You can map attributes from the Essbase cube to the existing model.
See:
After completing the attribute mapping or dragging procedure,
This section describes the mapping of each dimension in Essbase to the existing Business Model and Mapping Layer. From each Dimension in Essbase, the attributes must be dragged into the corresponding Dimension in the Business Model and Mapping layer.
Amount Type in the physical layer must be mapped to Dim-Amount Type in the logical layer.

Date-Fiscal Calendar in physical layer must be mapped to Dim-Date Fiscal Calendar in the logical layer. The mappings of Date-Fiscal Calendar Dimension are show below:
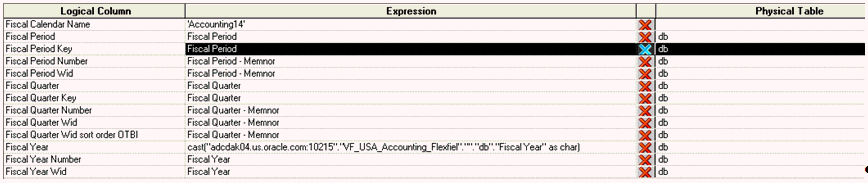
Note: | The Fiscal year attribute must be shown in the Expression column of the preceding figure. Here, VF_USA_Accounting_Flexfied is the name of the cube. In addition, the Fiscal Calendar Name should be determined as explained in section Balance Fact–Modeling and typed in as well. |
Ledger Dimension attributes are mapped to Dim-Ledger and Dim-Ledger Set in the Business Model and Mapping layer. Ledger dimension mapping is shown below:

Note: | Chart of Account should be determined as explained in Balance Fact–Modeling. |
Ledger Set dimension mapping is shown below:

The mapping starts from the top level in the Essbase Dimension hierarchy to the Business Model and Mapping layer. For example, in the Business Model and Mapping layer:
XSegment Tree Filter attribute from the Essbase Dimension maps to the XSegment Tree Filter attribute
Level X Code attribute of Essbase Dimension maps to Segment Level Xcode
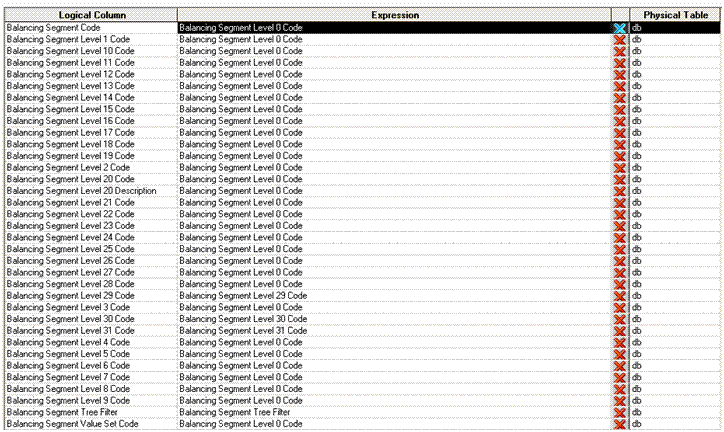
Balancing Segment Level 31 Code in Essbase Dimension maps to Balancing Segment Level 31 Code attribute
Balancing Segment Level 0 Code in Essbase Dimension maps to Balancing Segment Code attribute
XSegment Level 0 Code in Essbase Dimension maps to the Leaf level attribute X Segment Code
Because the Essbase hierarchy does not have 32 levels, and the Logical Dimension has 32 levels, the intermediate levels must be mapped to the Leaf level from Essbase hierarchy. This is true for all the segment Dimensions. For example, if the Essbase Dimension Hierarchy has Level 31 code, Level 30 code, Level 29 Code, and Level 0 Code, then all the Level 0 code of Essbase Dimension must be mapped to all the attributes from Xsegment Level 28 Code until Leaf level as shown in the figure below.
Balancing Segment in the Essbase cube should be mapped to Dim - Balancing Segment in the Business Model and Mapping layer also as shown below:
Similar mappings must be done for Cost Center Dimension in the Essbase cube that gets mapped to Dim - Cost center in the logical layer and Account Segment in Essbase cube that gets mapped to the Dim - Natural account Segment.
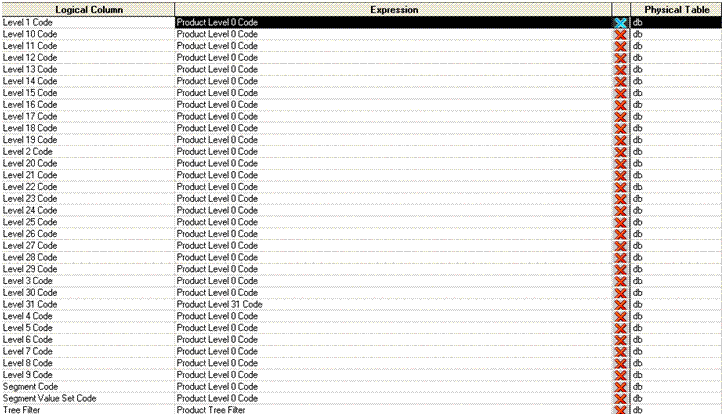
For Non Qualified Segment dimensions, the Essbase dimensions can be mapped to any of the GL Segment dimensions Dim-GL Segment1 to Dim-GL Segment10. For example, Product Dimension in Essbase is mapped to Dim - GL Segment1 as shown below:
The currency dimension in Essbase maps to Dim - Currency in logical layer as shown below:

The Currency Type dimension in Essbase maps to Dim - Currency Type in logical layer as shown below:

Dragging the database (just below the Essbase cube) from the physical layer into the Business Model and Mapping layer model (Core). Drag and drop functionality maps to the existing dimensions of the cube if the Dimension is already present in the Business Model and Mapping layer. If not, it creates a Dimension.
If you have created a hierarchy with the same name as that of the renamed dimensions, you must delete the following hierarchies from the Business Model and Mapping layer:
Dim-Date Fiscal Calendar
Dim-Natural Account Segment
Dim-Balancing Segment
Dim-Currency
Dim-Cost Center
Dim-Amount Type
Currency Type
All the Non Qualified Segment Dimension hierarchies (Dim-Segment X)
Note: | Because of dragging, within each mapped dimension, additional attributes were created. You must delete them as well as the attributes with names similar to Dim-X. XX-member, xx-Member Key should be deleted also. |
For example, before dragging, Dim - Date Fiscal Calendar has the following attributes:


However, after dragging, the following attributes are created and must be deleted:
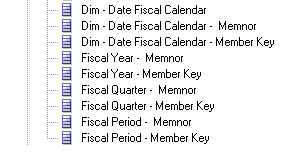
The lists of attributes created for each dimension, which must be deleted, are displayed in the following figures:
Currency:

Amount Type:

Segment Dimensions:

Note: | This example of Balancing Segment Hierarchy stops at Level 27 and then has the leaf level. However, there may be more or fewer attributes, depending on the hierarchy of the Segment Dimensions. |
Because of dragging, a dimension Currency Type is created in the Business Model and Mapping layer apart from the existing Dim - Currency Type.
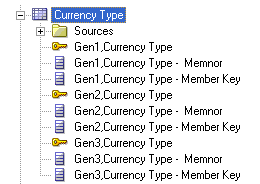
Also, a new hierarchy is created inside the existing Currency Type dimensions hierarchy and must be deleted.
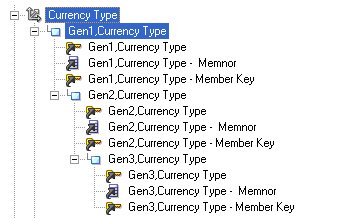
Attributes of Currency Type Dimension must be manually mapped. Gen2, Currency Type and Gen3, Currency Type (attributes) in the physical layer that are highlighted in the figure below must be mapped to Currency Type and Converted Currency Type attributes in Dim - Currency Type in the Business Model and Mapping layer.
After the cube is dragged and dropped, it creates a new dimension called Ledger and also creates a new hierarchy inside the Ledger Hierarchy starting from Gen1, Ledger. You must manually delete this new Dimension (Ledger) and its corresponding hierarchy (hierarchy inside Ledger starting from Gen1.Ledger) from the Business Model and Mapping layer, because this dimension is manually mapped.
In the physical layer, the Ledger Dimension present in the Essbase cube should be mapped to Ledger Dimension and LedgerSet Dimension in the Business Model and Mapping layer.
 To map the Ledger and LedgerSet Dimensions in the Business Model and Mapping layer:
To map the Ledger and LedgerSet Dimensions in the Business Model and Mapping layer:
Drag the Gen2,Ledger(attribute), Gen2.Legder_Id_Alias from Gen2,Ledger (Generation) of the Essbase Cube to the LedgerSet Name, LedgerSet Key of the Dim - LedgerSet.
Drag the Gen3,Ledger (attribute), Gen3,Ledger_Id_Alias and Gen3, Ledger- Default from Gen3, Ledger (Generation) of the Essbase cube to the Ledger Name, Ledger Key, and Ledger Description attributes of Dim - Ledger.
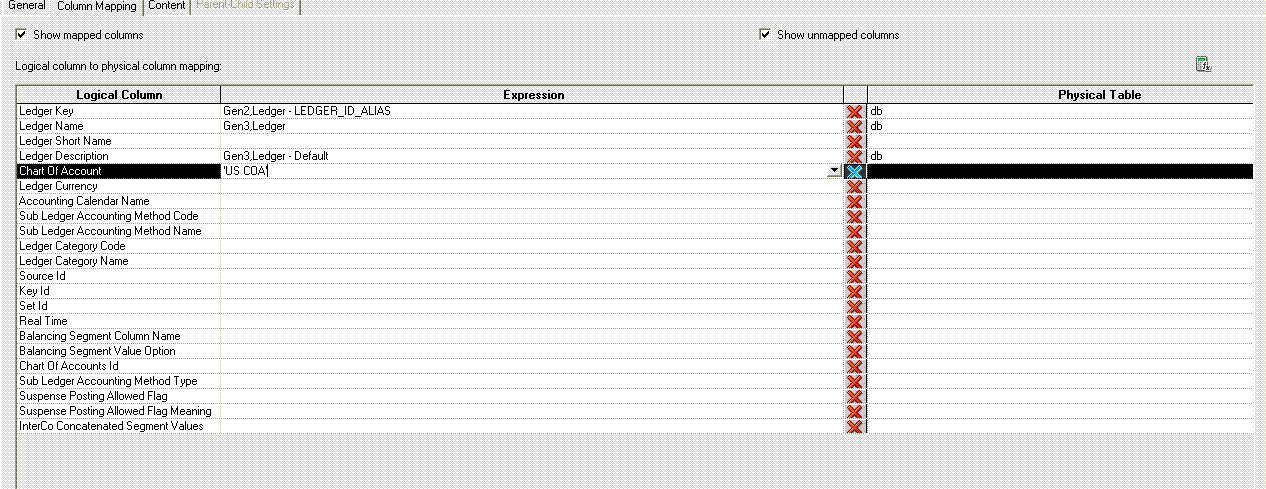
You must map the Essbase Logical Table Source (LTS) to Chart of Account attribute in Ledger Dimension for redirection in the fact.
To map the Chart of Accounts attribute, in the Column Mapping tab of Essbase LTS, enter <COA name> for the cube. This is the same name used in the Fact’s Fragmentation content. See step 3 under the section Balance Fact–Modeling.
You must create additional mappings that need to be done in Dim - Date Fiscal Calendar for the proper redirection and federation to Essbase cube sources. Similar to the mapping for Chart Of Accounts attributes, you must do a few manual mappings for the Time dimension.
 To perform additional mappings for the time dimension:
To perform additional mappings for the time dimension:
In the column mapping, for the Essbase cube LTS, the Calendar Name of the cube must be written directly. To obtain the Calendar Name of the cube, see The Business Model and Mapping Layer Changes.
Drag the Fiscal Year attribute from the physical layer of the cube into the Fiscal Year Number and Fiscal Year Wid. You must enter and map Fiscal Year as shown below.

A dimension called Scenario is created in the Business Model and Mapping layer by dragging the cube. You must manually delete this dimension and its hierarchy, because only Actual Balances is supported, and this condition is added in the Fact. See Balance Fact–Modeling.