B Understanding Media Objects on the Web Server
This section provides an overview of jas.ini settings required to access Media Objects on the HTML Server, and the process by which the web server accesses these objects from the network. The last section describes how to secure Media Objects on web-based client machines.
B.1 Required jas.ini Settings
Ensure that these parameters are set in the [OWWEB] section of the jas.ini file.
| Parameter | Recommended Setting | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MO QUEUE= | Site-dependent path | Identifies the media object directory location on your HTML Server. This path must translate into virtual path /jde/moqueue/ for the web browser. |
| FtpPort= | 21 | Specifies the default port to be used for FTP. |
| FtpUsr= | anonymous | Specifies the user id to be used for FTP access to the media Object File Server. |
| FtpPwd= | anonymous | Specifies the password to be used for FTP access to the media Object File Server. |
| UseMOWinNTShare= | TRUE | Specifies that the web server use the Microsoft Windows file sharing mechanism for fetching Media Object files from their location into the cached location of the web server.
Note: If this setting is TRUE, media object queue paths set in P98MOQUE must be accessible by the owner of the application server from the application server machine (the application server is the server program hosting web servlets). To test the accessibility of a media object queue path, log in as the owner of the application server, open Windows Explorer, and paste the path to the media object queue into the address field. The path should be accessible without entering a user ID and password. If this path is not accessible, you can change the media object queue setting to a path accessible by the owner of the application server. For example, you can specify a path on the application server machine as the media object queues directory. |
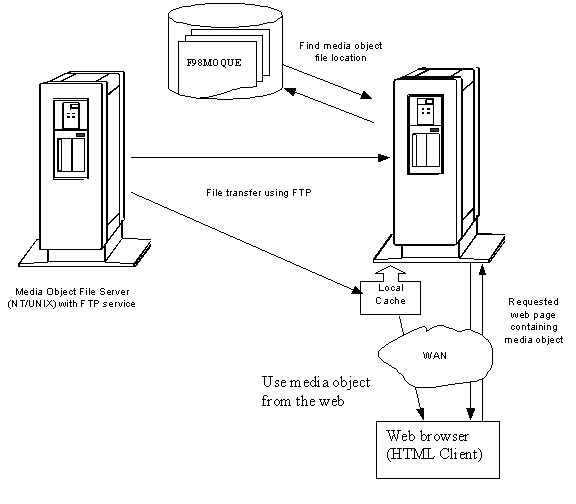
B.2 How Media Objects are Displayed by the HTML Server
This section explains how Media Objects are sent to the HTML client by the HTML Server.
-
A user selects attachments on an application which has support for media objects.
-
The Media Object window displays the image, file, or OLE objects, and the user selects one of these objects.
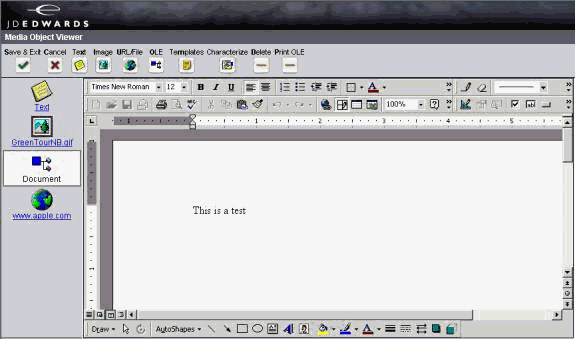
-
The request goes to the web server.
-
The web server reads the location of the object from the Media Object queue table (F98MOQUE), finds the file, and caches it in the location specified by the MO QUEUE path.
If UseMOWinNTShare is TRUE, files are transferred using Microsoft Windows file sharing mechanism, otherwise files are transferred using FTP protocol.
This diagram illustrates the process: