| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 Administration Guide Oracle VM Server for SPARC |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 Administration Guide Oracle VM Server for SPARC |
Part I Oracle VM Server for SPARC 2.1 Software
1. Overview of the Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software
2. Installing and Enabling Software
4. Setting Up Services and the Control Domain
12. Performing Other Administration Tasks
Part II Optional Oracle VM Server for SPARC Software
13. Oracle VM Server for SPARC Physical-to-Virtual Conversion Tool
14. Oracle VM Server for SPARC Configuration Assistant
15. Using the Oracle VM Server for SPARC Management Information Base Software
Oracle VM Server for SPARC Management Information Base Overview
Logical Domains Manager and the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB
Parsing the XML-Based Control Interface
Providing Fault and Recovery Information
Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Object Tree
Installing and Configuring the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Software
Installing and Configuring the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Software (Task Map)
Install the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Software Package
Load the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Module Into the SMA
Remove the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Software Package
Create the Initial snmpv3 User
Querying the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB
Retrieve Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Objects
Retrieving Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Information
Environment Variables Table (ldomEnvVarsTable)
Domain Policy Table (ldomPolicyTable)
Service Processor Configuration Table (ldomSPConfigTable)
Domain Resource Pool and Scalar Variables
Virtual CPU Table (ldomVcpuTable)
Cryptographic Units Table (ldomCryptoTable)
Using Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Module Traps
Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Trap Descriptions
Domain State Change (ldomStateChange)
Virtual CPU Change (ldomVCpuChange)
Virtual Memory Change (ldomVMemChange)
Virtual Disk Service Change (ldomVdsChange)
Virtual Disk Change (ldomVdiskChange)
Virtual Switch Change (ldomVswChange)
Virtual Network Change (ldomVnetChange)
Virtual Console Concentrator Change (ldomVccChange)
Virtual Console Group Change (ldomVconsChange)
Starting and Stopping a Domain
16. Logical Domains Manager Discovery
17. Using the XML Interface With the Logical Domains Manager
This section describes how to monitor logical domains (domains) by querying the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB. This section also provides descriptions of the various types of MIB output.
This section covers the following topics:
Before you can query the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB, you must set environment variables for the shell that you use. This procedure describes how to set these variables for the C shell, Bourne shell, and Korn shell.
% setenv PATH /usr/sfw/bin:$PATH % setenv MIBDIRS /opt/SUNWldmib/lib/mibs:/etc/sma/snmp/mibs % setenv MIBS +SUN-LDOM-MIB
$ PATH=/usr/sfw/bin:$PATH; export PATH $ MIBDIRS=/opt/SUNWldmib/lib/mibs:/etc/sma/snmp/mibs; export MIBDIRS $ MIBS=+SUN-LDOM-MIB; export MIBS
When a system has large number of domains, the SNMP agent might time out before being able to respond to an SNMP request. To increase the timeout value, use the -t option to specify a longer timeout value. For example, the following snmpwalk command sets the timeout value to 20 seconds:
# snmpwalk -t 20 -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomTable
You can also use the -t option to specify the timeout value for the snmpget and snmptable commands.
# snmpget -v version -c community-string host MIB-object
Use the snmpwalk or snmptable command.
# snmpwalk -v version -c community-string host MIB-object # snmptable -v version -c community-string host MIB-object
Example 15-1 Retrieving a Single Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB Object (snmpget)
The following snmpget command queries the value of the ldomVersionMajor object. The command specifies snmpv1 (-v1) and a community string (-c public) for the localhost host.
# snmpget -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMajor.0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMajor.0 = INTEGER: 1
Example 15-2 Retrieving Object Values From ldomTable (snmpwalk)
The following examples show how to use the snmpwalk command to retrieve object values from ldomTable.
The following snmpwalk -v1 command returns the values for all objects in the ldomTable table:
# snmpwalk -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomTable SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomName.1 = STRING: primary SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomName.2 = STRING: LdomMibTest_1 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomAdminState.1 = INTEGER: 0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomAdminState.2 = INTEGER: 0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomOperState.1 = INTEGER: active(1) SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomOperState.2 = INTEGER: bound(6) SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumVCpu.1 = INTEGER: 32 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumVCpu.2 = INTEGER: 2 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMemSize.1 = INTEGER: 3968 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMemSize.2 = INTEGER: 256 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMemUnit.1 = INTEGER: megabytes(2) SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMemUnit.2 = INTEGER: megabytes(2) SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumCrypto.1 = INTEGER: 8 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumCrypto.2 = INTEGER: 0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumIOBus.1 = INTEGER: 2 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomNumIOBus.2 = INTEGER: 0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomUUID.1 = STRING: c2c3d93b-a3f9-60f6-a45e-f35d55c05fb6 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomUUID.2 = STRING: af0b05f0-d262-e633-af32-a6c4e81fb81c SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMacAddress.1 = STRING: 00:14:4f:86:63:2a SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMacAddress.2 = STRING: 00:14:4f:fa:78:b9 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomHostID.1 = STRING: 0x8486632a SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomHostID.2 = STRING: 0x84fa78b9 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomFailurePolicy.1 = STRING: ignore SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomFailurePolicy.2 = STRING: ignore SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMaster.1 = STRING: SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomMaster.2 = STRING:
The following snmpwalk commands use snmpv2c and snmpv3 to retrieve the contents of ldomTable:
# snmpwalk -v2c -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomTable # snmpwalk -v 3 -u test -l authNoPriv -a MD5 -A testpassword localhost \ SUN-LDOMMIB::ldomTable
Example 15-3 Retrieving Object Values From ldomTable in Tabular Form (snmptable)
The following examples show how to use the snmptable command to retrieve object values from ldomTable in tabular form.
The following snmptable -v1 command shows the contents of ldomTable in tabular form:
# snmptable -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomTable
The following snmptable command shows the contents of ldomTable in tabular form by using snmpv2c.
Note that for the v2c or v3 snmptable command, use the -CB option to specify only GETNEXT, not GETBULK, requests to retrieve data.
# snmptable -v2c -CB -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomTable
This section describes the information that you can retrieve from the Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB in the form of tables or scalar objects.
ldomTable is used to represent each domain in the system. Information includes resource constraints for virtual CPUs, memory, cryptographic units, and I/O buses. The table also includes other domain information, such as the universally unique identifier (UUID), MAC address, host ID, failure policy, and master domain.
Table 15-1 Domain Table (ldomTable)
|
ldomEnvVarsTable describes the OpenBoot PROM environment variables that all domains use.
Table 15-2 Environment Variables Table (ldomEnvVarsTable)
|
ldomPolicyTable describes the dynamic resource management (DRM) policies that apply to all domains.
Table 15-3 Domain Policy Table (ldomPolicyTable)
|
ldomSPConfigTable describes the service processor (SP) configurations for all domains.
Table 15-4 Service Processor Configuration Table (ldomSPConfigTable)
|
The following resources can be assigned to domains:
Virtual CPU (vcpu)
Memory (mem)
Cryptographic unit (mau)
Virtual switch (vsw)
Virtual network (vnet)
Virtual disk server (vds)
Virtual disk server device (vdsdev)
Virtual disk (vdisk)
Virtual console concentrator (vcc)
Virtual console (vcons)
Physical I/O device (io)
The following scalar MIB variables are used to represent resource pools and their properties.
Table 15-5 Scalar Variables for CPU Resource Pool
|
Table 15-6 Scalar Variables for Memory Resource Pool
|
Table 15-7 Scalar Variables for Cryptographic Resource Pool
|
Table 15-8 Scalar Variables for I/O Bus Resource Pool
|
ldomVcpuTable describes the virtual CPUs that all domains use.
Table 15-9 Virtual CPU Table (ldomVcpuTable)
|
A domain's memory space is referred to as real memory, that is, virtual memory. Host platform memory space that is detected by the hypervisor is referred to as physical memory. The hypervisor maps blocks of physical memory to form a block of real memory that is used by a domain.
The following example shows that the requested memory size can be split between two memory blocks instead of being assigned to a single large memory block. Assume that a domain requests 521 Mbytes of real memory. The memory can be assigned two 256-Mbyte blocks on the host system as physical memory by using the {physical-address, real-address, size} format.
{0x1000000, 0x1000000, 256}, {0x2000000, 0x2000000,256}
A domain can have up to 64 physical memory segments assigned to a guest domain. So, an auxiliary table, instead of a display string, is used to hold each memory segment. A display string has a 255-character limit.
ldomVmemTable describes the properties of virtual memory that domains use.
Table 15-10 Virtual Memory Table (ldomVmemTable)
|
ldomVmemPhysBindTable is an auxiliary table that contains physical memory segments for all domains.
Table 15-11 Virtual Memory Physical Binding Table (ldomVmemPhysBindTable)
|
A virtual disk service (vds) and the physical device to which it maps (vdsdev) provide the virtual disk capability to the Oracle VM Server for SPARC technology. A virtual disk service exports a number of local volumes (physical disks or file systems). When a virtual disk service is specified, the following are included:
Complete /dev path of the backing device (vdsdev)
Unique name (volume name) for the device being added to the service
One or more disks, disk slices, and file systems can be bound to a single disk service. Each disk has a unique name and volume name. The volume name is used when the disk is bound to the service. The Logical Domains Manager creates virtual disk clients (vdisk) from the virtual disk service and its logical volumes.
ldomVdsTable describes the virtual disk services for all domains.
Table 15-12 Virtual Disk Service Table (ldomVdsTable)
|
ldomVdsdevTable describes the virtual disk service devices that all virtual disk services use.
Table 15-13 Virtual Disk Service Device Table (ldomVdsdevTable)
|
ldomVdiskTable describes the virtual disks for all domains.
Table 15-14 Virtual Disk Table (ldomVdiskTable)
|
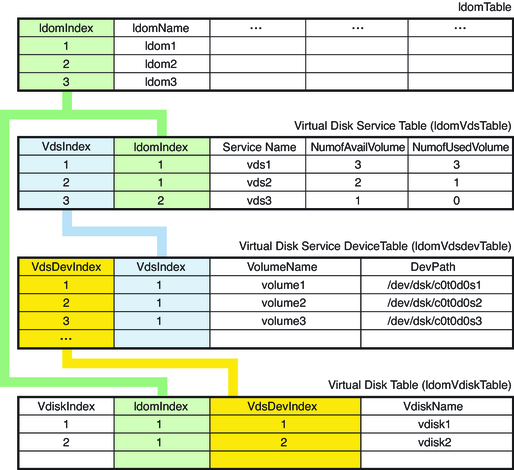
The following figure shows how indexes are used to define relationships among the virtual disk tables and the domain table. The indexes are used as follows:
ldomIndex in ldomVdsTable and ldomVdiskTable points to ldomTable.
VdsIndex in ldomVdsdevTable points to ldomVdsTable.
VdsDevIndex in ldomVdiskTable points to ldomVdsdevTable.
Figure 15-3 Relationship Among Virtual Disk Tables and the Domain Table
Oracle VM Server for SPARC virtual network support enables guest domains to communicate with each other and with external hosts through a physical Ethernet device. The virtual network contains the following main components:
Virtual switch (vsw)
Virtual network device (vnet)
After you create a virtual switch on a service domain, you can bind a physical network device to the virtual switch. After that, you can create a virtual network device for a domain that uses the virtual switch service for communication. The virtual switch service communicates with other domains by connecting to the same virtual switch. The virtual switch service communicates with external hosts if a physical device is bound to the virtual switch.
ldomVswTable describes the virtual switch services for all domains.
Table 15-15 Virtual Switch Service Table (ldomVswTable)
|
ldomVnetTable describes the virtual network devices for all domains.
Table 15-16 Virtual Network Device Table (ldomVnetTable)
|
The Oracle VM Server for SPARC service domain provides a virtual network terminal service (vNTS). vNTS provides a virtual console service, called a virtual console concentrator (vcc), with a range of port numbers. Each virtual console concentrator has multiple console groups (vcons), and each group is assigned a port number. Each group can contain multiple domains.
ldomVccTable describes the virtual console concentrators for all domains.
Table 15-17 Virtual Console Concentrator Table (ldomVccTable)
|
ldomVconsTable describes the virtual console groups for all virtual console services.
Table 15-18 Virtual Console Group Table (ldomVconsTable)
|
ldomVconsVccRelTable contains index values to show the inter-table relationships among a domain, a virtual console concentrator, and console groups.
Table 15-19 Virtual Console Relationship Table (ldomVconsVccRelTable)
|
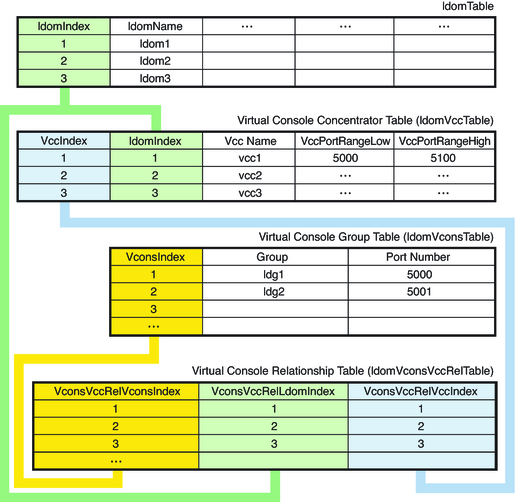
The following figure shows how indexes are used to define relationships among the virtual console tables and the domain table. The indexes are used as follows:
ldomIndex in ldomVccTable and ldomVconsVccRelTable points to ldomTable.
VccIndex in ldomVconsVccRelTable points to ldomVccTable.
VconsIndex in ldomVconsVccRelTable points to ldomVconsTable.
Figure 15-4 Relationship Among Virtual Console Tables and the Domain Table
ldomCryptoTable describes the cryptographic units that all domains use. A cryptographic unit is sometimes referred to as a modular arithmetic unit (MAU).
Table 15-20 Cryptographic Units Table (ldomCryptoTable)
|
ldomIOBusTable describes the physical I/O devices and PCI buses that all domains use.
Table 15-21 I/O Bus Table (ldomIOBusTable)
|
ldomCoreTable describes the core information, such as core-id and cpuset, for all domains.
Table 15-22 Core Table (ldomCoreTable)
|
The Logical Domains Manager protocol supports Logical Domains versions, which consists of a major number and a minor number. The Oracle VM Server for SPARC MIB has scalar variables to describe the Logical Domains version information.
Table 15-23 Scalar Variables for Logical Domains Version Information
|
The values for ldomVersionMajor and ldomVersionMinor are equivalent to the version shown by the ldm list -p command. For example:
$ ldm ls -p VERSION 1.5 ... $ snmpget -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMajor.0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMajor.0 = INTEGER: 1 $ snmpget -v1 -c public localhost SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMinor.0 SUN-LDOM-MIB::ldomVersionMinor.0 = INTEGER: 5