |
|
Description |
Description |
|
Mail Enabled |
mailEnabled=”${mailEnabled}” |
|
Mail NickName |
mailNickname |
|
Display Name |
__NAME__ |
|
Security Enabled |
securityEnabled |
|
OIM Org Name |
OIM Organization Name Note: This is a connector attribute. The value of this attribute is used internally by the connector to specify the organization of the groups in Oracle Identity Manager. |
1.8.3 Reconciliation Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
Reconciliation rules for target resource reconciliation are used by the reconciliation engine to determine the identity to which Oracle Identity Manager must assign a newly discovered account on the target system.
This section discuss the following topics related to users and groups reconciliation rule for target resource reconciliation:
1.8.3.1 Target Resource Reconciliation Rules for Users and Groups
Reconciliation Rule for Users
Reconciliation rules for target resource reconciliation are used by the reconciliation engine to determine the identity to which Oracle Identity Manager must assign a newly discovered account on the target system. The Office 365 connector can perform reconciliation of both users and groups. Therefore, the connector has reconciliation rules defined for both users and groups.
The following is the process-matching rule for users:
Rule name: Office 365 User Recon Rule
Rule element: User Login Equals User Principal Name
-
User Loginis the User ID field of the OIM User form. -
User Principal Nameis the unique login name for user in target.
Reconciliation Rule for Groups
The following is the process-matching rule for groups:
Rule name: Office365 Groups Recon Rule
Rule element: Organization Name Equals OIM Org Name.
-
Organization Nameis the Organization Name field on the OIM User form. -
OIM Org Nameis the organization name of the group in Oracle Identity Manager. OIM Org Name is the value specified in the Organization Name attribute of the Office365 Group Recon scheduled job.
1.8.3.2 Viewing Reconciliation Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
After you deploy the connector, you can view the reconciliation rules for users and groups on the Reconciliation Rule Builder form in Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Log in to the Oracle Identity Manager Design Console.
- Expand Development Tools and then double-click Reconciliation Rules.
- Search for and open one of the following reconciliation rules:
-
For Users: Office365 User Recon Rule
Figure 1-2 shows the target resource reconciliation rule for users.
Figure 1-2 Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation of Users
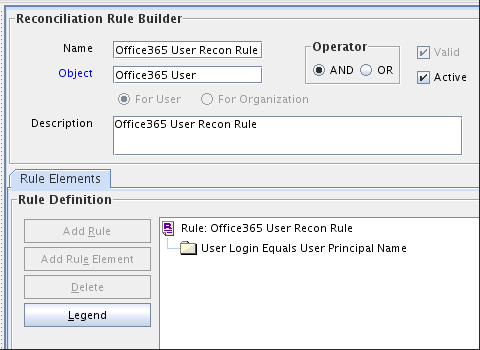
Description of "Figure 1-2 Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation of Users" -
For Groups: Office365 Groups Recon Rule
Figure 1-3 shows the target resource reconciliation rule for groups.
Figure 1-3 Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation of Groups
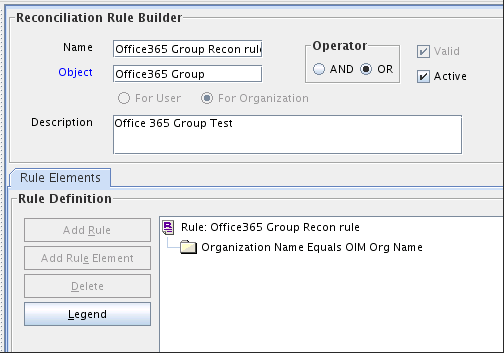
Description of "Figure 1-3 Reconciliation Rule for Target Resource Reconciliation of Groups"
-
1.8.4 Reconciliation Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
Reconciliation action rules define that actions the connector must perform based on the reconciliation rules defined for Users and Groups.
This section discusses the following topics related to reconciliation action rules for target resource reconciliation:
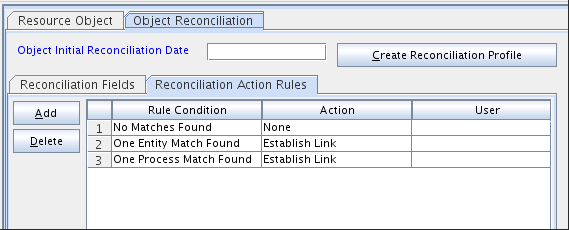
1.8.4.1 Target Resource Reconciliation Action Rules for Users and Groups
Reconciliation action rules specify the actions the connector must perform based on the result of the processing of a reconciliation event. The reconciliation action rules for both users and groups are the same.
Table 1-14 Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation of Users and Groups
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Create User |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
1.8.4.2 Viewing Reconciliation Action Rules for Target Resource Reconciliation
1.9 Connector Objects Used During Provisioning
Provisioning involves creating or modifying user data on the target system through Oracle Identity Manager.
This section discusses the following topics:
1.9.1 Provisioning Functions
These are the supported provisioning functions and the adapters that perform these functions for the Office 365 connector.
The Adapter column in Table 1-15 gives the name of the adapter that is used when the function is performed.
Table 1-15 User Provisioning Functions
| Function | Adapter |
|---|---|
|
Create User |
adpOFFICE365CREATEOBJECT |
|
Update User |
adpOFFICE365UPDATEATTRIBUTEVALUE |
|
Delete user |
adpOFFICE365DELETEOBJECT |
|
Enable user |
adpOFFICE365ENABLETASK |
|
Disable user |
adpOFFICE365DISABLETASK |
|
Change or reset password |
adpOFFICE365UPDATEATTRIBUTEVALUE |
|
Update child table values |
adpOFFICE365UPDATECHILDTABLEVALUE |
|
Add child table values |
adpOFFICE365ADDCHILDTABLEVALUES |
|
Remove child table values for a user |
adpOFFICE365REMOVECHILDTABLEVALUES |
1.9.2 User Fields for Provisioning
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition maps process form fields with Office 365 fields. This lookup definition is used for performing user provisioning operations.
In this lookup definition, entries are in the following format:
-
Code Key: Name of the process form field
-
Decode: Name of the target system user attribute at the Graph API level
Table 1-16 lists the entries in this lookup definition.
Table 1-16 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.ProvAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Process Form Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
User Principal Name |
__NAME__ |
|
Change Password On Next Login |
passwordProfile.forceChangePasswordNextLogin |
|
Preferred Language |
preferredLanguage |
|
Account Enabled |
accountEnabled=”$(accountEnabled)” |
|
Roles~Role Name[Lookup] |
__ROLE__~__ROLE__~objectId |
|
Country |
country |
|
Display Name |
displayName |
|
Licenses~Licesnse Name[Lookup] |
assignedLicenses~assignedLicenses~skuId |
|
Status |
__ENABLE__ |
|
Object Id |
__UID__ |
|
City |
city |
|
Group Names~Group Name[Lookup] |
__GROUP__~__GROUP__~objectId |
|
Usage Location |
usageLocation |
|
FirstName |
givenName |
|
Last Name |
surname |
|
Manager |
manager |
|
Mail NickName |
mailNickname |
1.9.3 Group Fields for Provisioning
The Lookup.Office365.GM.ProvAttrMap lookup definition maps user resource object fields and target system attributes. This lookup definition is used for performing group provisioning operations.
In this lookup definition, entries are in the following format:
-
Code Key: Name of the process form field
-
Decode: Name of the target system group attribute at the Graph API level
Table 1-17 lists the group fields of the target system for which you can specify or modify values during provisioning operations.
Table 1-17 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.GM.ProvAttrMap Lookup Definition
| Group Field on Oracle Identity Manager | Office 365 Field |
|---|---|
|
ObjectId |
__UID__ |
|
Description |
description |
|
Mail Enabled |
mailEnabled |
|
Mail Nickname |
mailNickname |
|
Display Name |
__NAME__ |
|
Security Enabled |
securityEnabled |
1.10 Connector Objects Used During Trusted Source Reconciliation
Trusted source reconciliation involves fetching data about newly created or modified accounts on the target system and using that data to create or update OIM Users.
The Office365 Trusted User Reconciliation scheduled task is used to initiate a trusted source reconciliation run. This scheduled task is discussed in Office365 Trusted User Reconciliation.
See Also:
Trusted Source Reconciliation in Oracle Fusion Middleware Administering Oracle Identity Manager for generic information about connector reconciliation
This section discusses the following connector objects:
1.10.1 User Fields for Trusted Source Reconciliation
The Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted lookup definition maps user fields of the OIM User form with corresponding field names in the target system. This lookup definition is used for performing trusted source reconciliation runs. Values for the user identity fields in this lookup definition are fetched from the target system during a trusted source reconciliation run.
Table 1-18 Entries in the Lookup.Office365.UM.ReconAttrMap.Trusted Lookup Definition
| Code Key (Resource Object Field) | Decode (Office 365 Field) |
|---|---|
|
User Principal Name |
__NAME__ |
|
Preferred Language |
preferredLanguage |
|
Country |
country |
|
Display Name |
displayName |
|
Status[TRUSTED] |
__ENABLE__ |
|
Object Id |
__UID__ |
|
Last Name |
surname |
|
Usage Location |
UsageLocation |
|
FirstName |
givenName |
|
Manager |
manager |
1.10.2 Reconciliation Rule for Trusted Source Reconciliation
Reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation is invoked when Oracle Identity Manager tries to determine the user record that is associated with a change on your target system (a trusted source).
This section discusses the following topics related to reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation:
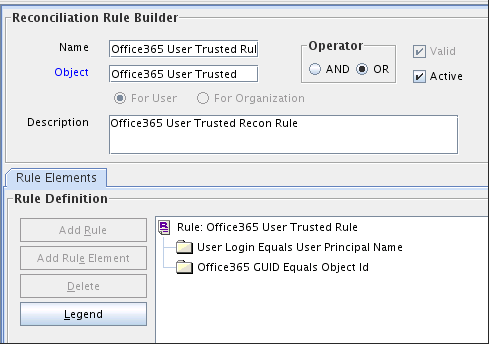
1.10.2.1 Trusted Source Reconciliation Rule for Users
Reconciliation rule for trusted source reconciliation is invoked when Oracle Identity Manager tries to determine the user record that is associated with a change on your target system (a trusted source).
The following is the entity matching rule for users:
Rule name: Office 365 User Trusted Rule
Rule element: (User Login Equals User Principal Name) OR (Office365 GUID Equals Object Id)
-
User Loginis the User ID field of the OIM User form. -
User Principal Nameis the unique login name of a user.
-
Office365 GUIDis a UDF (user-defined field) for mapping target object ID with an OIM User. -
Object Idis the Object Id for an Office365 user.
1.10.3 Reconciliation Action Rules for Trusted Source Reconciliation
Reconciliation action rules specify the actions the connector must perform based on the result of the processing of a reconciliation event.
This section discusses the following topics related to reconciliation action rules:
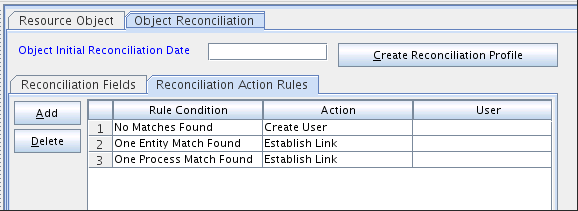
1.10.3.1 Trusted Source Reconciliation Action Rules for Users
Table 1-19 Action Rules for Trusted Source Reconciliation
| Rule Condition | Action |
|---|---|
|
No Matches Found |
Create User |
|
One Entity Match Found |
Establish Link |
|
One Process Match Found |
Establish Link |
1.10.3.2 Viewing Reconciliation Action Rules for Trusted Source Reconciliation
After you deploy the connector, you can view reconciliation action rules on the Object Reconciliation tab of a resource object in Oracle Identity Manager Design Console
1.11 Roadmap for Deploying and Using the Connector
The following is the organization of information in the rest of this guide:
-
Deploying the Office 365 Connector describes procedures that you must perform on Oracle Identity Manager and the target system during each stage of connector deployment.
-
Using the Office 365 Connector describes guidelines on using the connector and the procedure to configure reconciliation runs and perform provisioning operations.
-
Extending the Functionality of the Office365 Connector describes procedures that you can perform if you want to extend the functionality of the connector.
-
Files and Directories on the Office 365 Connector Installation Media lists the files and directories that comprise the connector installation media.