7 Using Cloud Control with JD Edwards EnterpriseOne
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 7.8, "Members of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain"
-
Section 7.9, "Updating the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain (Refresh Discovery)"
-
Section 7.14, "Runtime Metrics (Status, User Count, and Performance)"
-
Section 7.15, "Configuration Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne"
-
Section 7.17, "Removing the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain"
-
Section 7.18, "Starting and Stopping Components of Enterprise Manager Environments"
7.1 Additional Information for Cloud Control
For additional information, refer to these Cloud Control resources:
-
Enterprise Manager Documentation
http://docs.oracle.com/cd/E63000_01/index.htmThe above Oracle web site includes HTML and PDF versions of these documents:
-
Enterprise Manager Concepts
-
Administrator's Guide
-
Basic Installation Guide
-
Advanced Installation and Configuration Guide
-
Administrator's Guide for Software and Server Provisioning and Patching
-
Oracle Enterprise Manager List of Books
-
7.2 Using Cloud Control for the First Time
The Cloud Control console provides support for creating and managing Cloud Control administrator accounts. The Cloud Control administrators you create and manage in the Cloud Control console are granted privileges and roles to log in to the Cloud Control console and to manage specific target types and to perform specific management tasks.
During installation, these tasks are performed automatically:
-
A default Super Administrator SYSMAN account is created with the password you specify.
-
The SYSMAN account is automatically configured to receive email notifications, if you provide the email notification settings during installation. Email notifications are set up with default Notification Rules for critical conditions.
After installation, you can immediately log in to the Cloud Control console with the SYSMAN username and your password to perform management tasks. The next step is to create a new Super Administrator account to monitor and manage the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne targets.
Note:
The SYSMAN account owns the database schema containing the Management Repository and should not be used after the initial log in.7.3 Accessing the Cloud Control Console
To access Cloud Control, use the syntax of one of these URLs:
https://<Oracle Management Service_hostname>.<domain>:<port>/em
For example:
https://machine_host.company.com:7799/em
7.4 Cloud Control Home Page
On Select Enterprise Manager Home, you can choose a grid home page from the options shown on this screen. If these options do not match your job profile or role, use SYSMAN > Welcome Page and select one of the options displayed to make any other page in Enterprise Manager as your home page. Alternately, you can also use SYSMAN > Set Current Page as My Home to select any other Enterprise Manager page as your Home Page. For instructions on making the JD Edwards Domain your home page in Enterprise Manager, refer to the Tip in the section in this chapter entitled: Section 7.7, "JDE EnterpriseOne Domain Home Page".
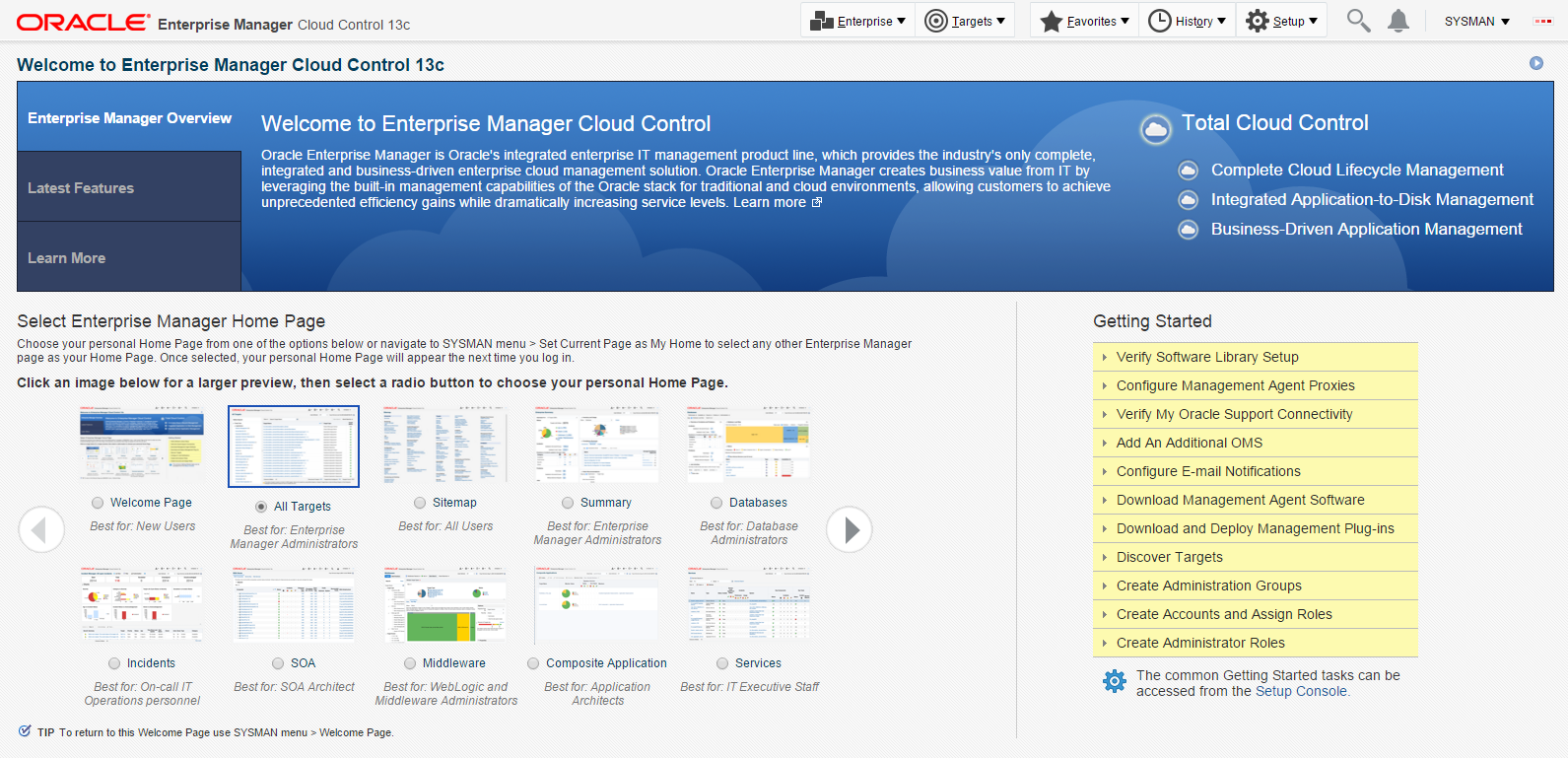
Description of the illustration ''emgc_home.png''
7.5 Targets
To view all existing Cloud Control targets, click the Targets dropdown menu. This control displays rows that further define targets by type, such as groups, systems, services, hosts, databases, middleware (application servers), and composite applications.
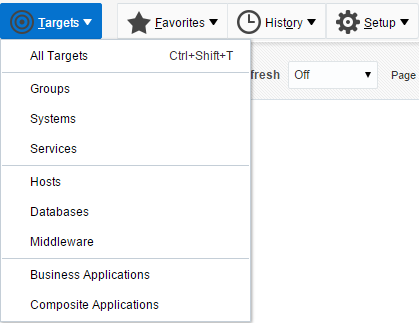
Description of the illustration ''targets_pulldown.png''
7.6 Adding the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain
To add the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne domain to Cloud Control:
Description of the illustration ''target_add_jde_pulldown.png''
-
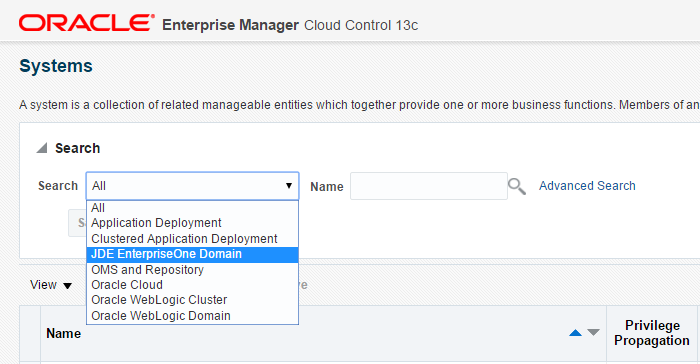
Navigate to Targets, Systems, and use the Search dropdown menu to select JDE EnterpriseOne Domain.
Description of the illustration ''target_add.png''
-
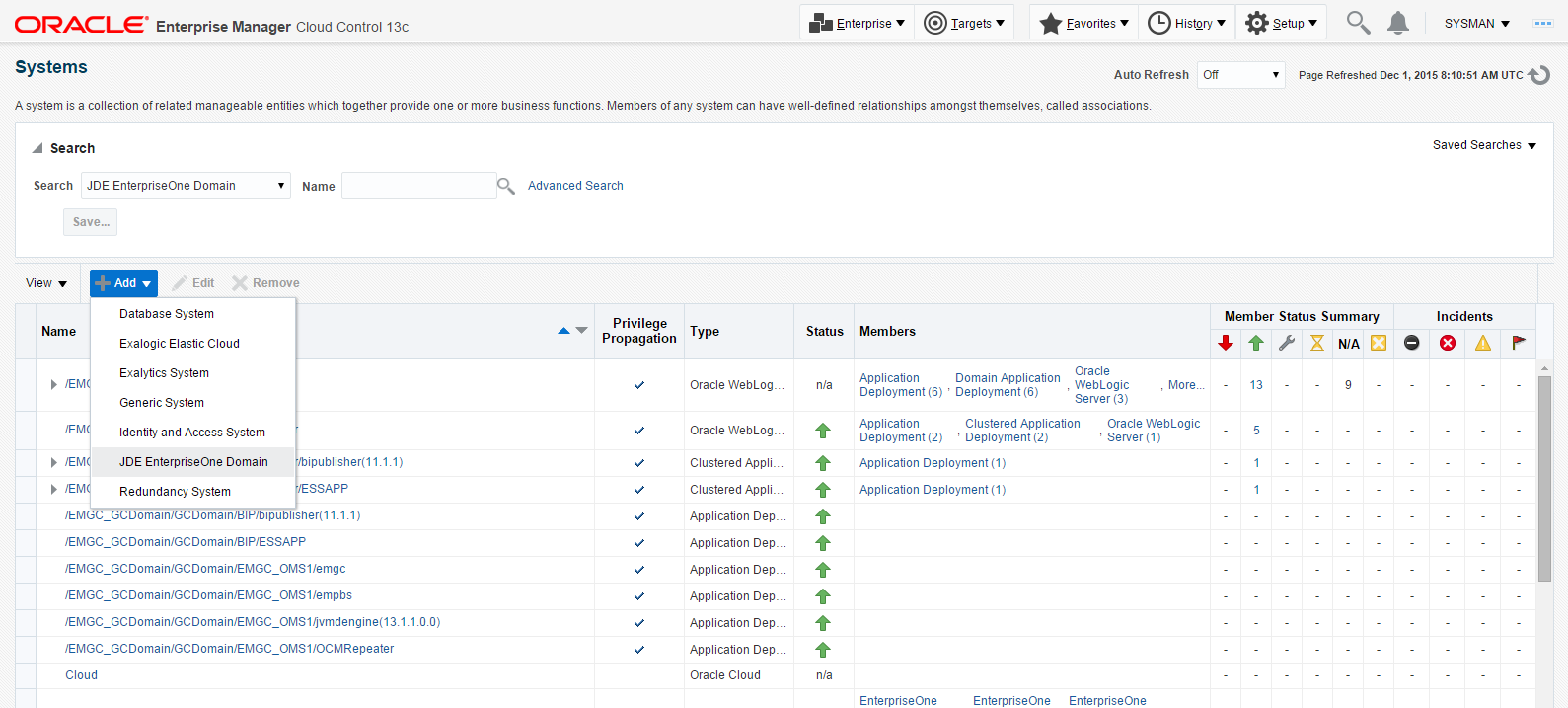
On the Systems form, with the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain selected, select JDE EnterpriseOne Domain from the Add dropdown menu.
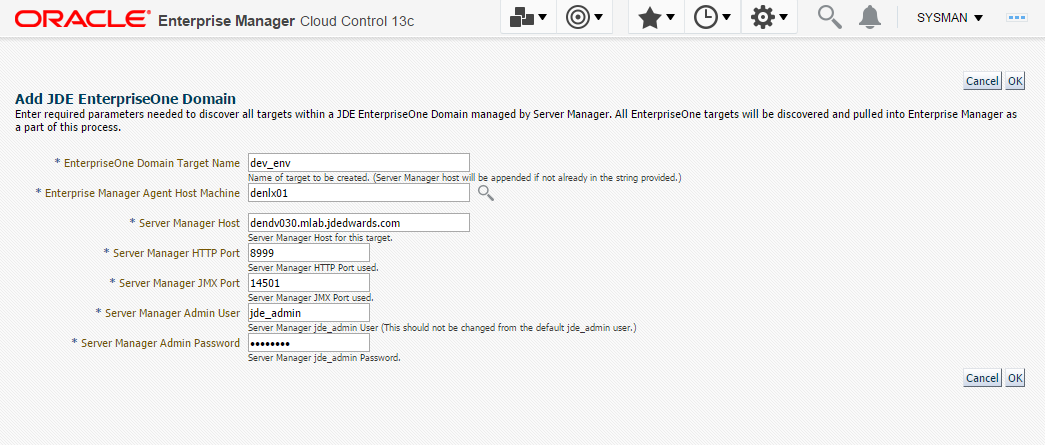
Description of the illustration ''add_jde_domain.png''
-
On the Add JDE EnterpriseOne Domain form, complete these fields:
-
EnterpriseOne Domain Target Name
Enter the name of the domain for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne. The name of the Server Manager host will be appended to this name if you do not specify it.
For example, enter dev_env.
-
Enterprise Manager Agent Host Machine
Enter the machine name on which the Enterprise Manager agent is installed. For example, enter denlx01.
Note:
It is recommended that you type the machine name in the field instead of using the search button to locate the machine name. -
Server Manager Host
Enter the fully qualified machine name of your Server Manager host. For example, enter denv030.mlab.jdedwards.com.
-
Server Manager HTTP Port
Enter the HTTP port that will be used to connect to Server Manager. The default value is 8999.
-
Server Manager JMX Port
Enter the JMX port that will be used to connect to Server Manager. The default value is 14501.
-
Server Manager Admin User
The default value, which should not be changed, is jde_admin.
-
Server Manager Admin Password
Enter a valid value for the password of your Server Manager administrator.
-
-
Click the OK button to add the domain.
-
As Cloud Control adds the JD Edwards Domain and associated targets, it performs the following functions:
-
Discovering: JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain
-
Creating: JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain target
-
Saving: JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain targets discovered
After the processing is complete, the home page for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain is displayed, as shown in the following example:
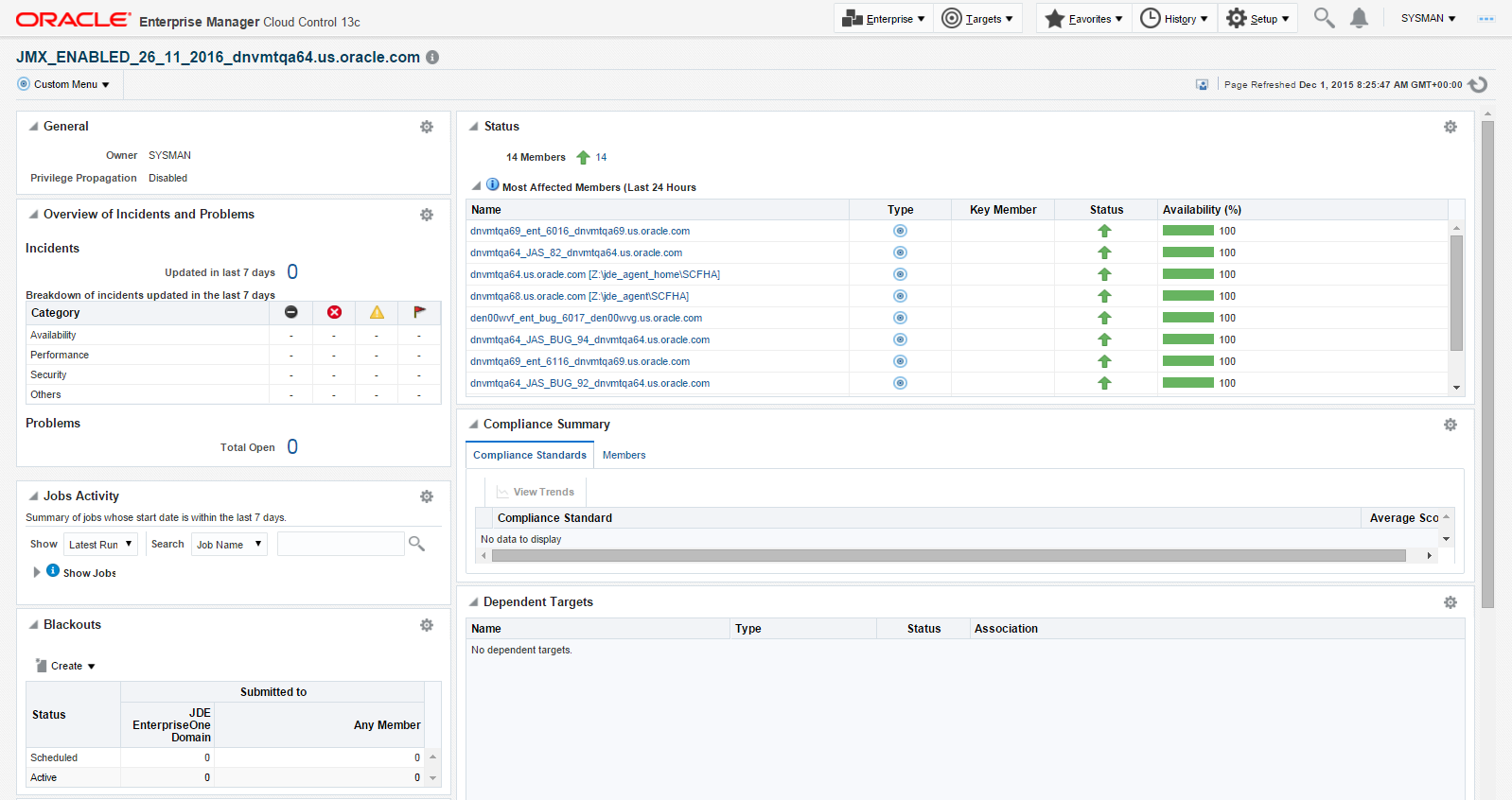
Description of the illustration ''jde_domain_home_page.png''
-
7.7 JDE EnterpriseOne Domain Home Page
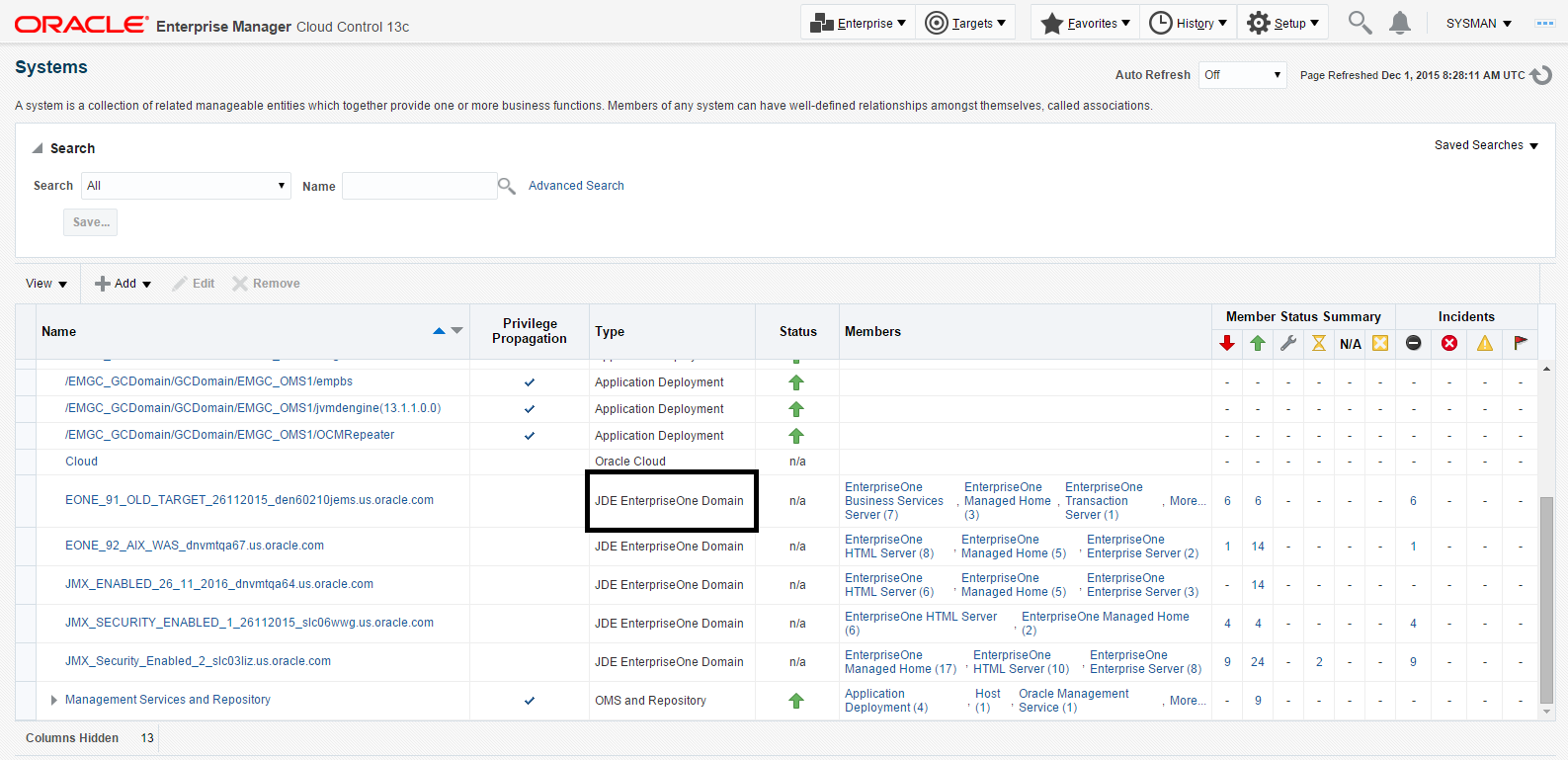
Description of the illustration ''target_jde_circled.png''
-
Navigate to Targets, Systems, and select the row where the Type column value is JDE EnterpriseOne Domain.
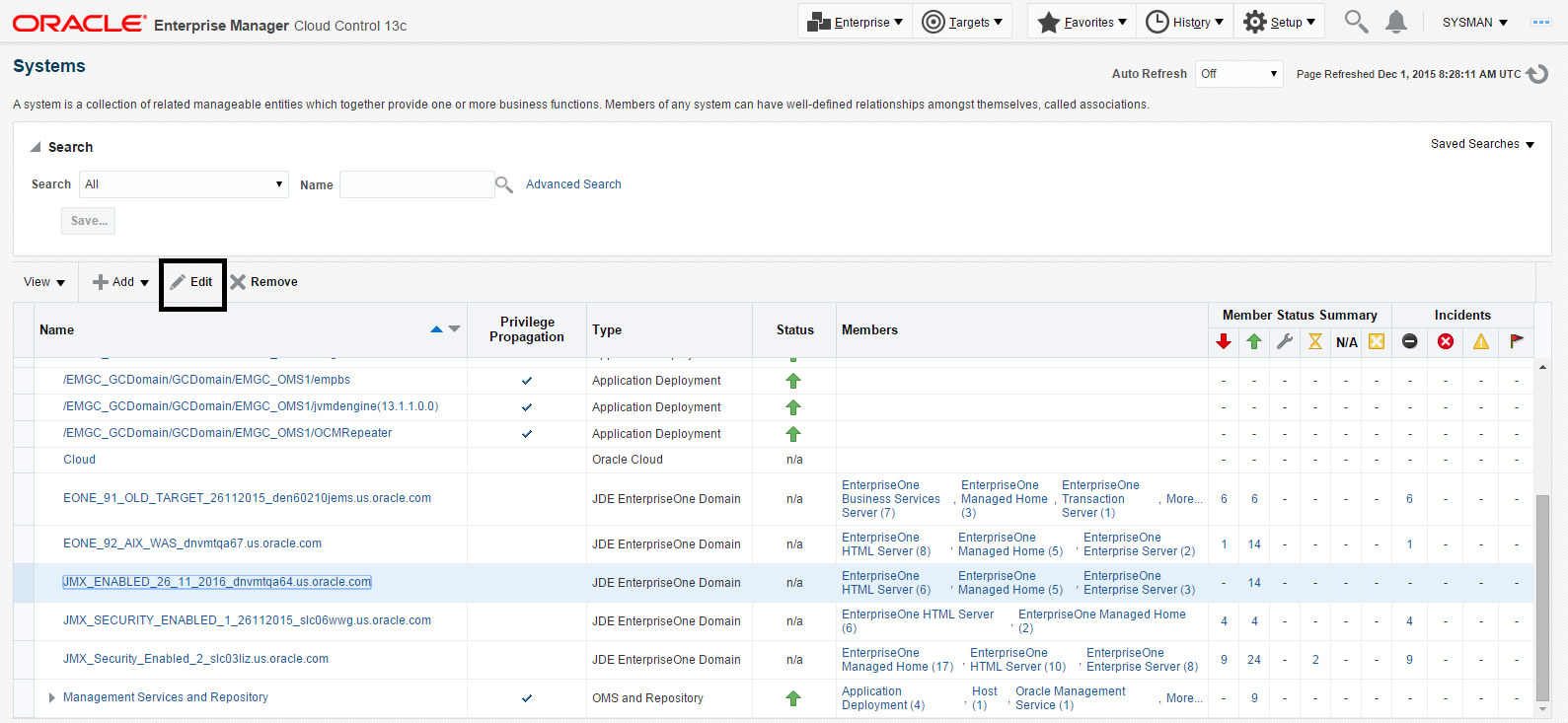
Description of the illustration ''target_jde_edit_button.png''
-
On the Systems form, with the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain row highlighted, click the Edit button to display the Home page of the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain, as shown in the following example:
Tip:
If your server is not listed, it may be because the Enterprise Manager default for the maximum number of servers to be shown in this list is 10. Refer to the Enterprise Manager documentation to customize this value.
Description of the illustration ''jde_domain_home_page.png''
-
Alternatively, to navigate to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain Home page, on the Systems form, on the row with the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain, click the hyperlink in the Name column where the Type column value is JDE EnterpriseOne Domain. This is shown in the following example:
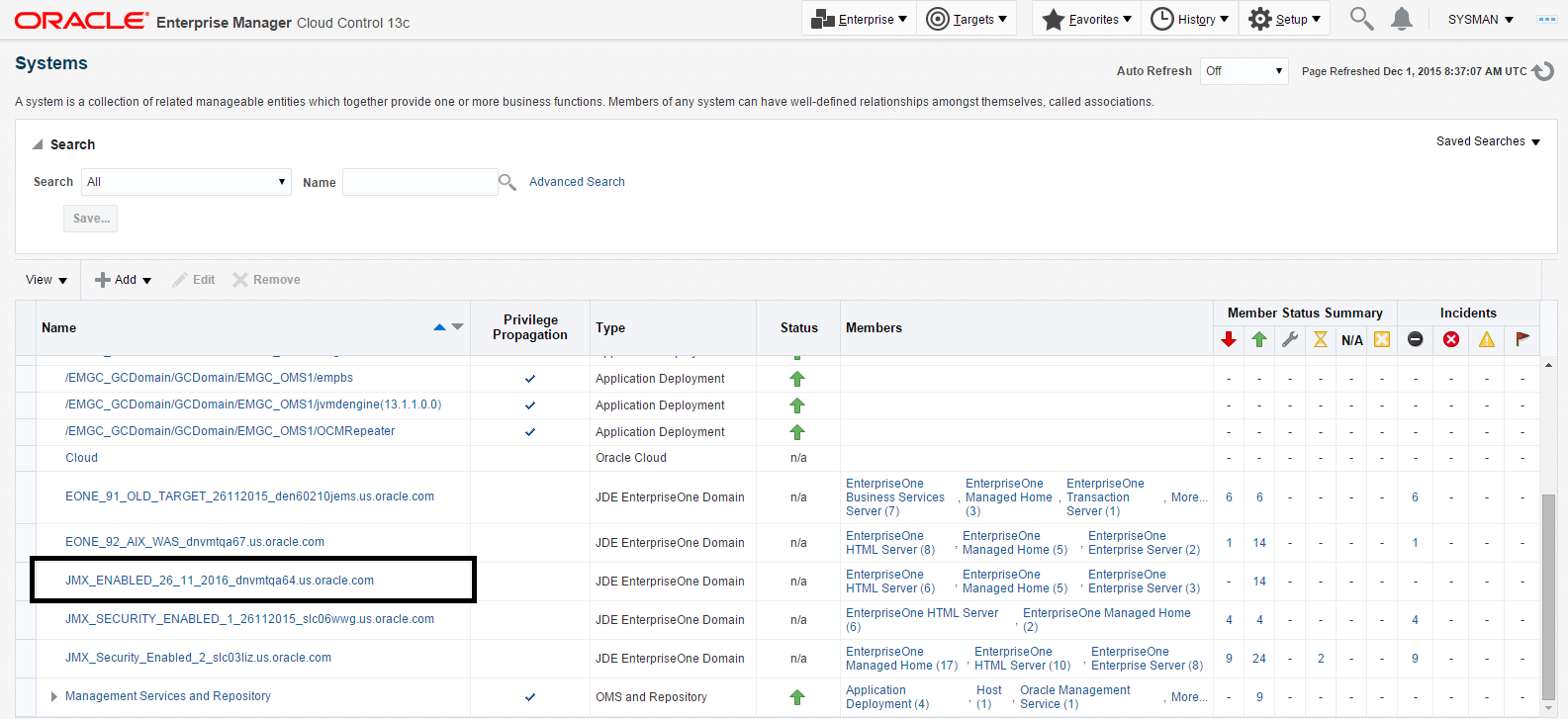
Description of the illustration ''target_jde_name.png''
-
Optionally you can set the JD Edwards Domain as your Cloud Control home page, with the JD Edwards Domain page as the current page in your Cloud Control session, navigate Sysman, Set Current Page as My Home (see below figure).
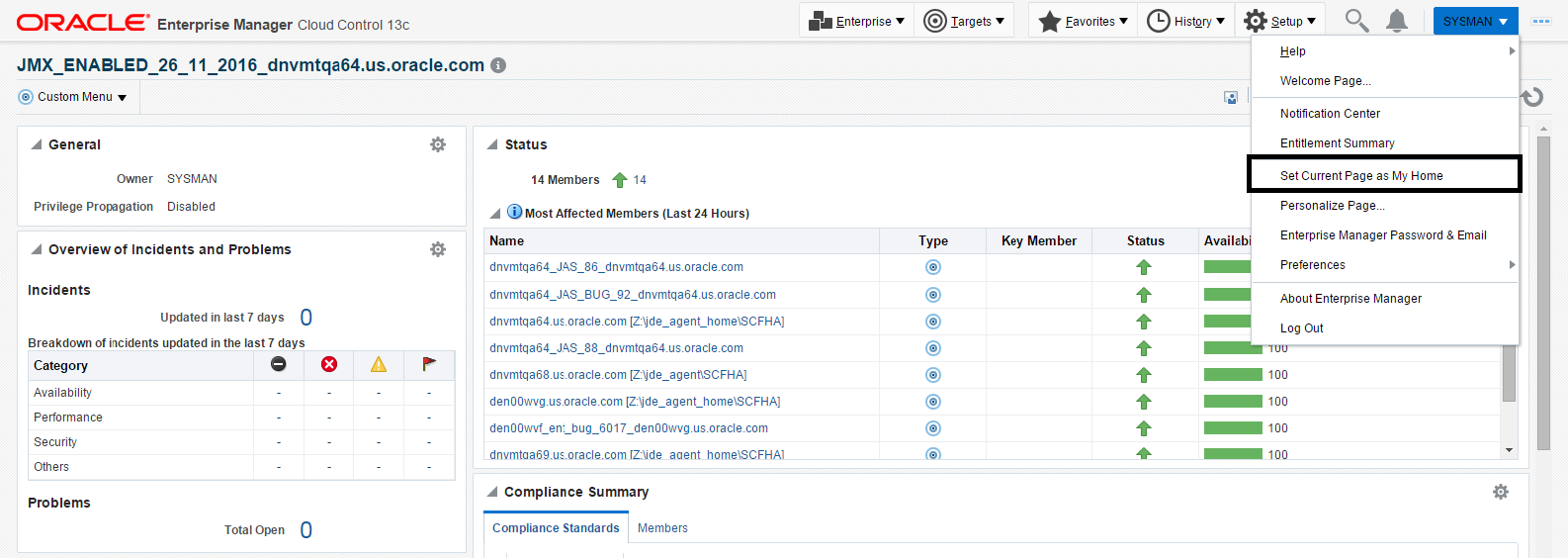
Description of the illustration ''set_current_page_home.png''
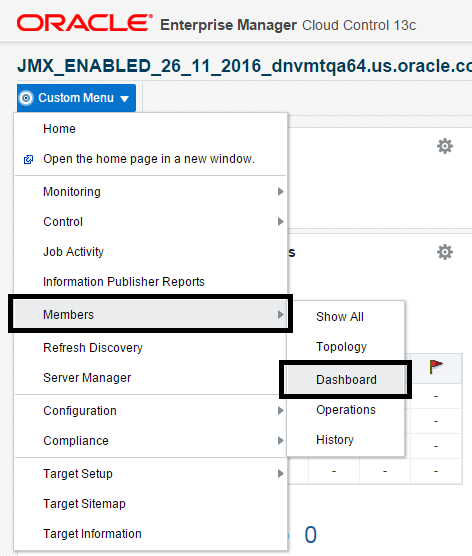
7.8 Members of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain
To display members of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain:
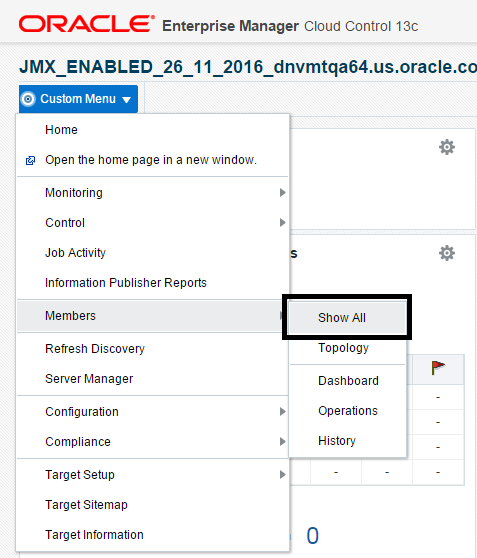
Description of the illustration ''custom_members.png''
-
With the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain displayed, navigate to Custom Menu, Members, Show All.
-
Cloud Control displays a list of members as shown in the following example:
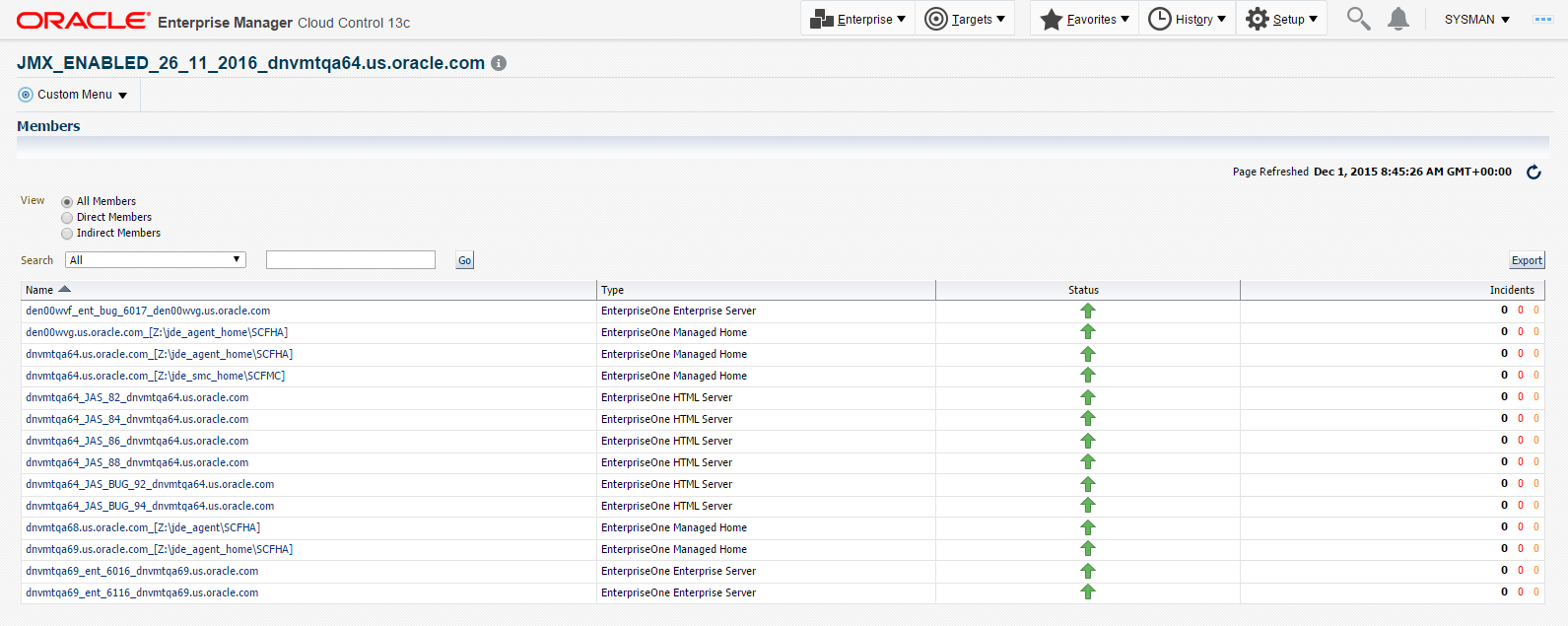
Description of the illustration ''members_example.png''
7.9 Updating the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain (Refresh Discovery)
To update the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne domain to Cloud Control, use Refresh Discovery as described below.
-
On the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain Home Page, navigate to Custom Menu, Refresh Discovery.
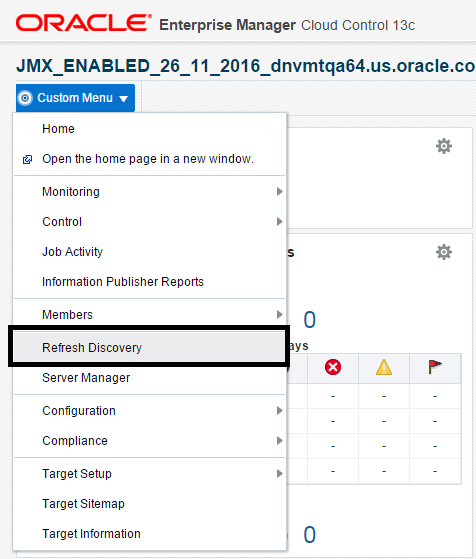
Description of the illustration ''custom_refresh.png''
-
Cloud Control displays the following warning:
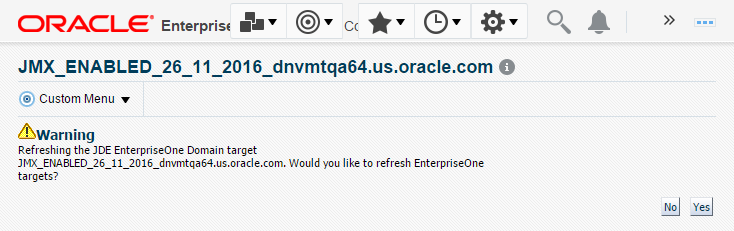
Description of the illustration ''refresh_discovery_warning.png''
-
On the Warning screen, verify the target and click the Yes button to complete the refresh action.
The Cloud Control system refreshes the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain and associated targets. When the process is complete, the system displays the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain Home Page.
7.10 Configuration Topology
There are several methods to display the configuration topology of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain.
-
On the JD EnterpriseOne Domain home page, choose either of these navigations:
Custom Menu, Members, Topology
Custom Menu, Configuration, Topology
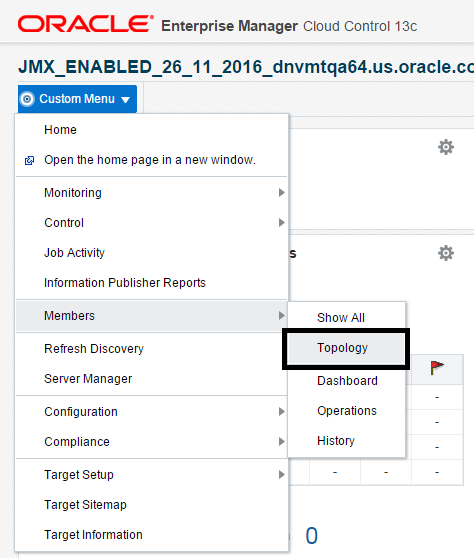
Description of the illustration ''config_topology_one.png''
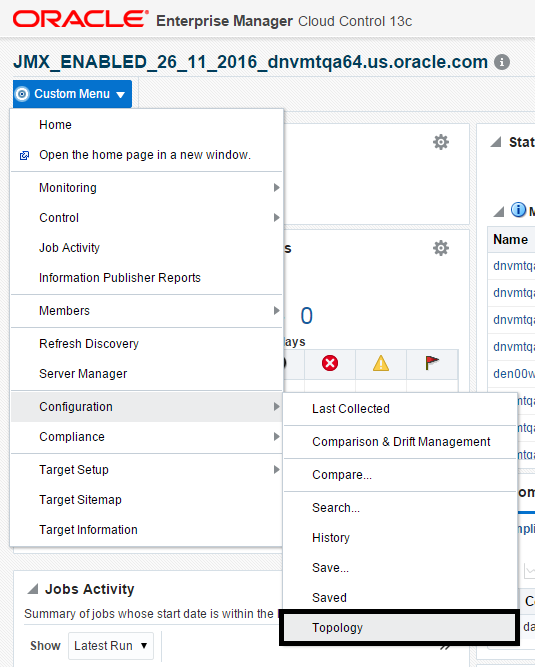
Description of the illustration ''config_topology.png''
-
Cloud Control displays a topology graphic as shown in the following example:
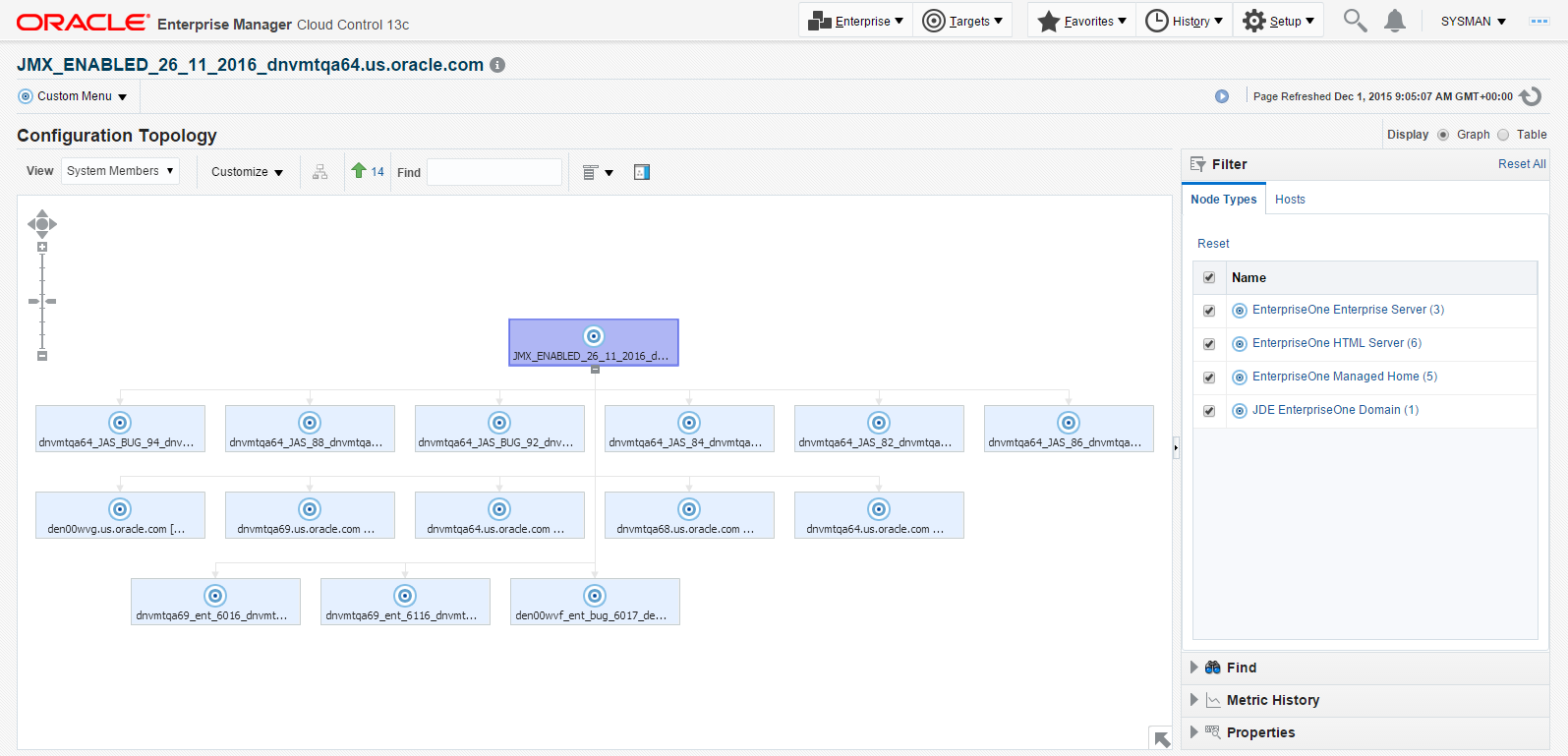
Description of the illustration ''config_topology_graph.png''
7.11 System Monitoring Dashboard
Use the System Dashboard to view the health of managed targets within a group or system in real time. The System Dashboard presents information using intuitive icons and graphics that let you spot recent changes and quickly identify and respond to problems. You can:
-
Customize the display attributes to match information requirements of managed targets.
-
Monitor status for recent problems.
Description of the illustration ''dashboard.png''
To access the System Monitoring Dashboard, navigate to Custom Menu, Members, Dashboard. The following example illustrates the dashboard for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain.
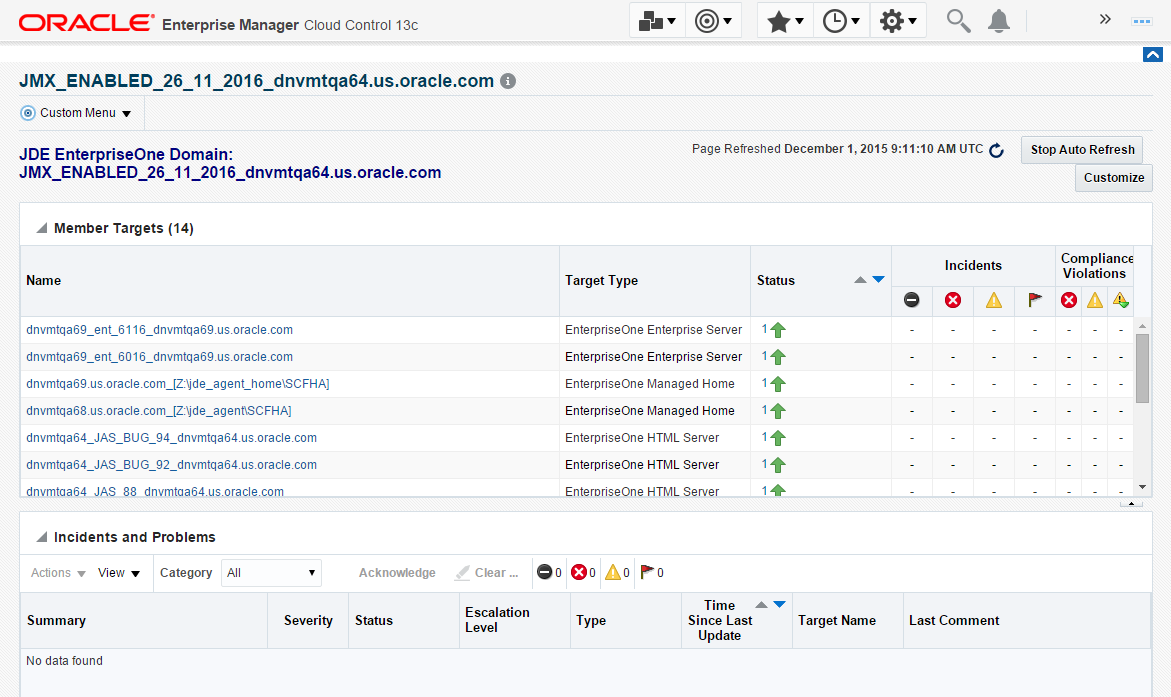
Description of the illustration ''dashboard_jde.png''
7.12 Monitoring Configuration
Cloud Control automatically sets up monitoring configuration for the JDE EnterpriseOne targets.
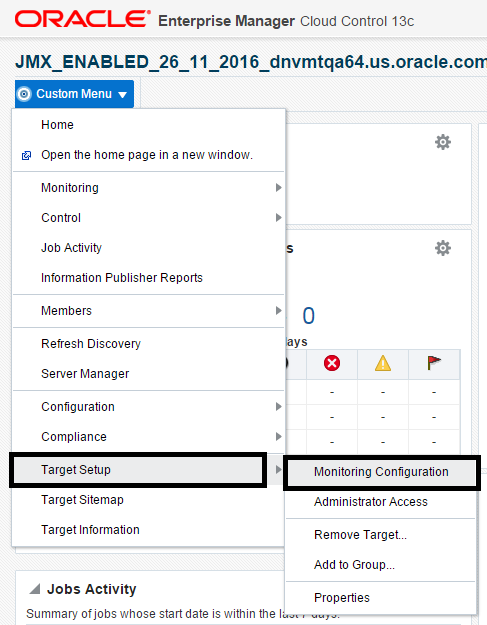
Description of the illustration ''target_monitor_nav.png''
-
To confirm, with a JDE target selected (for example, the HTML Server), navigate to Custom Menu, Target Setup, Monitoring Configuration.
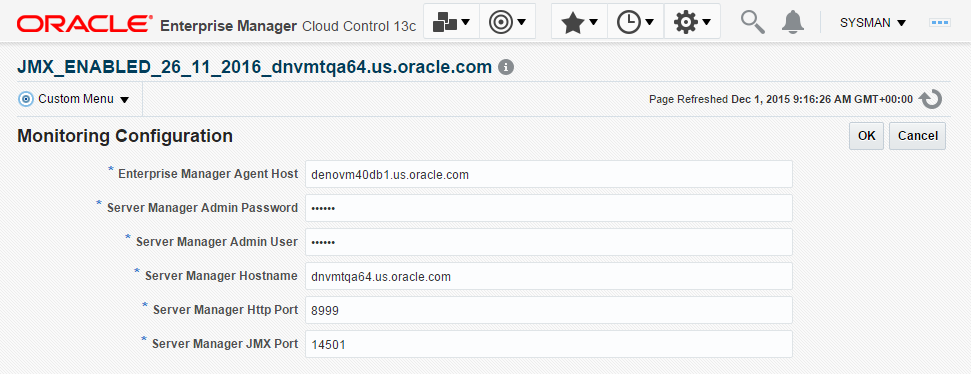
Description of the illustration ''monitoring_configuration.png''
If the Monitoring section of the screen indicates that monitoring is automatically enabled for the target's availability and performance, no further monitoring configuration is necessary. You can edit the metric thresholds from the target's home page.
7.13 Latest Configuration Data
Use this procedure to obtain the latest configuration data for members of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain. This allows you to see configuration information that is in files such as the jde.ini and jas.ini. In addition to viewing the configuration information, you can Export or Detach it.
-
With a JD Edwards EnterpriseOne target selected, navigate to EnterpriseOne HTML Server, Configuration, Last Collected.
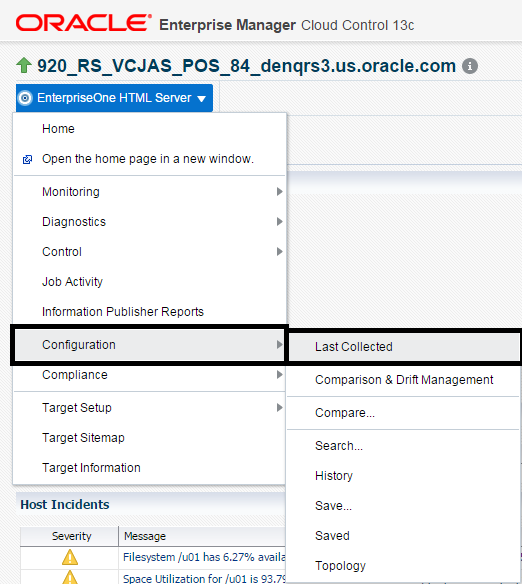
Description of the illustration ''last_collected.png''
-
Cloud Control displays the latest configuration for the selected Target.
The following example illustrates the latest configuration for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server.
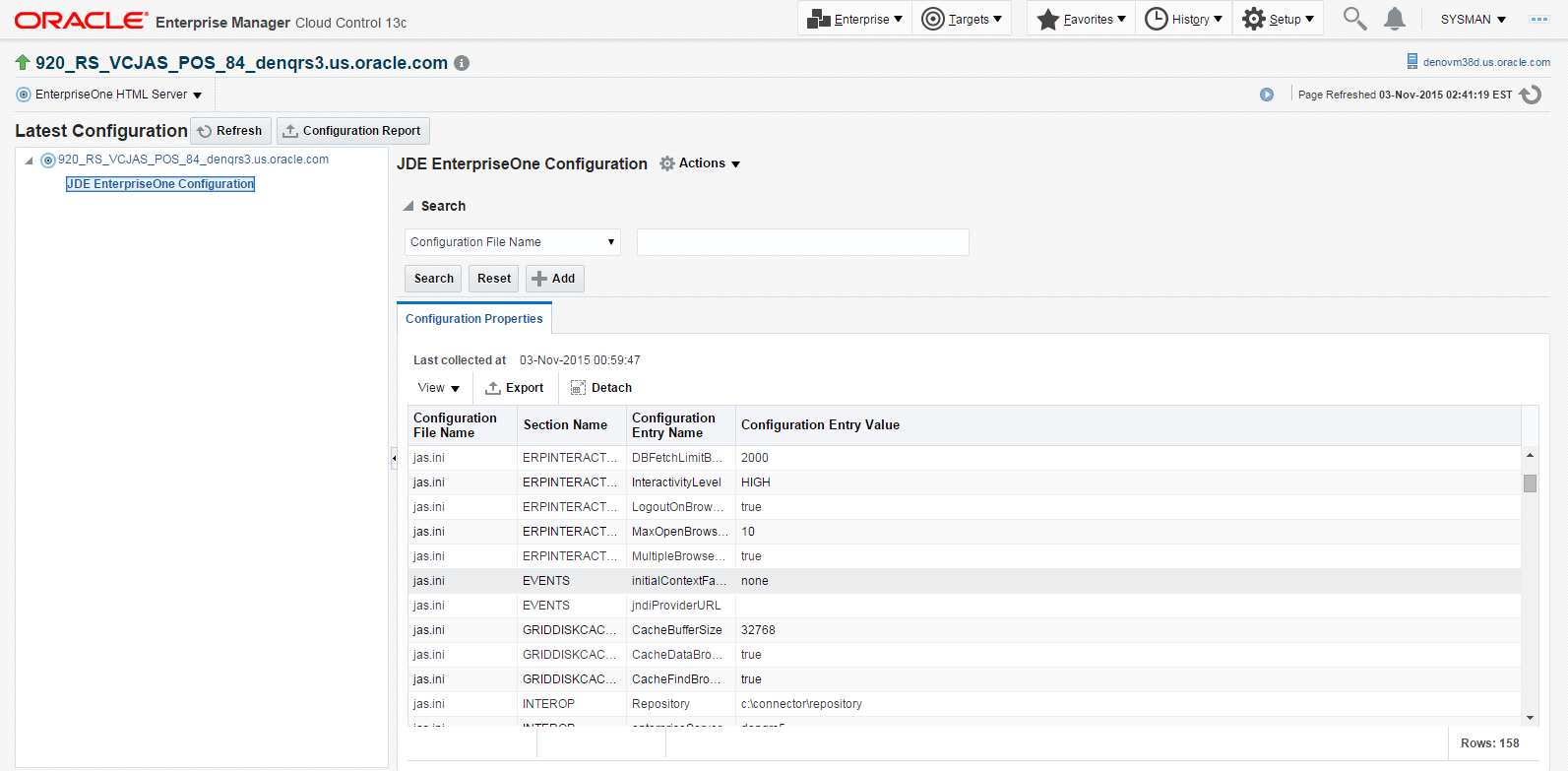
Description of the illustration ''latest_config_jas_node.png''
The following example illustrates the latest configuration for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server.
Description of the illustration ''last_collected_ent_svr.png''
-
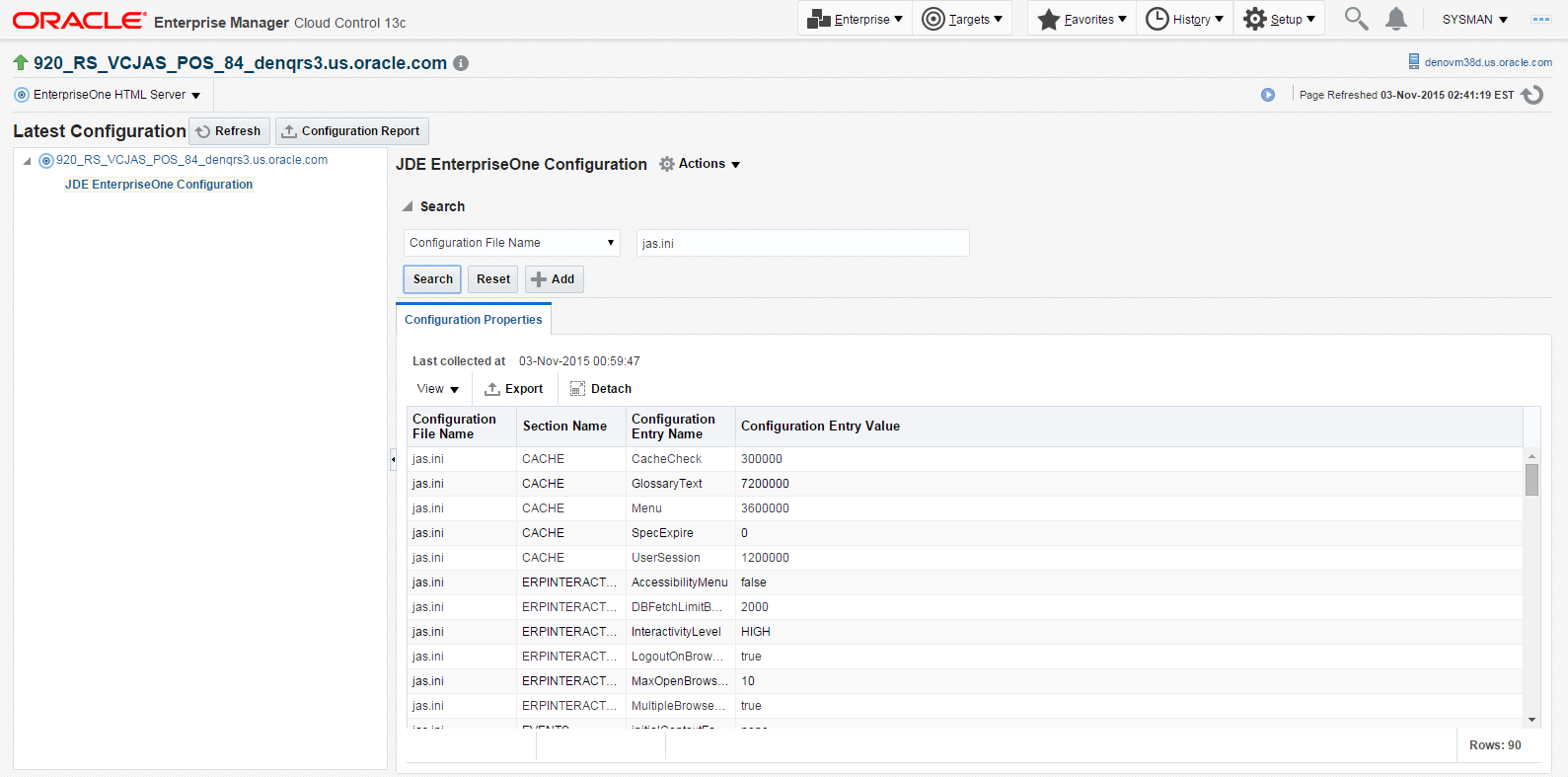
To display additional configuration details, expand the node for the Target and click the subnode.
The following example illustrates a JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server with the JDE EnterpriseOne Configuration subnode expanded.
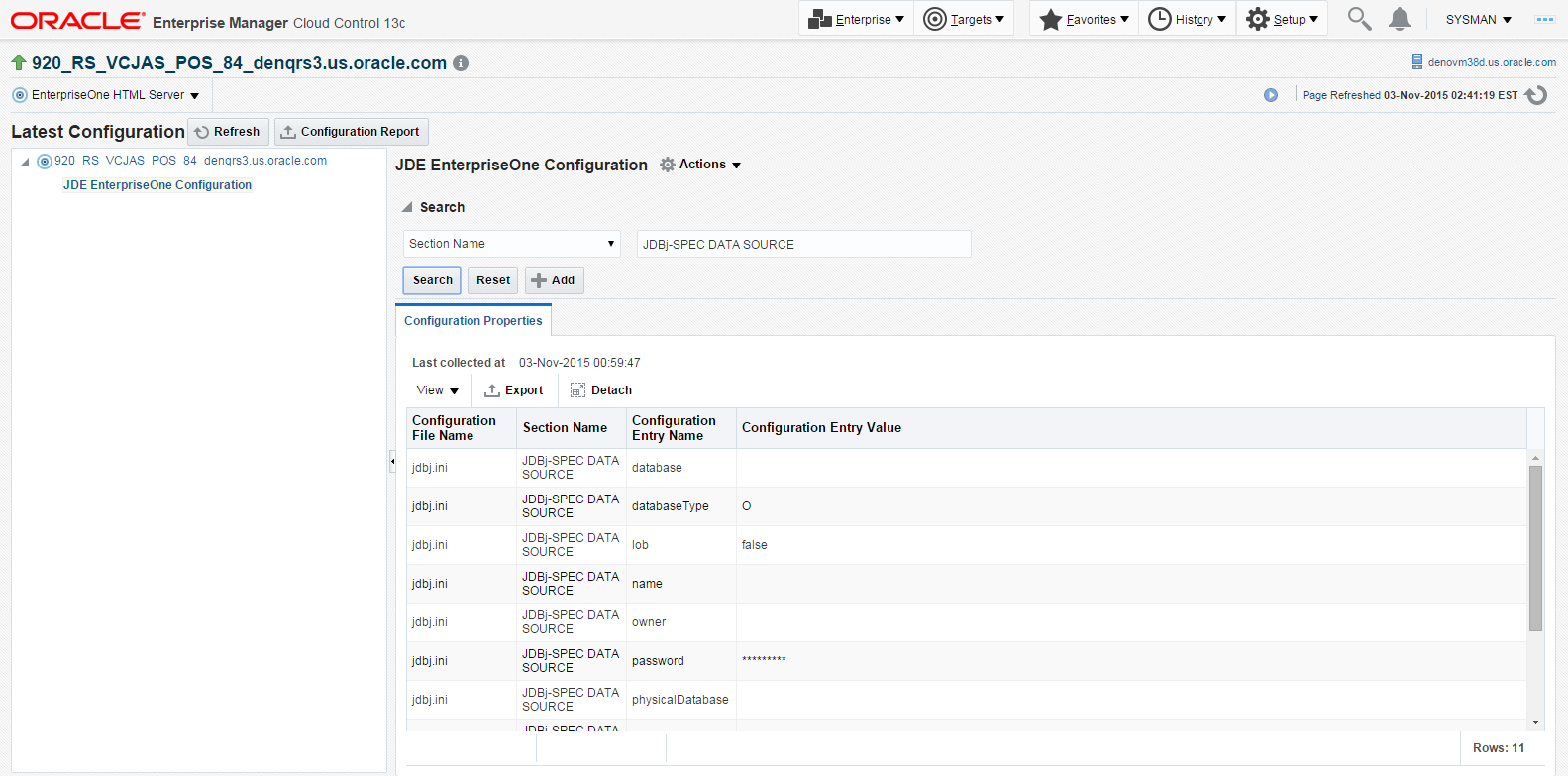
Description of the illustration ''config_browser_subnode.png''
7.14 Runtime Metrics (Status, User Count, and Performance)
You can use Cloud Control to monitor the status of all members of the JD Edwards domain. Cloud Control can also monitor the performance of these JD Edwards EnterpriseOne servers:
-
Enterprise Server
-
HTML Web Server

Description of the illustration ''members_example.png''
-
On the Members for JDE EnterpriseOne Domain form, you can view the following details for each member:
-
Status
-
Alerts
-
Policy Violations
-
-
For EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server and EnterpriseOne HTML Server member types, you can view the following performance data:
-
Home tab
User Count
-
Performance tab
Call Object Kernel Average Execute Time
-
Java Heap
-
Call Object Kernel Timeout Errors
Following are examples for each JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Server Type (Enterprise Server and HTML Server, respectively).
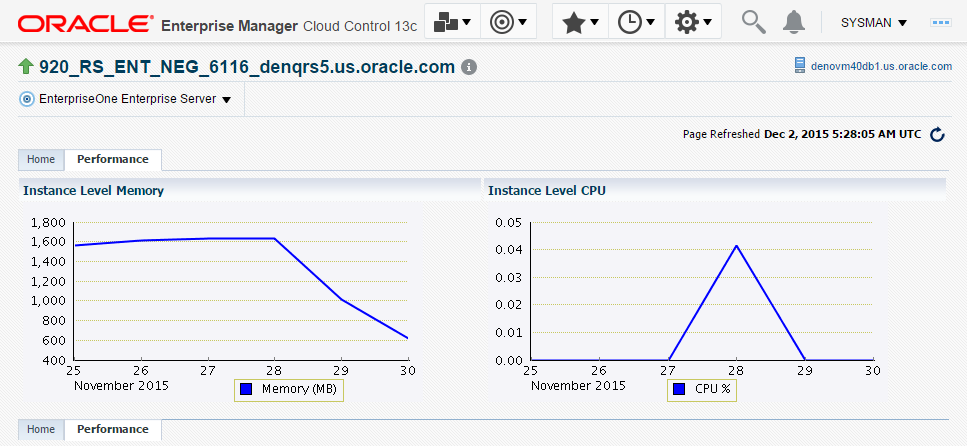
Description of the illustration ''performance_ent.png''
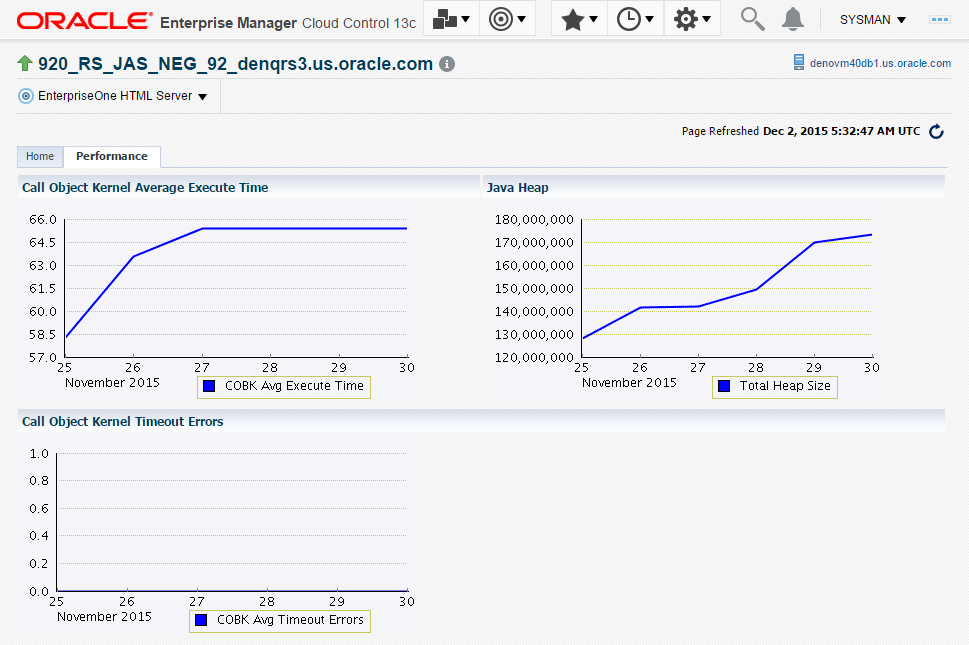
Description of the illustration ''performance_html.png''
-
7.15 Configuration Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne
You can view all configuration metrics for these JDE EnterpriseOne member Types:
-
Section 7.15.1, "All Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server"
-
Section 7.15.2, "All Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server"
7.15.1 All Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server
Use this procedure to view all metrics for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server
-
On Members for JDE EnterpriseOne Domain (or also from the Dashboard for the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain), click the link for the Name of the EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server.
Description of the illustration ''monitor_all_metrics.png''
-
With the JDE EnterpriseOne target displayed in Cloud Control, navigate to EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server, Monitoring, All Metrics.
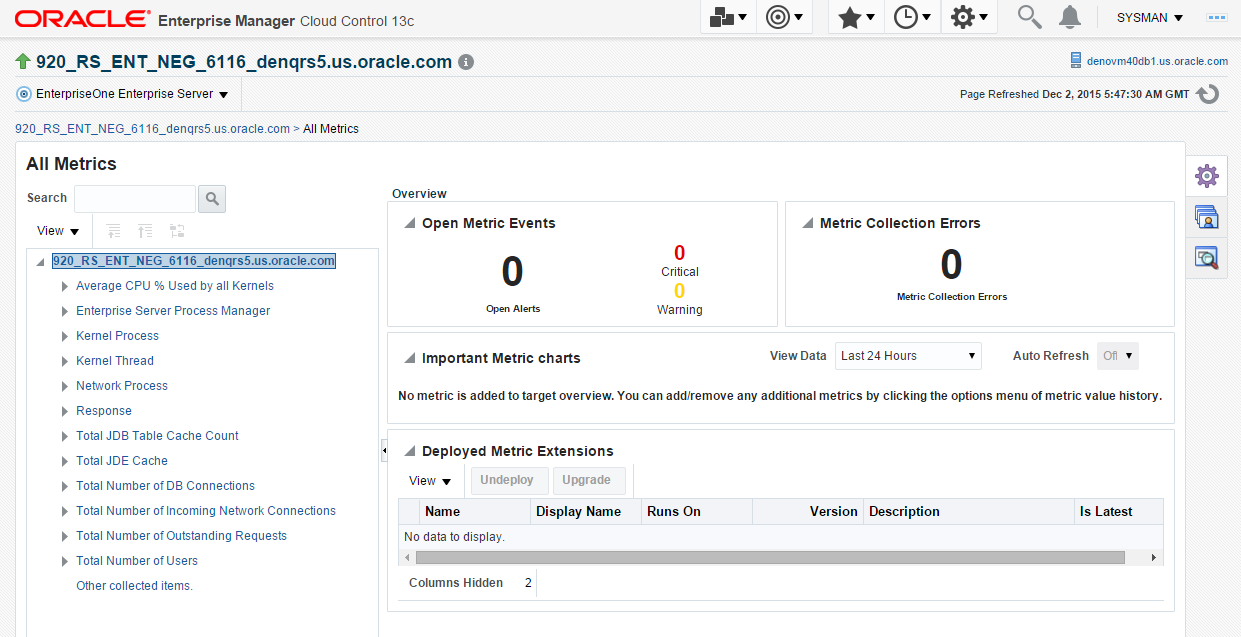
Description of the illustration ''metrics_ent.png''
-
On the All Metrics form, you can view any of the metrics that are available for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server. These metrics include:
-
Average CPU % Used by All Kernels
-
Enterprise Server Process Manager
-
Kernel Process
-
Kernel Thread
-
Network Process
-
Response
-
Total JDB Table Cache Count
-
Total JDE Cache
-
Total Number of DB Connections
-
Total Number of Incoming Network Connections
-
Total Number of Outstanding Requests
-
Total Number of Users
-
Other collected items
-
-
You can expand a metric node to view its subnodes. The following screen is an example of the metrics when you click on the Average CPU % Used By All Kernels node.

Description of the illustration ''average_cpu.png''
-
You can also click on subnodes to display additional information. The following screen is a sample of the metrics shown when you click on the Average CPU % subnode of the Average CPU % Used By All Kernels node.
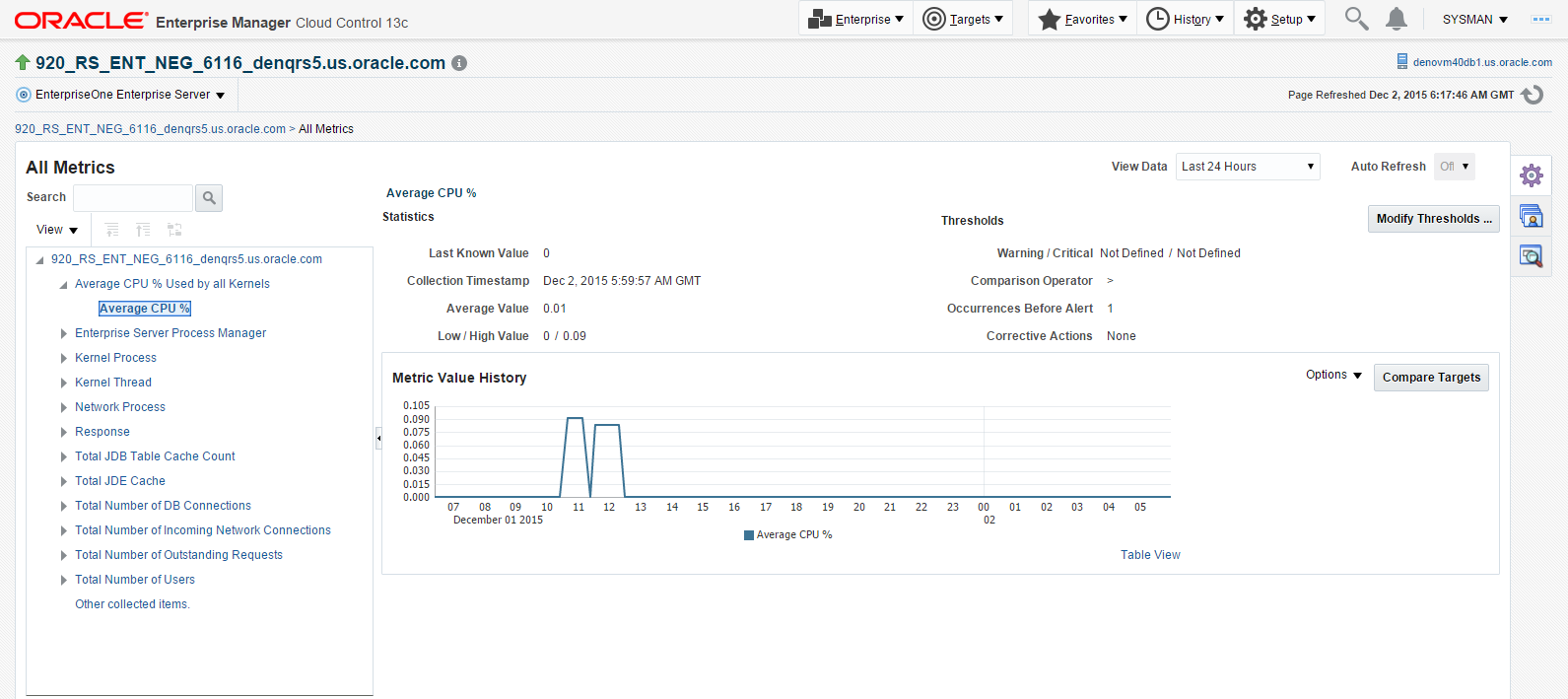
Description of the illustration ''avg_cpu.png''
7.15.2 All Metrics for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server
Use this procedure to view all metrics for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne HTML Server.
-
On Members for JDE EnterpriseOne Domain, click the link for the Name for the EnterpriseOne HTML Server.
Description of the illustration ''monitor_all_metrics_h.png''
-
With the JDE EnterpriseOne target displayed in Cloud Control, navigate to EnterpriseOne HTML Server, Monitoring, All Metrics.
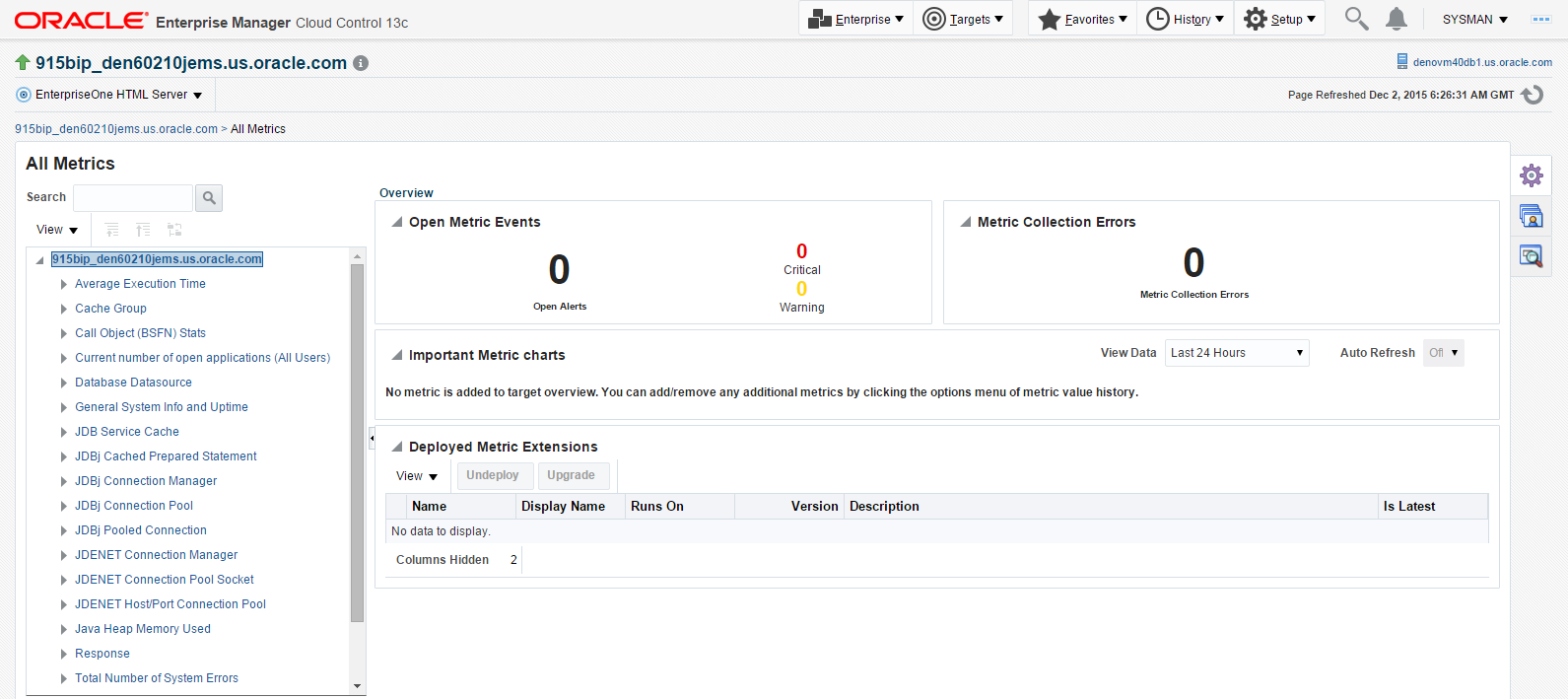
Description of the illustration ''metrics_html.png''
-
On the All Metrics form, you can view any of the metrics that are available for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server. These metrics include:
-
Average Execution Time
-
Cache Group
-
Call Object (BSFN) Stats
-
Current number of open applications (All Users)
-
Database Datasource
-
General System Info and Uptime
-
JDB Service Cache
-
JDBj Cache Prepared Statement
-
JDBj Connection Manager
-
JDBj Pooled Connection
-
JDENET Connection Manager
-
JDENET Connection Pool Socket
-
Java Heap Memory Used
-
Response
-
Total Number of System Errors
-
Total Number of Timeout Errors
-
Total number of current users
-
Other collected items
-
You can expand a metric node to view its subnodes. The following screen is an example of the metrics when you click on the Call Object (BSFN) Stats node.
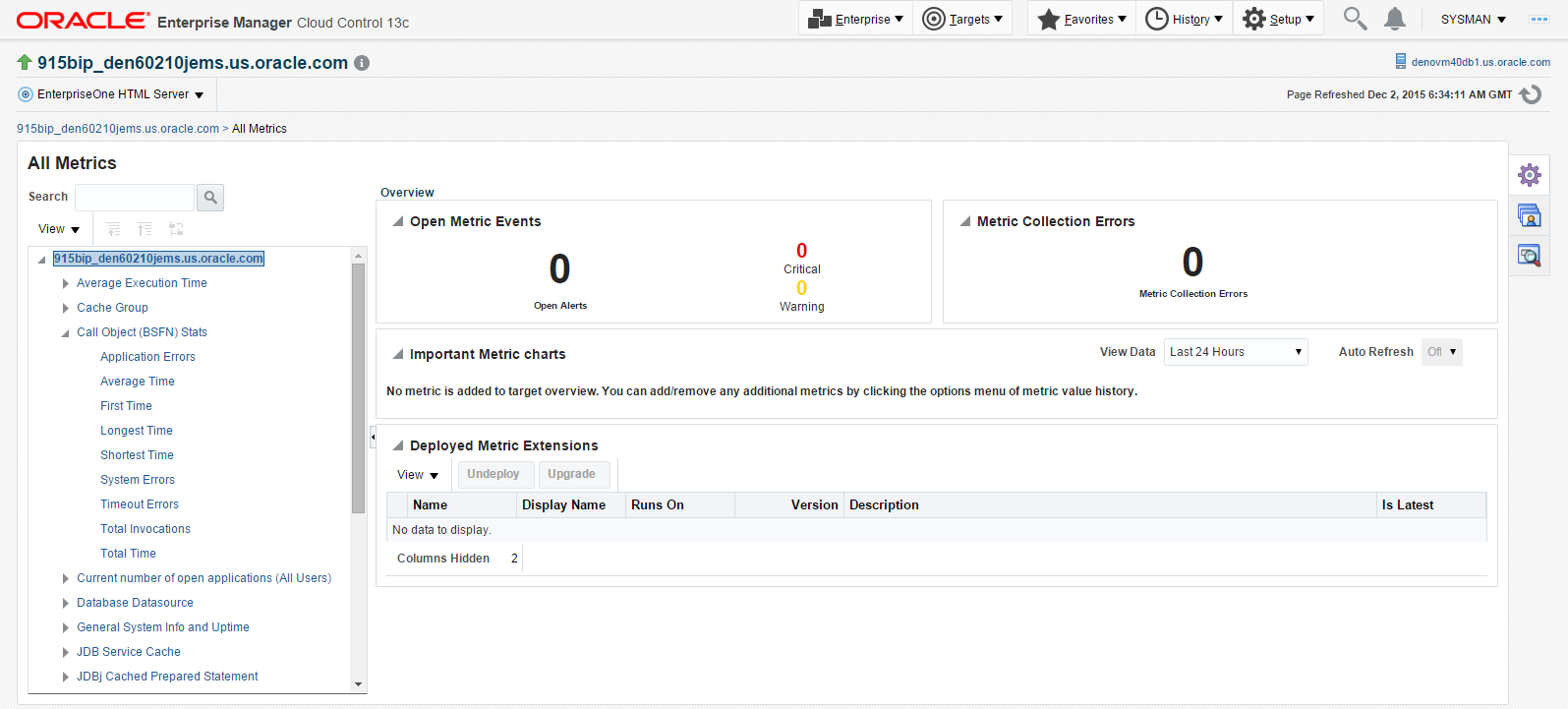
Description of the illustration ''call_object_stats.png''
-
You can also click on subnodes to display additional information. The following screen is an example of the metrics shown when you click on the Application Errors subnode of the Call Object (BSFN) Stats node.
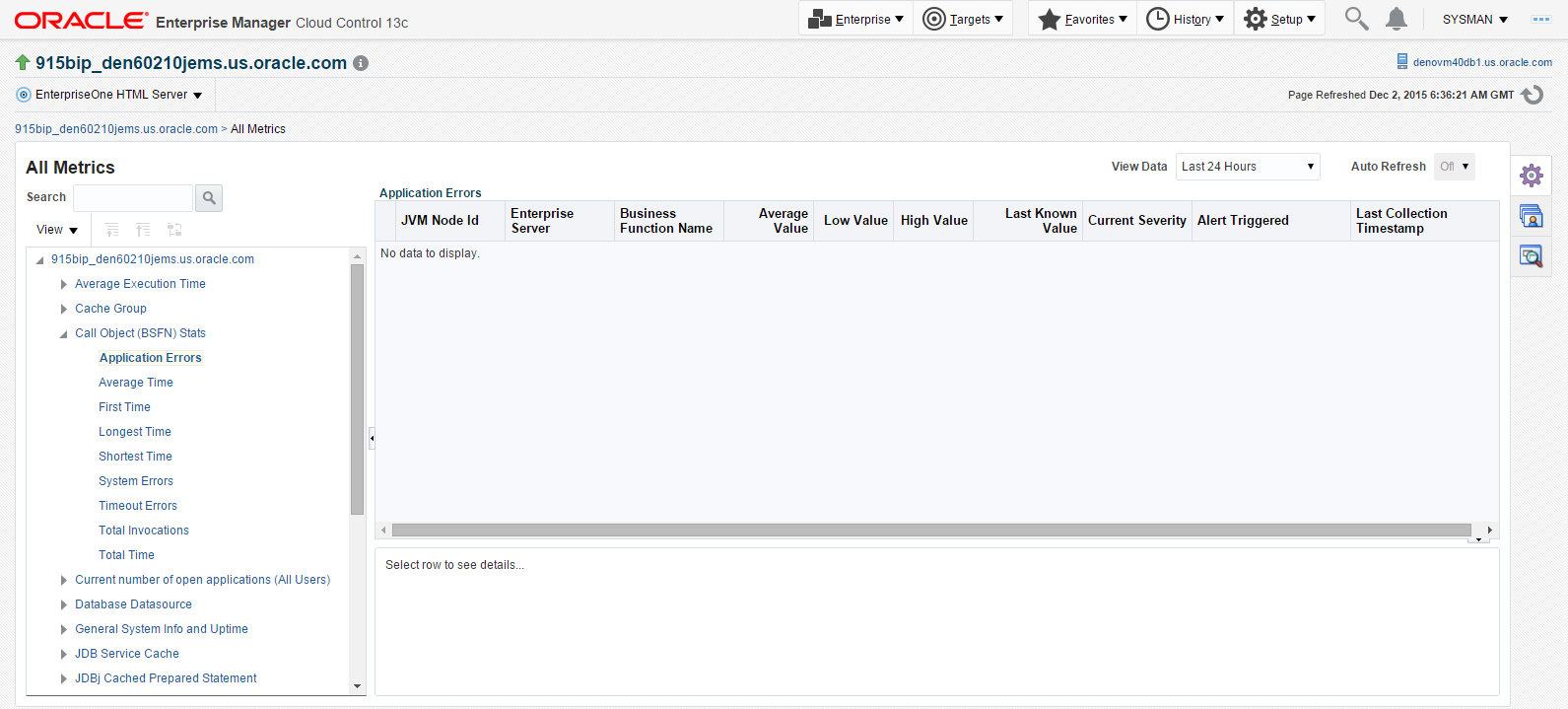
Description of the illustration ''application_errors.png''
-
7.16 Accessing Server Manager from Cloud Control
You can directly access the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Server Manager used in the installation of Enterprise Manager. On the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain Home Page, navigate to Custom Menu, Server Manager.
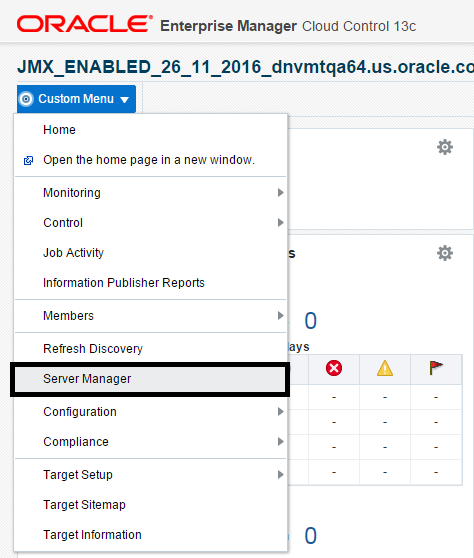
Description of the illustration ''server_manager.png''
You will be redirected to the Server Manager login page with this URL syntax:
http://SM_Host:SM Port/manage/home
where SM_Host and SM_Port are retrieved from the monitoring configuration. For example, the URL might be:
http://globalwin2.mlab.jdedwards.com:8999/manage/home
The Server Manager target machine is derived from the values in these fields on Monitoring Configuration:
-
Server Manager Hostname
-
Server Manager HTTP Port
For example:
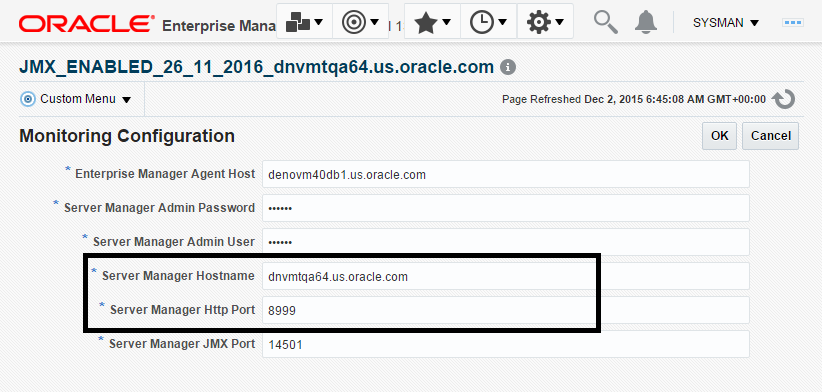
Description of the illustration ''monitoring_config_example.png''
Below is the Server Manager login page that is displayed when you are redirected.
Description of the illustration ''server_manager_redirect.png''
After you enter valid credentials for this Server Manager, the Server Manager Home page is displayed as shown in the following example:
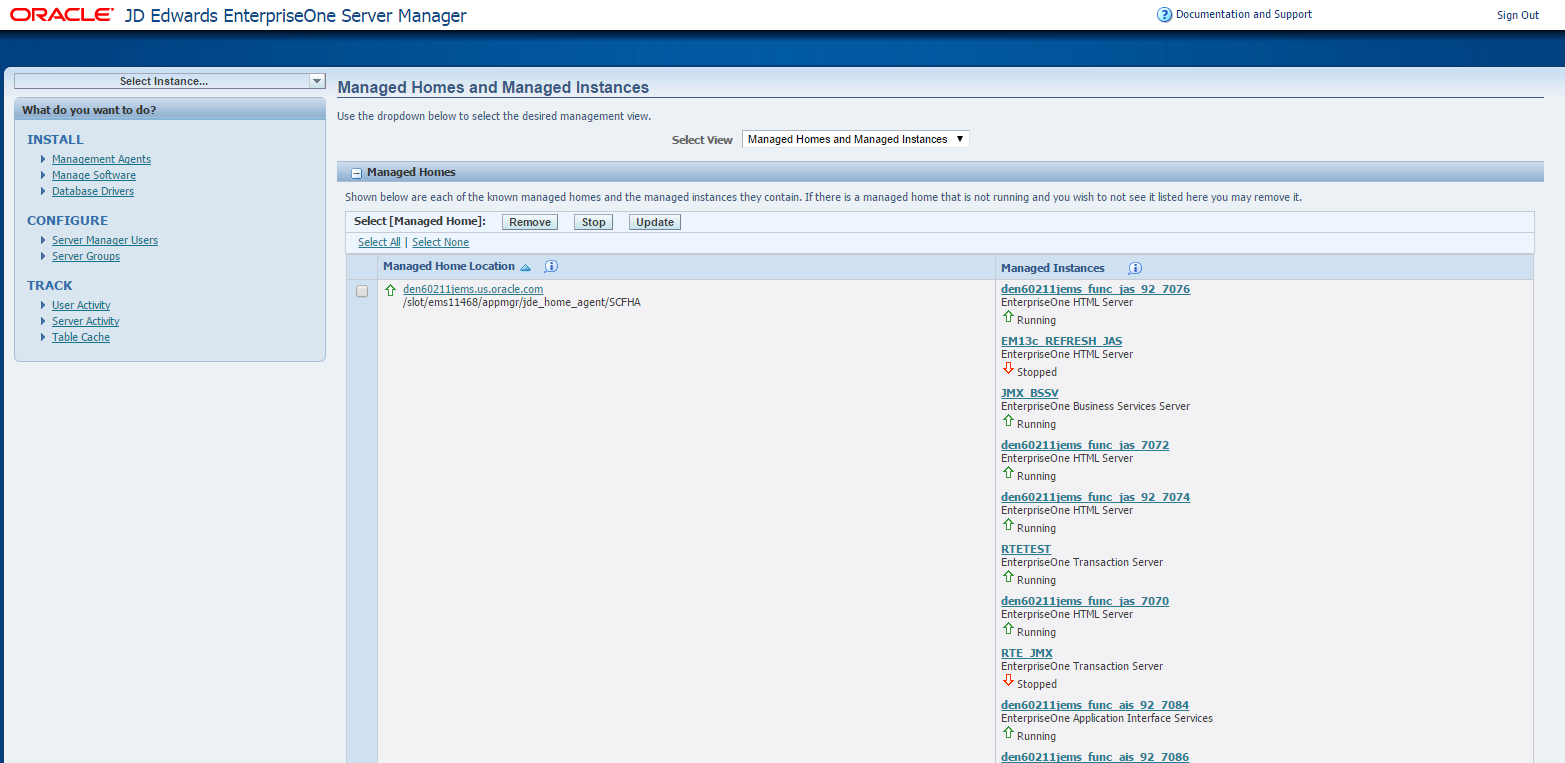
Description of the illustration ''server_manager_home.png''
7.17 Removing the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Domain
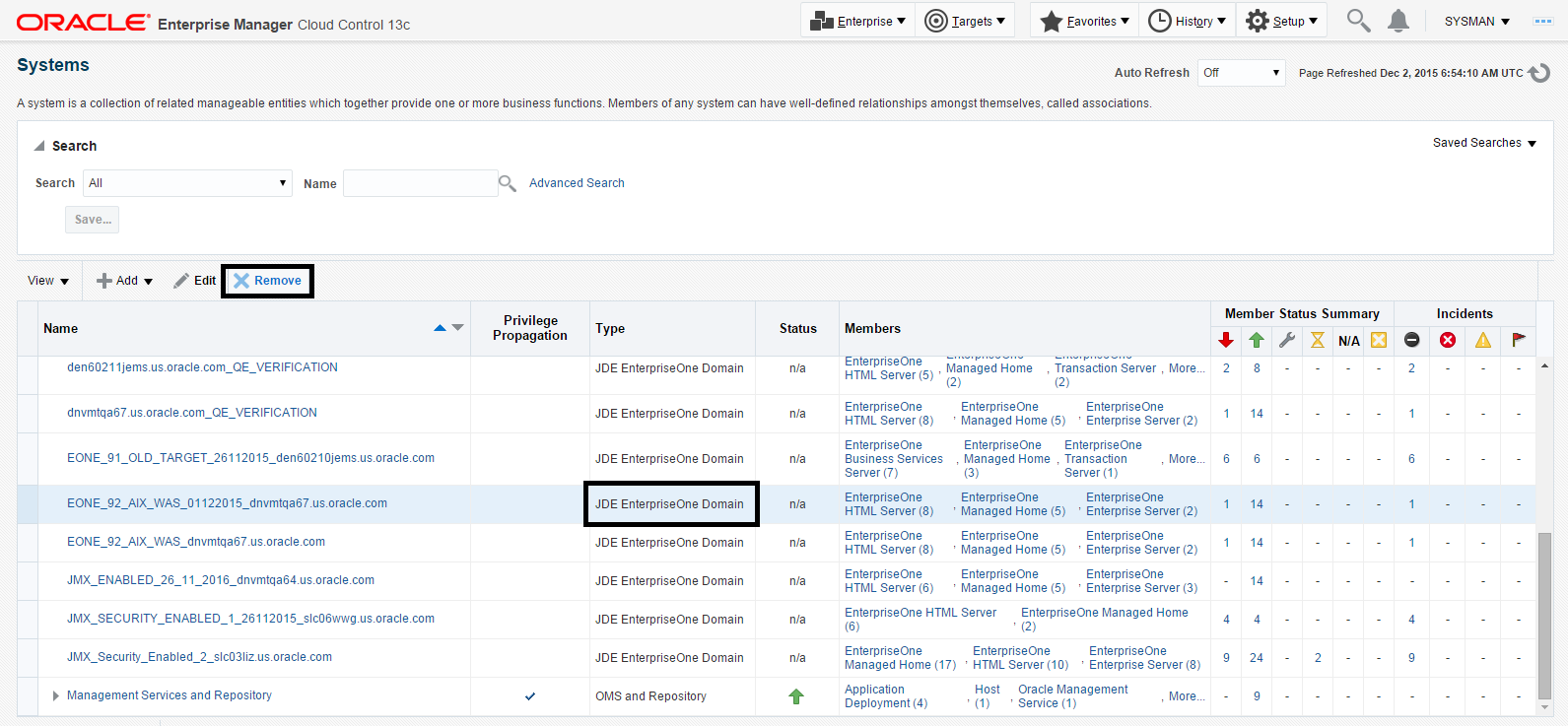
Description of the illustration ''remove_domain.png''
-
Navigate to Targets, Systems, and with the JDE EnterpriseOne Domain selected, click the Remove button.
-
Cloud Control displays a warning and lists the Domain target and associated EnterpriseOne targets that will be deleted.
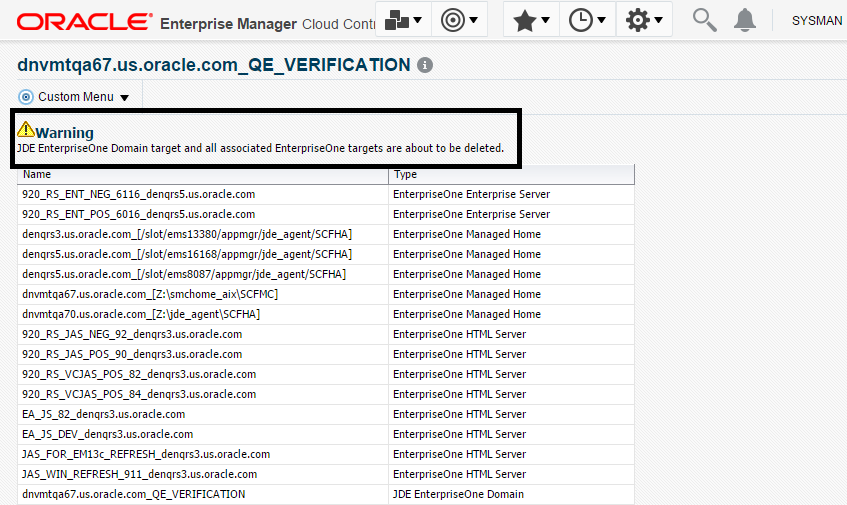
Description of the illustration ''remove_domain_warning.png''
-
As shown in the screen below, click the Yes button to confirm the deletion.
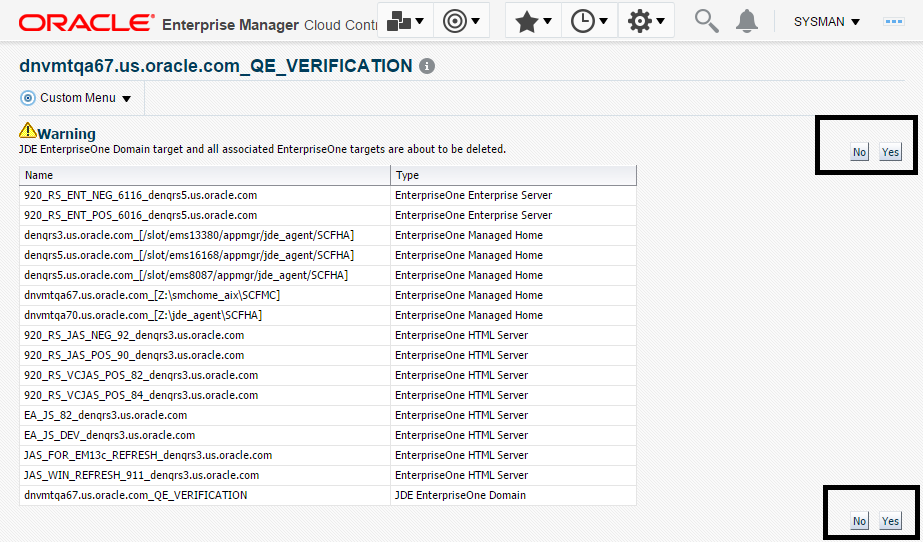
Description of the illustration ''remove_domain_yes.png''
After you click the Yes button, Cloud Control displays a progress screen indicating the deletion of the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne targets.
After the processing is complete for deleting the system domain target, Cloud Control returns to the All Targets page.
7.18 Starting and Stopping Components of Enterprise Manager Environments
This section discusses:
-
Section 7.18.1, "Starting Enterprise Manager Environment Components"
-
Section 7.18.2, "Stopping Enterprise Manager Environment Components"
7.18.1 Starting Enterprise Manager Environment Components
Use these commands to start Enterprise Manager environment components:
-
Start database
sqlplus '/as sysdba' sql> startup
-
Start Database Listener
/u01/app/oracle/home/bin/lsnrctl start
-
Start WebLogic Node Manager
Stop ADMIN SERVER from console in case it is running without Node Manager /u01/app/emgc13/wlserver_12.1/server/bin/setWLSEnv.sh /u01/app/emgc13/wlserver_12.1/server/bin/startNodeManager.sh
-
Start OMS
/u01/app/emgc13/oms/bin/emctl start oms
-
Start Agent
/u01/app/emgc13/agent/agent_inst/bin/emctl start agent
7.18.2 Stopping Enterprise Manager Environment Components
Use these commands to stop Enterprise Manager environment components:
-
Stop Agent
/u01/app/emgc13/agent/agent_inst/bin/emctl stop agent
-
Stop OMS (this stops the OMS Server)
/u01/app/emgc13/oms/bin/emctl stop oms
-
Stop Database Listener
/u01/app/oracle/home/bin/lsnrctl stop
-
Stop Database
sqlplus '/as sysdba' sql> shutdown immediate